|
Marius (general)
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times. Rising from a family of smallholders in a village called Ceraetae in the district of Arpinum, Marius acquired his initial military experience serving with Scipio Aemilianus at the Siege of Numantia in 134 BC. He won election as tribune of the plebs in 119 BC and passed a law limiting aristocratic interference in elections. Barely elected praetor in 115 BC, he next became the governor of Further Spain where he campaigned against bandits. On his return from Spain he married Julia, the aunt of Julius Caesar. Marius attained his first consulship in 107 BC and became the commander of Roman forces in Numidia, where he brought an end to the Jugurthine War. By 105 BC Rome faced an invasion by the Cimbri and Teutones, and the '' comitia centuriata'' elected Marius consul for a second ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the Roman censor, censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding ''fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its Roman provinces, provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former King of Rome, kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social War (91–87 BC)
The Social War (from Latin , "war of the allies"), also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought largely from 91 to 88 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies () in Roman Italy, Italy. Some of the allies held out until 87 BC. The war started in late 91 BC, with the rebellion of Ascoli Piceno, Asculum. Other Italian towns quickly declared for the rebels and the Roman response was initially confused. By the new year, the Romans had levied huge armies to crush the rebels but found initial headway difficult; by the end of the year, however, they were able to cut the Italian rebels into two, isolating them into northern and southern sectors. The Italian rebels attempted to invade Etruria and Umbria at the start of 89 BC but were defeated. In the south, they were defeated by Lucius Cornelius Sulla, who for his victories would win a consulship the next year. The Romans retained the initiative and by 88 BC, the conflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
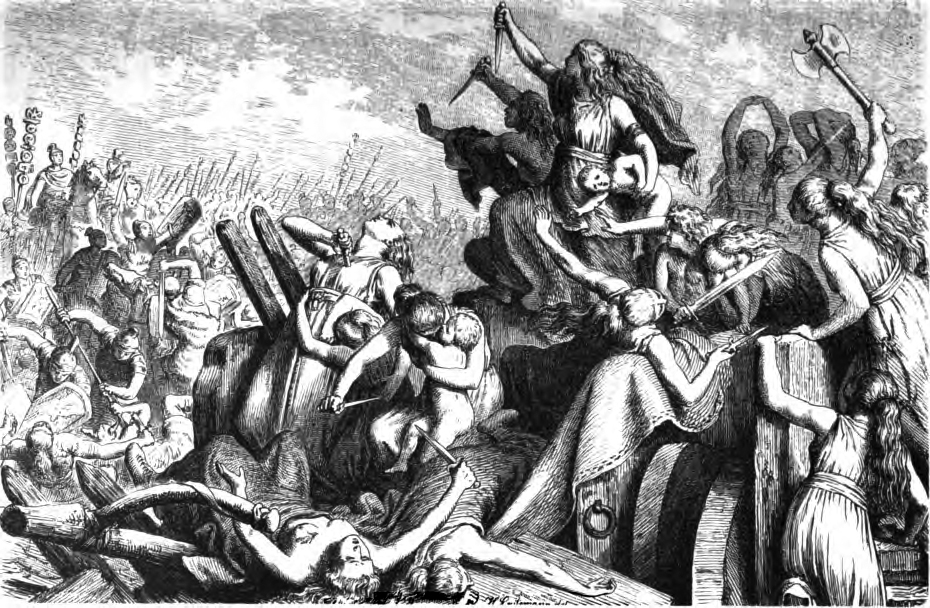
Battle Of Vercellae
The Battle of Vercellae or Battle of the Raudine Plain was fought on 30 July 101 BC on a plain near Vercellae in Gallia Cisalpina (modern-day Northern Italy). A Celto-Germanic confederation under the command of the Cimbric king Boiorix was defeated by a Roman Republic, Roman army under the joint command of the Consul (Roman), consul Gaius Marius and the proconsul Quintus Lutatius Catulus. The battle marked the end of the Cimbrian War, Germanic threat to the Roman Republic. Background In 113 BC, a large migrating Germanic peoples, Germanic-Celts, Celtic alliance headed by the Cimbri and the Teutones entered the Roman sphere of influence. They invaded Noricum (located in present-day Austria and Slovenia) which was inhabited by the Taurisci people, friends and allies of Rome. The Senate commissioned Gnaeus Papirius Carbo (consul 113 BC), Gnaeus Papirius Carbo, one of the consuls, to lead a substantial Roman army to Noricum to force the barbarians out. An engagement, later calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aquae Sextiae
The Battle of Aquae Sextiae (Aix-en-Provence) took place in 102 BC. After a string of Roman defeats (see: the Battle of Noreia, the Battle of Burdigala, and the Battle of Arausio), the Romans under Gaius Marius finally defeated the Teutones and Ambrones as they attempted to advance through the Alps into Italy. Local lore associates the name of the mountain, Mont St. Victoire, with the Roman victory at the battle of Aquae Sextiae, but Frédéric Mistral and other scholars have debunked this theory. Background According to ancient sources, sometime around 120–115 BC, the Germanic tribe of the Cimbri left their homeland around the North Sea due to climate changes. They supposedly journeyed to the south-east and were soon joined by their neighbours the Teutones. On their way south they defeated several other Germanic tribes, but also Celtic and Germano-Celtic tribes. A number of these defeated tribes joined their migration. In 113 BC the Cimbri-Teutones confederation, led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutones
The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late second century BC. Some generations later, Julius Caesar compared them to the Germanic peoples of his own time, and used this term for all northern peoples located east of the Rhine. Later Roman authors followed his identification. However, there is no direct evidence about whether or not they spoke a Germanic language. Evidence such as the tribal name, and the names of their rulers, as they were written up by Roman historians, indicates a strong influence from Celtic languages. On the other hand, the indications that classical authors gave about the homeland of the Teutones is considered by many scholars to show that they lived in an area associated with early Germanic languages, and not in an area associated with Celtic languages. Name The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimbri
The Cimbri (, ; ) were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic, Gaulish, Germanic, or even Cimmerian people. Several ancient sources indicate that they lived in Jutland, which in some classical texts was called the Cimbrian peninsula. There is no direct evidence for the language they spoke, though some scholars argue that it was a Germanic language, while others argue that it was Celtic. Together with the Teutones and the Ambrones, they fought the Roman Republic between 113 and 101 BC during the Cimbrian War. The Cimbri were initially successful, particularly at the Battle of Arausio, in which a large Roman army was routed. They then raided large areas in Gaul and Hispania. In 101 BC, during an attempted invasion of the Italian peninsula, the Cimbri were decisively defeated at the Battle of Vercellae by Gaius Marius, and their king, Boiorix, was killed. Some of the surviving captives are reported to have been among the rebellious gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii state in the east (Capital: Cirta) and the Masaesyli state in the west (Capital: Siga). During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into the first unified Berbers, Berber state for Numidians in present-day Algeria. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and an ally of Roman Empire, Rome and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its foundation, was bordered by the Moulouya River to the west, Africa (Roman province), Africa Proconsularis and Cyrenaica to the east. the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south so that Numidia entirely surrounded Carthage except towards the sea. befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Further Spain
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a Roman province located in Hispania (on the Iberian Peninsula) during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania (modern Portugal, Extremadura and a small part of Salamanca province) and Gallaecia (modern Northern Portugal and Galicia). Its capital was Corduba. Etymology ''Hispania'' is the Latin term given to the Iberian Peninsula. The term can be traced back to at least 200 BC when the term was used by the poet Quintus Ennius. The word is possibly derived from the Punic אי שפן ''I-Shaphan'' meaning "coast of hyraxes", in turn a misidentification on the part of Phoenician explorers of its numerous rabbits as hyraxes. Ulterior is the comparative form of ulter, which means "that is beyond". According to ancient historian Cassius Dio, the people of the region came from many different tribes. They did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor
''Praetor'' ( , ), also ''pretor'', was the title granted by the government of ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected ''magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective itself: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his ''castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. The minimum age for holding the praetorship was 39 during the Roman Republic, but it was later changed to 30 in the early Empire. History of the title The status of the ''pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribune Of The Plebs
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune () was the first office of the Roman Republic, Roman state that was open to the plebs, plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate and Roman magistrate, magistrates. These tribunes had the power to convene and preside over the ''Plebeian Council, Concilium Plebis'' (people's assembly); to summon the senate; to propose legislation; and to intervene on behalf of plebeians in legal matters; but the most significant power was to veto the actions of the Roman consul, consuls and other magistrates, thus protecting the interests of the plebeians as a class. The tribunes of the plebs were typically found seated on Tribune bench, special benches set up for them in the Roman Forum. The tribunes were sacrosanct, meaning that any assault on their person was punishable by death. In Roman Empire, imperial times, the powers of the tribunate were granted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Numantia
The Celtiberian oppidum of Numantia was attacked more than once by Roman forces, but the siege of Numantia refers to the culminating and pacifying action of the long-running Numantine War between the forces of the Roman Republic and those of the native population of Hispania Citerior. The Numantine War was the third of the Celtiberian Wars and it broke out in 143 BC. A decade later, in 133 BC, the Roman general and hero of the Third Punic War, Scipio Aemilianus Africanus, subjugated Numantia, the chief Celtiberian city. Roman preparation In late 135 BC, the Roman Senate reappointed Scipio consul on popular demand and sent him to Hispania to finish what lesser generals had failed to complete. Scipio found morale low among the troops stationed in Iberia. The chance of plunder being low, there were few enticements to enlistment. Scipio nevertheless raised an army of 20,000 with 40,000 allied and mercenary troops, especially Numidian cavalry and 12 elephants led by Jugurt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |