|
Marion Nunataks
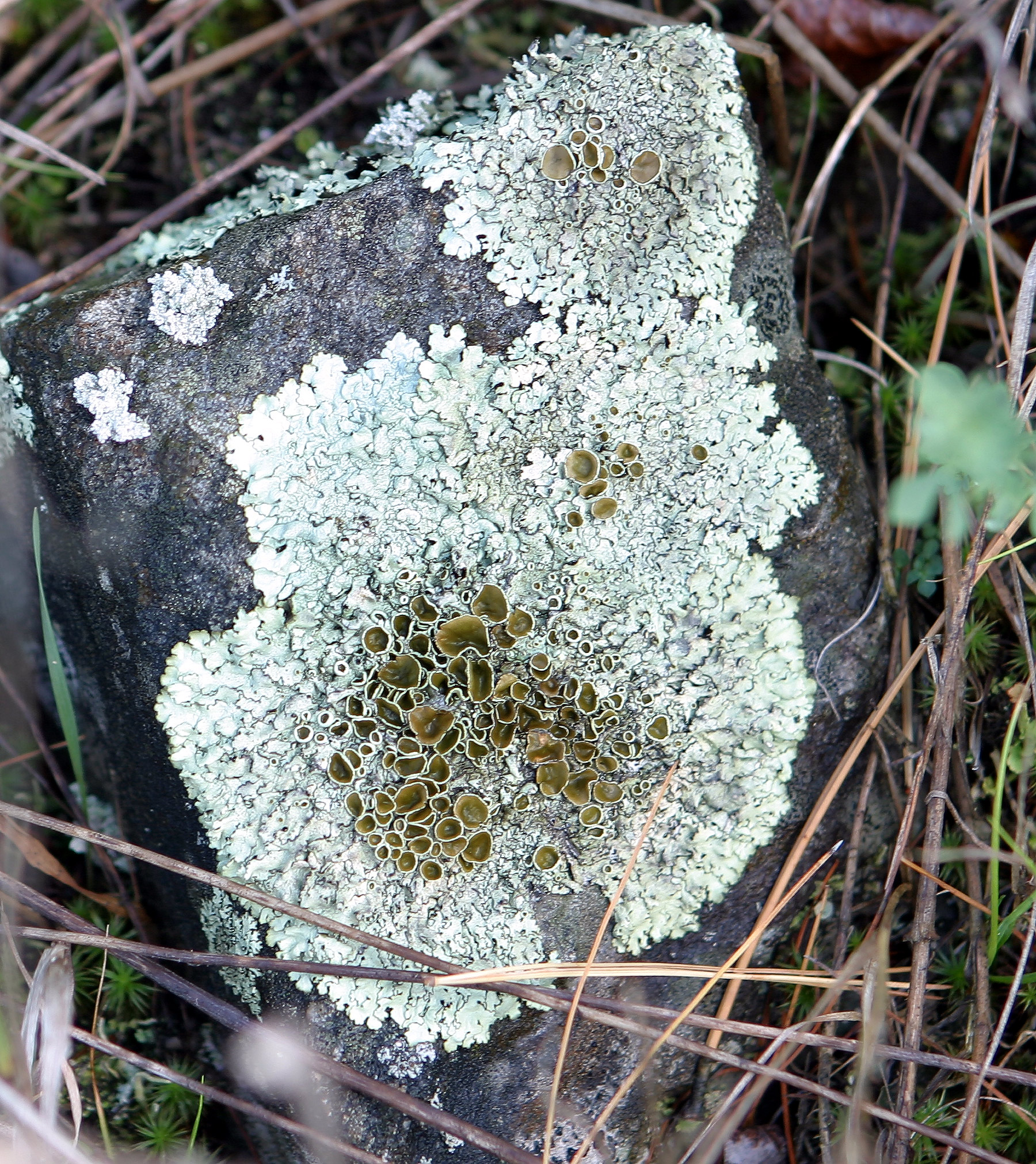
The Marion Nunataks are a small group of nunataks rising to about on Charcot Island, in the eastern Bellinghausen Sea of Antarctica. They form a 12 km chain of rocky outcrops on the mid-north coast of the island, stretching from Mount Monique at the western end to Mount Martine in the east. History They were discovered and roughly mapped on 11 January 1910 by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and named by him in association with Mount Monique and Mount Martine after his daughter, Marion. They were photographed from the air on 9 February 1947 in the course of the US Navy's Operation Highjump and mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. Antarctic Specially Protected Area Some 176 km2 of land encompassing the nunataks is protected as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.170 for its biological values. It includes two species of lichen that have not been recorded elsewhere in Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcot Island, Antarctica
Charcot may refer to: People * Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893), French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot's name is associated with many diseases, anatomical structures and conditions including: :* Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease, a form of peroneal muscular atrophy :* Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms :* Charcot–Leyden crystals :* Charcot's cholangitis triad of symptoms of ascending cholangitis :* Charcot's neurologic triad of symptoms of multiple sclerosis :* Some anterolateral central arteries in the brain are known as Charcot's artery :* Neuropathic arthropathy, Charcot's joint or Charcot foot :* Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a motor neurone disease known as both Charcot's disease and Lou Gehrig's disease :* Charcot Wilbrand syndrome or visual agnosia, inability to recognize visual stimuli * Jean-Baptiste Charcot (1867–1936), French explorer and physician, son of Jean-Martin Charcot Places in Antarctica * Charcot Bay * Charcot Cove * Charcot Island * Charcot Plate, a tectonic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey
The Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (FIDASE) was an aerial survey of the Falkland Islands Dependencies The Falkland Islands Dependencies was the constitutional arrangement from 1843 until 1985 for administering the various British territories in List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands, Sub-Antarctica and Antarctica which were governed from t ... and the Antarctic Peninsula which took place in the 1955–56 and 1956–57 southern summers. Funded by the Colonial Office and organized by Peter Mott, the survey was carried out by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd. The expedition was based at Deception Island and utilized the ''Oluf Sven'', two Canso flying-boats, and several helicopters. The photographic collection, held by the British Antarctic Survey as the United Kingdom Antarctic Mapping Centre, comprises about 12,800 frames taken on 26,700 kilometers of ground track. References {{reflist British Antarctic Territory Surveying of the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martin in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is part of the larger peninsula of West Antarctica, protruding from a line between Cape Adams (Weddell Sea) and a point on the mainland south of the Eklund Islands. Beneath the ice sheet that covers it, the Antarctic Peninsula consists of a string of bedrock islands; these are separated by deep channels whose bottoms lie at depths considerably below current sea level. They are joined by a grounded ice sheet. Tierra del Fuego, the southernmost tip of South America, is about away across the Drake Passage. The Antarctic Peninsula is in area and 80% ice-covered. The marine ecosystem around the western continental shelf of the Antarctic Peninsula (WAP) has been subjected to rapid Climate change in Antarctica, clima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets. Description By definition, ice caps are not constrained by topographical features (i.e., they must lie over the top of mountains). By contrast, ice masses of similar size that ''are'' constrained by topographical features are known as ice fields. The ''dome'' of an ice cap is usually centred on the highest point of a massif. Ice flows away from this high point (the ice divide) towards the ice cap's periphery. Ice caps significantly affect the geomorphology of the area they occupy. Plastic moulding, gouging and other glacial erosional features become present upon the glacier's retreat. Many lakes, such as the Great Lakes in North America, as well as numerous valleys have been formed by glacial action over hundreds of thousands of years. The Antarctic and Greenland contain 99% of the ice volume on earth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
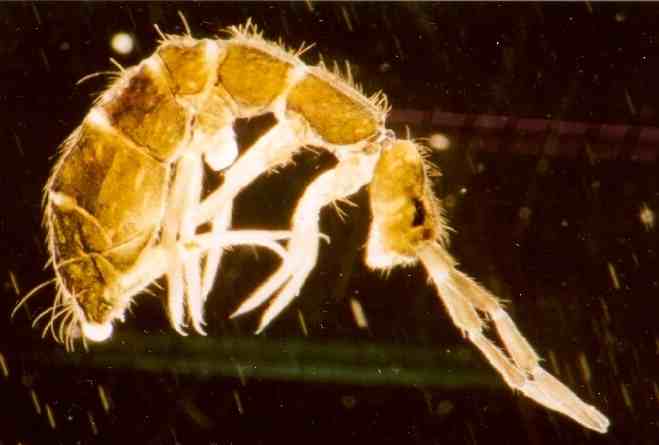
Collembola
Springtails (class Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects. Although the three lineages are sometimes grouped together in a class called Entognatha because they have internal mouthparts, they do not appear to be any more closely related to one another than they are to insects, which have external mouthparts. Springtails are omnivorous, free-living organisms that prefer moist conditions. They do not directly engage in the decomposition of organic matter, but contribute to it indirectly through the fragmentation of organic matter and the control of soil microbial communities. The word ''Collembola'' is from Ancient Greek 'glue' and 'peg'; this name was given due to the existence of the collophore, which was previously thought to stick to surfaces to stabilize the creature. Early DNA sequence studies suggested that Collembola represent a separate evolutionary line from the other Hexapoda, but others disagree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise Marchantiophyta, liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaf, leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a plant stem, stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing sporangium, spores. They are typically tall, though some species ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Specially Protected Area
An Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) is an area on the continent of Antarctica, or on nearby islands, which is protected by scientists and several different international bodies. The protected areas were established in 1961 under the Antarctic Treaty System The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms ..., which governs all the land and water south of 60 latitude and protects against human development. A permit is required for entry into any ASPA site. The ASPA sites are protected by the governments of Australia, New Zealand, United States, United Kingdom, Chile, France, Argentina, Poland, Russia, Norway, Japan, India, Italy, and Republic of Korea. There are currently 72 sites. List of ASPA sites See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Highjump
Operation HIGHJUMP, officially titled The United States Navy Antarctic Developments Program, 1946–1947, (also called Task Force 68), was a United States Navy (USN) operation to establish the Antarctic research base Little America (exploration base), Little America IV. The operation was organized by Rear admiral (United States)#Rear admiral, Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd, Jr., USN, Officer in Charge, Task Force 68, and led by Rear Admiral Ethan Erik Larson, USN, Commanding Officer, Task Force 68. Operation HIGHJUMP commenced 26 August 1946 and ended in late February 1947. Task Force 68 included 4,700 men, 70 ships, and 33 aircraft. HIGHJUMP's objectives, according to the U.S. Navy report of the operation, were: # Training personnel and testing equipment in frigid conditions; # Consolidating and extending the United States' sovereignty over the largest practicable area of the Antarctic continent (publicly denied as a goal before the expedition ended); # Determining the feasibility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit language, Inuit ) is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They often form natural pyramidal peaks. Isolated nunataks are also called glacial islands, and smaller nunataks rounded by glacial action may be referred to as rognons. The word is of Greenlandic language, Greenlandic origin and has been used in English since the 1870s. Description The term ''nunatak'' is typically used in areas where a permanent ice sheet is present and the ridge protrudes above the sheet.J. J. Zeeberg, ''Climate and Glacial History of the Novaya Zemlya Archipelago, Russian Arctic''. pp. 82–84 Nunataks present readily identifiable landmark reference points in glaciers or ice caps and are often named. While some are isolated, they can also form dense clusters, such as Queen Louise Land in Greenland. Nunataks are generally angular and jagged, hampering the formation of glacial ice on thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Charcot
Jean-Baptiste Étienne Auguste Charcot, better known in France as Commandant Charcot, (15 July 1867 in Neuilly-sur-Seine near Paris – 16 September 1936 at sea (30 miles north-west of Reykjavik, Iceland), was a French scientist, medical doctor and polar scientist. His father was the neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893). As a sportsman, he was French rugby XV champion in 1896 and also won a double silver medal in sailing at the 1900 Summer Olympics. Life Jean-Baptiste Charcot was appointed leader of the French Antarctic Expedition with the ship ''Français'' exploring the west coast of Graham Land from 1904 until 1907. The expedition reached Adelaide Island in 1905 and took pictures of the Palmer Archipelago and Loubet Coast. From 1908 until 1910, another expedition followed with the ship '' Pourquoi Pas ?'', exploring the Bellingshausen Sea and the Amundsen Sea and discovering Loubet Land, Marguerite Bay, Mount Boland and Charcot Island, which was named after his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |