|
Marine Geology
Marine geology or geological oceanography is the study of the history and structure of the ocean floor. It involves geophysical, Geochemistry, geochemical, Sedimentology, sedimentological and paleontological investigations of the ocean floor and coastal zone. Marine geology has strong ties to geophysics and to physical oceanography. Marine geological studies were of extreme importance in providing the critical evidence for sea floor spreading and plate tectonics in the years following World War II. The deep ocean floor is the last essentially unexplored frontier and detailed mapping in support of economic (petroleum and metal mining), natural disaster mitigation, and academic objectives. History The study of marine geology dates back to the late 1800s during the 4-year HMS Challenger expedition, ''Challenger'' expedition. HMS ''Challenger'' hosted nearly 250 people, including sailors, engineers, carpenters, marines, officers, and a 6-person team of scientists, led by Charles Wy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
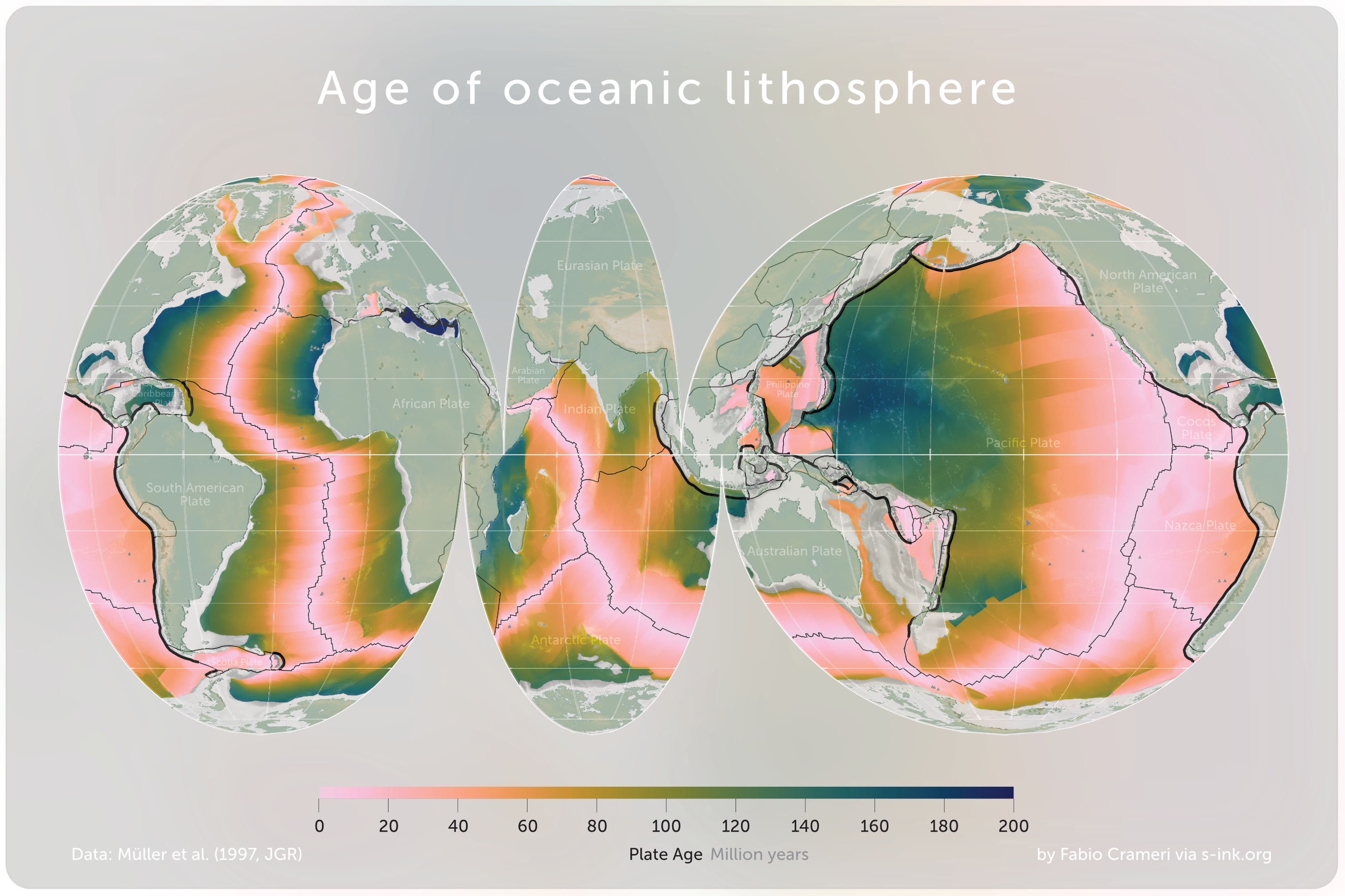
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a Divergent boundary, divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from Mantle (geology), mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Hemisphere
The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and west of the antimeridian (which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to pole). It is also used to refer to Afro-Eurasia (Africa and Eurasia) and Australia, in contrast with the Western Hemisphere, which includes mainly North and South America. The Eastern Hemisphere may also be called the "Oriental Hemisphere", and may in addition be used in a cultural or geopolitical sense as a synonym for the European term, "Old World." Geography The almost perfect circle (the earth is an oblate that is wider around the equator), drawn with a line, demarcating the Eastern and Western Hemispheres must be an arbitrarily decided and published convention, unlike the equator (an imaginary line encircling Earth, equidistant from its poles), which divides the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The prime meridian at 0° longit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, the term Western Hemisphere is often used as a metonym for the Americas or the "New World", even though geographically the hemisphere also includes parts of other continents. Geography The Western Hemisphere consists of the Americas, excluding some of the Aleutian Islands to the southwest of the Alaskan mainland; the westernmost portions of Europe and Africa, both mainland and islands; the extreme eastern tip of the Russian mainland and islands ( North Asia); numerous territories in Oceania; and a large portion of Antarctica. The center of the Western Hemisphere is located in the Pacific Ocean at the intersection of the 90th meridian west and the Equator, among the Galápagos Islands. The nearest land is Genovesa Island at . The hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seafloor Spreading
Seafloor spreading, or seafloor spread, is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt Rocks
Basalt Rocks () are volcanic rock outcrops in the form of columnar basalt located in Sinop Province, northern Turkey. The area is a registered natural monument of the country. It is away from the center of Boyabat in Sinop Province, and situated in Fındıklık location nearbay Kurusaray village. The basalt columns were formed about 3-5 million years ago according to research carried out by geologists from Mineral Research and Exploration Co. (MTA) and Dokuz Eylül University. The basalt formations are situated in three neighboring valleys. The vertically-jointed basalt columns are in polygonal form as rectangular, pentagonal and hexagonal prism In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a Prism (geometry), prism with hexagonal base. Prisms are polyhedrons; this polyhedron has 8 face (geometry), faces, 18 Edge (geometry), edges, and 12 vertex (geometry), vertices.. As a semiregular polyhedro ...s, and are high. It covers an area of . The formation, structure, and the outlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The invention of the magnetometer is usually credited to Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1832. Earlier, more primitive instruments were developed by Christopher Hansteen in 1819, and by William Scoresby by 1823. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an aircraft's attitude and heading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergent Boundary
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two List of tectonic plates, tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rift (geology), rifts, which eventually become rift valleys. Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between Oceanic crust, oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges. Current research indicates that complex convection within the Earth's mantle allows material to rise to the base of the lithosphere beneath each divergent plate boundary. This supplies the area with huge amounts of heat and a reduction in pressure that melts Rock (geology), rock from the asthenosphere (or upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle) beneath the rift area, forming large flood basalt or lava flows. Each eruption occurs in only a part of the plate boundary at any one time, but when it does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate mineral, silicate rock between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. It has a mass of and makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 46% of Earth's radius and 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid but, on geologic time scales, it behaves as a viscosity, viscous fluid, sometimes described as having the consistency of caramel. Partial melting of the mantle at mid-ocean ridges produces oceanic crust, and partial melting of the mantle at subduction zones produces continental crust. Structure Rheology Earth's upper mantle is divided into two major rheology, rheological layers: the rigid lithosphere comprising the uppermost mantle (the lithospheric mantle), and the more ductile asthenosphere, separated by the Lithosphere-Asthenosphere boundary, lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. Lithosphere underlying ocean crust has a thickness of around , whereas lithosphere underlying cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Drift
Continental drift is a highly supported scientific theory, originating in the early 20th century, that Earth's continents move or drift relative to each other over geologic time. The theory of continental drift has since been validated and incorporated into the science of plate tectonics, which studies the movement of the continents as they ride on plates of the Earth's lithosphere. The speculation that continents might have "drifted" was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596. A pioneer of the modern view of mobilism was the Austrian geologist Otto Ampferer. The concept was independently and more fully developed by Alfred Wegener in his 1915 publication, "The Origin of Continents and Oceans". However, at that time his hypothesis was rejected by many for lack of any motive mechanism. In 1931, the English geologist Arthur Holmes proposed mantle convection for that mechanism. History Early history Abraham Ortelius , Theodor Christoph Lilienthal (1756), Alexan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Hammond Hess
Harry Hammond Hess (May 24, 1906 – August 25, 1969) was an American geologist and a United States Navy officer in World War II who is considered one of the "founding fathers" of the unifying theory of plate tectonics. He published theories on sea floor spreading, specifically on relationships between island arcs, seafloor gravity anomalies, and serpentinized peridotite, suggesting that the convection in the Earth's mantle is the driving force behind this process. Early life and education Harry Hammond Hess was born on May 24, 1906, in New York City to Julian S. Hess, a member of the New York Stock Exchange, and Elizabeth Engel Hess. He attended Asbury Park High School in Asbury Park, New Jersey. In 1923, he entered Yale University, where he intended to study electrical engineering but ended up graduating with a Bachelor of Science degree in geology. Hess failed his first time taking mineralogy at Yale and was told he had no future in the field. Despite this, he continued wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |