|
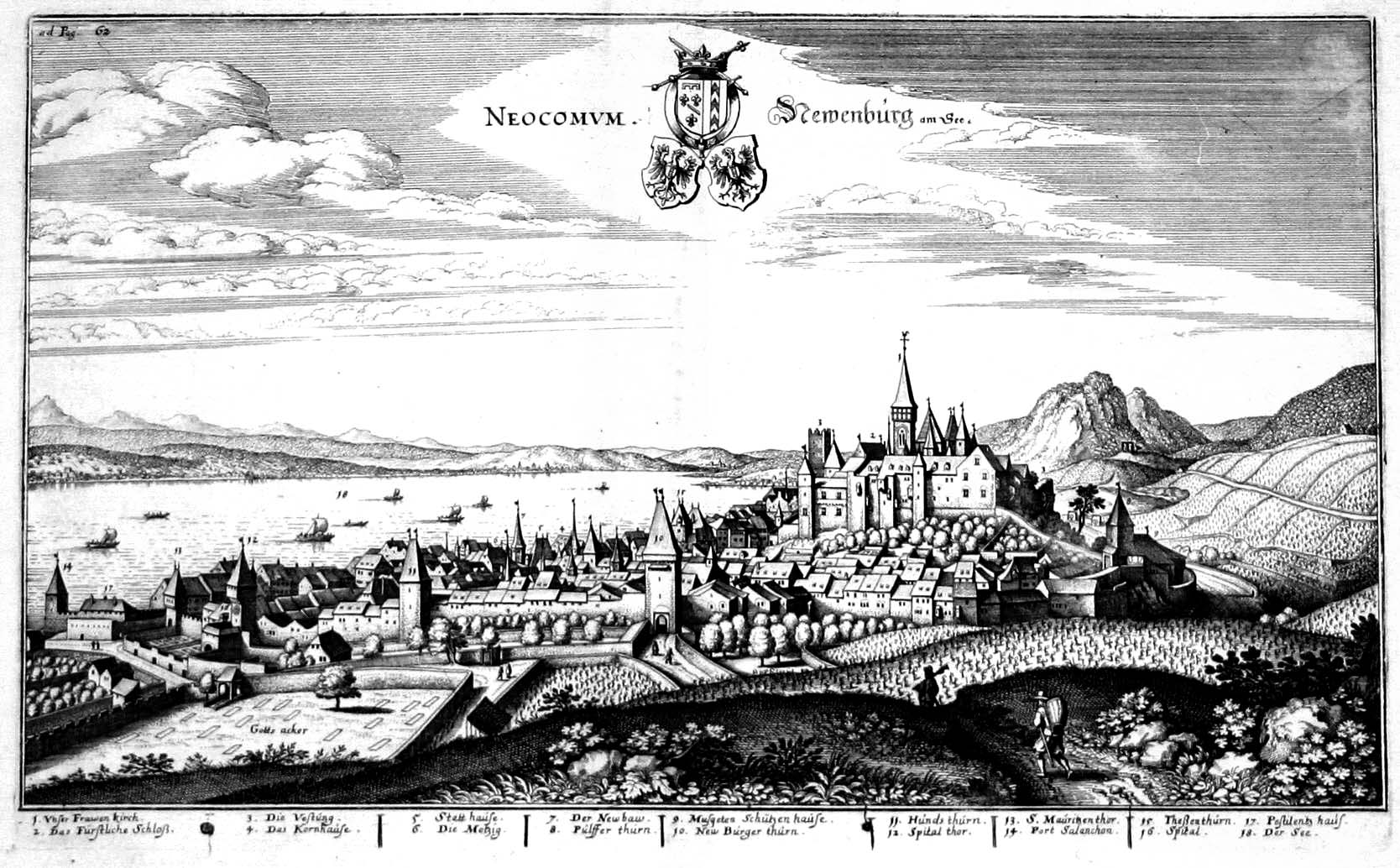
Marin-Epagnier
Marin-Epagnier was a municipality in the district of Neuchâtel in the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel. On 1 January 2009, Marin-Epagnier and Thielle-Wavre merged to form the new municipality of La Tène.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 14 January 2010 It is located at the northeastern tip of at an elevation of 455 meters, and, , a population of 3,925 people. It lies close to , at the boundary between [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Tène Culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and the Culture of Golasecca, Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences. La Tène culture's territorial extent corresponded to what is now Prehistory of France#The Iron Age, France, History of Belgium#Celtic and Roman periods, Belgium, Early history of Switzerland#Iron Age, Switzerland, History of Austria#Iron Age, Austria, History of England#Later Prehistory, England, History of Germany#Iron Age, Southern Germany, the History of the Czech lands#Iron Age, Czech Republic, Prehistoric Italy#Iron Age, Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thielle-Wavre
Thielle-Wavre is a former municipality in the district of Neuchâtel in the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel. On 1 January 2009, Marin-Epagnier and Thielle-Wavre merged to form the new municipality of La Tène.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 14 January 2010 The hamlet of Montmirail Montmirail may refer to:
Places
* Dentelles de Montmirail, a small chain of mountains in the Vaucluse department, southern France
* Montmirail, Marne, in the Marne department, France
**Battle of Montmirail, a battle fought in 1814 during the Six Da ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Blaise, Switzerland
Saint-Blaise () is a former municipality in the canton of Neuchâtel in Switzerland. On 1 January 2025 the former municipalities of Enges, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise and La Tène merged into the new municipality of Laténa. History Saint-Blaise is first mentioned in 1011 as ''Arins''. In 1209 it was mentioned as ''Sanctus Blasus''. The municipality was formerly known by its German name ''St Blasien'', however, that name is no longer used. Geography Saint-Blaise has an area, , of . Of this area, or 26.0% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 52.4% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 20.9% is settled (buildings or roads), or 0.6% is either rivers or lakes and or 0.2% is unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Neuchâtel
Lake Neuchâtel ( ; ; ) is a lake primarily in Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. The lake lies mainly in the canton of Neuchâtel, but is also shared by the cantons of Vaud, Fribourg, and Bern. It comprises one of the lakes in the Three Lakes Region (French: ''Pays des Trois-Lacs'', German: ''Drei-Seen-Land''), along with lakes Biel/Bienne and Morat/Murten. With a surface of , Lake Neuchâtel is the largest lake located entirely in Switzerland and the 59th largest lake in Europe. It is long and at its widest. Its surface is above sea level, and the maximum depth is . The total water volume is . The lake's drainage area is approximately and its culminating point is Le Chasseron at . In comparison to the Lake Geneva region, the Lake Neuchatel shoreline has experienced significant economic development with the completion of the regional motorway network. It is also known to have housed a Celtic agglomeration on pile-dwellings called La Tène and which gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuchâtel (district)
Neuchâtel (, ; ; ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel on Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 33,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". The castle after which the city is named was built by Rudolph III of Burgundy and completed in 1011. Originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the city was absorbed into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033. The domain of the counts of Neuchatel was first referred to as a city in 1214. The city came under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1806 to 1814. In 1848, Neuchâtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland. Neuchâtel is a centre of the Swiss watch industry, the site of micro-technology and hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watch
A watch is a timepiece carried or worn by a person. It is designed to maintain a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or another type of bracelet, including metal bands or leather straps. A pocket watch is carried in a pocket, often attached to a chain. A stopwatch is a type of watch that measures intervals of time. During most of their history, beginning in the 16th century, watches were mechanical devices, driven by clockwork, powered by winding a mainspring, and keeping time with an oscillating balance wheel. These are known as '' mechanical watches''. In the 1960s the electronic ''quartz watch'' was invented, powered by a battery and keeping time with a vibrating quartz crystal. By the 1980s it had taken over most of the watch market, in what became known as the quartz revolution (or the quartz crisis in Switzerland, whose renowned watch industry it decima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swisstopo
Swisstopo is the official name for the Swiss Federal Office of Topography, Switzerland's national mapping agency. The current name was made official in 2002. It had been used as the domain name for the homepage of the instituteswisstopo.admin.ch since 1997. Maps The main class of products produced by Swisstopo are topographical maps on seven different Scale (map), scales. Swiss maps have been praised for their accuracy and quality. Regular maps * 1:25.000. This is the most detailed map, useful for many purposes. Those are popular with tourists, especially for famous areas like Zermatt and St. Moritz. These maps cost CHF 13.50 each (2004). 208 maps on this scale are published at regular intervals. The first map published on this scale was ''1125 Chasseral'', in 1952. The last map published on this scale was ''1292 Maggia'', in 1972. Since 1956, composites have been published, starting with ''2501 St. Gallen''. They have the same information, but consist of several parts of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gules
In heraldry, gules () is the tincture with the colour red. It is one of the class of five dark tinctures called "colours", the others being azure (blue), sable (black), vert (green) and purpure (purple). Gules is portrayed in heraldic hatching by vertical lines, or indicated by the abbreviation g. or gu. when a coat of arms is tricked. Etymology The term ''gules'' derives from the Middle English ''goules'', which itself is an Old French word meaning "neckpiece made of red fur". ''Goules'' is derived from the Old French ''gole'' or ''guele'', both of which mean "throat", which are ultimately derived from the Latin ''gula'', also meaning "throat". Gules is similar to the English word ''gullet''. Arthur Charles Fox-Davies, A. C. Fox-Davies states that the term originates from the Persian language, Persian word , meaning "rose", but according to Brault there is no evidence to support this derivation. The modern French spelling of the tincture is ''gueules''. Both ''gules'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attitude (heraldry)
In heraldry, the term attitude describes the ''position'' in which a figure (animal or human) is emblazoned as a charge, a supporter, or as a crest. The attitude of a heraldic figure always precedes any reference to the tincture of the figure and its parts. Some attitudes apply only to predatory beasts, exemplified by the beast most usual to heraldry – the heraldic lion; other terms apply to docile animals, such as the doe, usually emblazoned as a "hind". Other heraldic attitudes, such as ''volant'' (flying), describe the positions of birds, exemplified by the bird most usual to heraldry – the heraldic eagle; moreover, birds also are described by the positions of their wings. The term ''naiant'' (swimming) applies to fish, swans, ducks, and geese. The term ''segreant'' is applied to the griffin, as an approximation of ''rampant'', and is applied to the dragon. Animal figures are positioned in profile, facing dexter (the viewer's left), and persons are shown ''affronté'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sable (heraldry)
In British heraldry, sable () is the tincture equivalent to black. It is one of the five dark tinctures called ''colours''. Sable is portrayed in heraldic hatching by criss-crossing perpendicular lines. Sable is indicated by the abbreviation s. or sa. when a coat of arms is tricked. Etymology Sable can be traced back to Middle English, Anglo-French, and ultimately to the Middle Low German ''sabel'', which refers to a species of marten known as a sable. This is related to the Middle High German ''zobel'', which is of Slav origin and akin to the Russian ''sobol, which likewise refers to the sable. Since at least the 14th century, sable has been used as a synonym for the colour black. Both ''sable'' and ''negro'' are used for black in Spanish heraldry. In Portugal, black is known as ''negro'', and in Germany the colour is called ''schwarz''. ''Sabel'' is the spelling used in Dutch heraldry. Poetic meanings The different tinctures are traditionally associated with particular hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat-of-arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its whole consists of a shield, supporters, a crest, and a motto. A coat of arms is traditionally unique to the armiger (e.g. an individual person, family, state, organization, school or corporation). The term "coat of arms" itself, describing in modern times just the heraldic design, originates from the description of the entire medieval chainmail "surcoat" garment used in combat or preparation for the latter. Rolls of arms are collections of many coats of arms, and since the early Modern Age centuries, they have been a source of information for public showing and tracing the membership of a noble family, and therefore its genealogy across time. History Heraldic designs came into general use among European nobility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blazon
In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct an accurate image. The verb ''to blazon'' means to create such a description. The visual depiction of a coat of arms or flag has traditionally had considerable latitude in design, but a verbal blazon specifies the essentially distinctive elements. A coat of arms or flag is therefore primarily defined not by a picture but rather by the wording of its blazon (though in modern usage flags are often additionally and more precisely defined using geometrical specifications). ''Blazon'' is also the specialized language in which a blazon is written, and, as a verb, the act of writing such a description. ''Blazonry'' is the art, craft or practice of creating a blazon. The language employed in ''blazonry'' has its own vocabulary and syntax, which becomes essential for comprehension when blazoning a complex coat of arms. Other armorial ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |