|
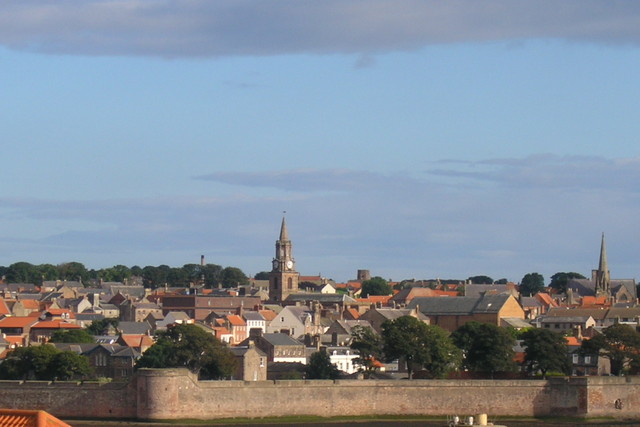
Marid Castle
Marid Castle (or Marid balance) is a historic military fortress located in the city of Dumat al-Jandal in the Al-Jawf region of Saudi Arabia, about 50 km from Sakaka. Built in the first century AD, it was first mentioned in the third century in the context of Queen Zenobia's campaign against Dumat al-Jandal and Tayma's rebellion, when her troops weren't able to capture the fortress. Etymology The castle of Marid was named for its rebellion and insurrection against those trying to storm it, as stated by Yaqout al-Hamwi. Location The castle is located on a hill rising to about 620 meters above sea level, and overlooks the city of Dumat al-Jandal, which is affiliated to the Al-Jawf region from the western side. That contributed to its importance, as the castle can oversee all parts of the town and observe any approaching friend or foe long before they arrive. History Marid fortress dates back to the first century. The oldest mention of it dates back to the third century AD when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumat Al-Jandal
Dumat al-Jandal (, ), also known as Al-Jawf or Al-Jouf (), which refers to Wadi Sirhan, is an ancient city of ruins and the historical capital of the Al Jawf Province, today in northwestern Saudi Arabia. It is located 37 km from Sakakah. The city stood north of the Nafud desert and at one end of Wadi Sirhan, at a major intersection of ancient trade routes part what is known as the incense route, with one branch linking the various sources of valuable goods in India and southern Arabia with Babylon, and another linking the Persian Gulf through Wadi Sirhan with southern Syria. Proceedings of a conference held in Berlin in 2011. It has a historical boundary wall and stands within an oasis. The ancient city of Duma was described as "the stronghold of the Arabians" on the Neo-Assyrian Esarhaddon Prism (cuneiforms on clay prism, 673-672 BC). Some scholars identify this site as territory of Dumah, one of the twelve sons of Ishmael mentioned in the Book of Genesis. Etym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Commission For Tourism And National Heritage
The Ministry of Tourism (MoT; ), before 2020 as the Saudi Commission for Tourism and National Heritage (SCTH), until 2015 as the Saudi Commission for Tourism and Antiquities (SCTA) and prior to 2008 as the Supreme Commission for Tourism (SCT), is a government ministry in Saudi Arabia that is concerned with the tourism sector of the country. Established in the year 2000 through a royal decree by King Fahd, it was transformed into a ministry in 2020. Foundation SCTH foundation has passed through several stages before reaching to its current structure by becoming the only public administration authorized and responsible for tourism and national heritage in the Kingdom. These stages are as follows: # On 12/01/1421 AH, (16/04/2000), Saudi Council of Ministers issued Resolution No. (9), approving the establishment of “Supreme Commission for Tourism” (SCT), stressing that tourism is one of the major productive sectors in retaining Saudi tourist within the country and increase inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Saudi Arabia
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourism In Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is the second biggest tourist destination in the Middle East with over 16 million visiting in 2017. Although most tourism in Saudi Arabia still largely involves religious pilgrimages, there is growth in the leisure tourism sector. As the tourism sector has been largely boosted lately, the sector is expected to a significant industry for Saudi Arabia, reducing its dependence on oil revenues. This is proved as tourism sector is expected to generate $25 billion in 2019. Potential tourist areas include the Hijaz and Sarawat Mountains, Red Sea diving and a number of ancient ruins. According to the World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC), in 2018, Travel and tourism in Saudi Arabia added 9% to the Kingdom's total economy which is worth $65.2 billion. In December 2013, Saudi Arabia announced its intention to begin issuing tourist visas for the first time in its history. Council of Ministers entrusted the Ministry of Tourism with visa issuing on the basis of certain regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Dumat Al-Jandal
Lake Dumat al-Jandal is an anthropogenic body of water, created in Dumat al-Jandal, Al-Jawf Province, northern Saudi Arabia, as a means of mitigating the risk of flooding caused by excess irrigation water from palm plantations. To accommodate the excess water, surface wells were constructed to facilitate its elevation and subsequent discharge over a neighboring hill, thereby forming the basis of this artificial lake. Lake Dumat al-Jandal is the largest unnatural lake in the Arabian Peninsula and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in particular. Description The lake is situated on a vast expanse on the banks of the Umar ibn al-Khattab Mosque and the historic Marid Castle, encompassed by mountains on multiple sides and overlooking the western side of the Dumat al-Jandal palm trees. Lake Dumat Al-Jandal is distinguished by its location within a desert setting. The lake was formed due to the irrigation project that commenced in 1987, with the water flowing from the surrounding hills i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castles In Saudi Arabia ...
This is a list of castles in Saudi Arabia. * Ajyad Fortress * Al-Faqir Fort * Al-Ukhaydir, Tabuk Province * Dhat al-Hajj * Kasbah * Marid Castle * Masmak fort * Qal'at al-Mu'azzam * Qal'at al-Qatif * Qamus * Qasr al-Farid * Qasr Ibrahim * Asfan Castle * Qishla of Jeddah * Qishla of Mecca * Qishlah * Shanqal Fort * Tarout Castle * Tarout Island * Uqair References {{Castles in Saudi Arabia * Saudi Arabia Lists of castles in the Middle East Castles Saudi Arabia Castles A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omar Ibn Al-Khattab
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Initially, Umar opposed Muhammad, who was his distant Qurayshite kinsman. However, after converting to Islam in 616, he became the first Muslim to openly pray at the Kaaba. He participated in nearly all of Muhammad’s battles and expeditions, and Muhammad conferred upon him the title ''al-Fārūq'' ("the Distinguisher") for his sound judgement. After Muhammad’s death in June 632, Umar pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr as the first caliph and served as his chief adviser. In 634, shortly before his death, Abu Bakr nominated Umar as his successor. During Umar’s reign, the caliphate expanded at an unprecedented rate, conquering the Sasanian Empire and more than two-thirds of the Byzantine Empire. His campaigns against the Sasanians r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherd
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z See also * Outline of archaeology * Table of years in archaeology * Glossary of history References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * External links About.com Archaeology Glossary {{Glossaries of science and engineering Archaeology Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
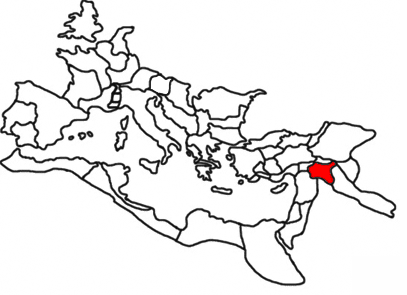
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arabs, Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' () to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BC, with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed into the Roman Empire by Emperor Trajan in 106 AD. Nabataeans' individual culture, easily identified by their characteristic finely potted painted ceramics, was adopted into the larger Greco-Roman culture. They converted to Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtain Wall (fortification)
A curtain wall is a defensive wall between fortified towers or bastions of a castle, fortress, or town. Ancient fortifications Evidence for curtain walls or a series of walls surrounding a town or fortress can be found in the historical sources from Assyria and Egypt. Some notable examples are ancient Tel Lachish in Israel and Buhen in Egypt. Curtain walls were built across Europe during the Roman Empire; the early 5th century Theodosian Walls of Constantinople influenced the builders of medieval castles many centuries later. Curtain wall castles In medieval castles, the area surrounded by a curtain wall, with or without towers, is known as the bailey. The outermost walls with their integrated bastions and wall towers together make up the enceinte or main defensive line enclosing the site. In medieval designs of castle and town, the curtain walls were often built to a considerable height and were fronted by a ditch or moat to make assault difficult. Walls were topped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamarix
The genus ''Tamarix'' (tamarisk, salt cedar, taray) is composed of about 50–60 species of flowering plants in the family Tamaricaceae, native to drier areas of Eurasia and Africa. The generic name originated in Latin and may refer to the Tamaris River in Hispania Tarraconensis (Spain). Description They are evergreen or deciduous shrubs or trees growing to in height and forming dense thickets. The largest, ''Tamarix aphylla'', is an evergreen tree that can grow to tall. They usually grow on saline soils, tolerating up to 15,000 ppm soluble salt, and can also tolerate alkaline conditions. Tamarisks are characterized by slender branches and grey-green foliage. The bark of young branches is smooth and reddish brown. As the plants age, the bark becomes gray-brown, ridged and furrowed. The leaves are scale-like, almost like that of junipers, long, and overlap each other along the stem. They are often encrusted with salt secretions. The pink to white flowers appear in dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |