|
Mariana Wolfner
Mariana Federica Wolfner is the Goldwin Smith Professor of molecular biology and genetics at Cornell University. Her research investigates sexual conflict in the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster''. She was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) in 2019 in recognition of her distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Early life and education Wolfner became interested in biology as a child. She decided to study at Cornell University because it was well known for genetics. During her undergraduate degree she worked in Gerald Fink's laboratory, studying the control of amino acids in yeast, and graduated in 1974. She moved to Stanford University for her graduate degree, where she was a doctoral student in the lab of David Hogness. She was one of the first to use recombinant DNA to isolate the genes in ''Drosophila''. Wolfner pioneered the use of cDNA hybridisation to isolate the genes which respond to ecdysone during metamorphosis. Resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson White in 1865. Since its founding, Cornell University has been a Mixed-sex education, co-educational and nonsectarian institution. As of fall 2024, the student body included 16,128 undergraduate and 10,665 graduate students from all 50 U.S. states and 130 countries. The university is organized into eight Undergraduate education, undergraduate colleges and seven Postgraduate education, graduate divisions on its main Ithaca campus. Each college and academic division has near autonomy in defining its respective admission standards and academic curriculum. In addition to its primary campus in Ithaca, Cornell University administers three satellite campuses, including two in New York City, the Weill Cornell Medicine, medical school and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a Multicellular organism, multicellular cluster with specialised Organelle, cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 micrometre, μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with Mold (fungus), molds, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
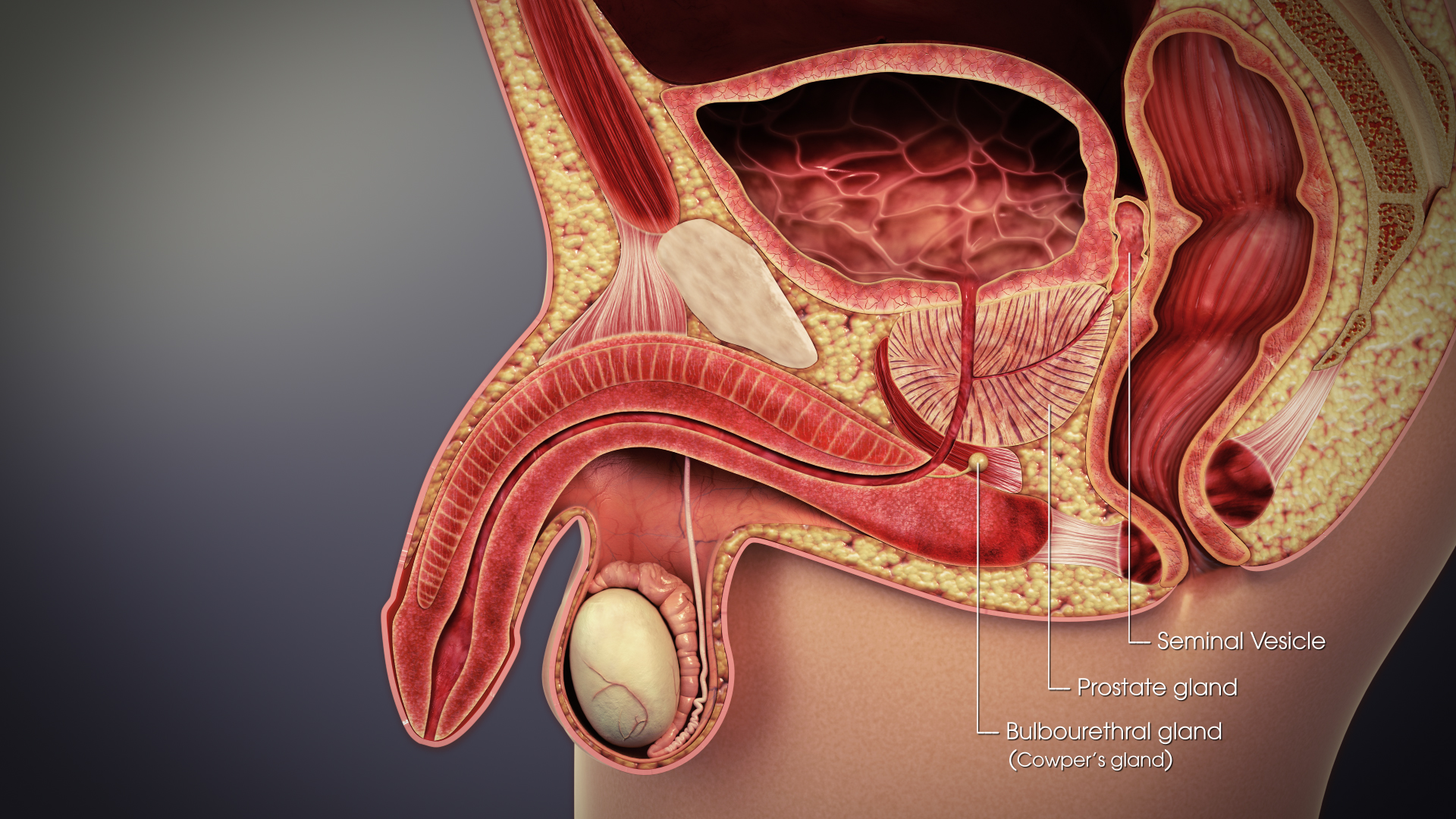
Male Accessory Gland
Male accessory glands (MAG) are the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands. These glands are found only in mammals. In insects, male accessory glands produce products that mix with the sperm to protect and preserve them, including seminal fluid proteins. Some insecticides can induce an increase in the protein content of the male accessory glands of certain types of insects. This has the unintended effect of increasing the number of offspring they produce. The accessory glands of male mammals secrete fluid for nourishment of sperm and sexual attraction. Accessory glands The male accessory glands are the ampullary gland, seminal vesicle, prostate, bulbourethral gland, and urethral gland. The products of these glands serve to nourish and activate the spermatozoa, to clear the urethral tract prior to ejaculation, serve as the vehicle of transport of the spermatozoa in the female tract, and to plug the female tract after placement of spermatozoa to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Ablation
Genetic may refer to: *Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms **Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes ***Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de novo ***Genetic mutation, a change in a gene ****Heredity, genes and their mutations being passed from parents to offspring **Genetic recombination, refers to the recombining of alleles resulting in a new molecule of DNA *Genetic relationship (linguistics), in linguistics, a relationship between two languages with a common ancestor language *Genetic algorithm In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to g ..., in computer science, a kind of search technique modeled on evolutionary biology See also * Genetic memory (other) {{disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminal Fluid Protein
Seminal fluid proteins (SFPs) or accessory gland proteins (Acps) are one of the non-sperm components of semen. In many animals with internal fertilization, males transfer a complex cocktail of proteins in their semen to females during copulation. These seminal fluid proteins often have diverse, potent effects on female post-mating phenotypes. SFPs are produced by the male accessory glands. Seminal fluid proteins frequently show evidence of elevated evolutionary rates and are often cited as an example of sexual conflict. Proteomics SFPs are best studied in mammals and insects, especially in the common fruit fly, ''Drosophila melanogaster''. Most species produce a wide variety of proteins that are transferred to females. For example, approximately 290 SFPs have been identified in ''D. melanogaster'', 46 in the mosquito '' Anopheles gambae'', and around 160 in humans. Elevated evolution Even between closely related species, the seminal fluid proteome can vary greatly. SFPs show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublesex
''Doublesex'' (''dsx'') is a gene that is involved in the sex determination system of many insects including the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster''. Sex determination The gene is expressed in both male and female flies and is subject to alternative splicing, producing the protein isoforms ''dsxf'' in females and the longer ''dsxm'' in males. The production of ''dsxf'' is caused by the presence of the female-specific version of the ''transformer'' (''tra'') gene. In a sense, the isoform of ''dsx'' informs a cell about the organism's sex; for instance, female genitals only develop if ''dsxf'' is present. In conjunction with the gene '' fruitless'', ''dsx'' also causes differences in the brain structure and behavior of males and females. Lay summary: Although the details of sex determination differ in the various species, there is a gene related to ''dsx'' in vertebrates (DMRT1) and in nematodes ( MAB-3). All of these are transcription factors with a zinc finger DNA-bindi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
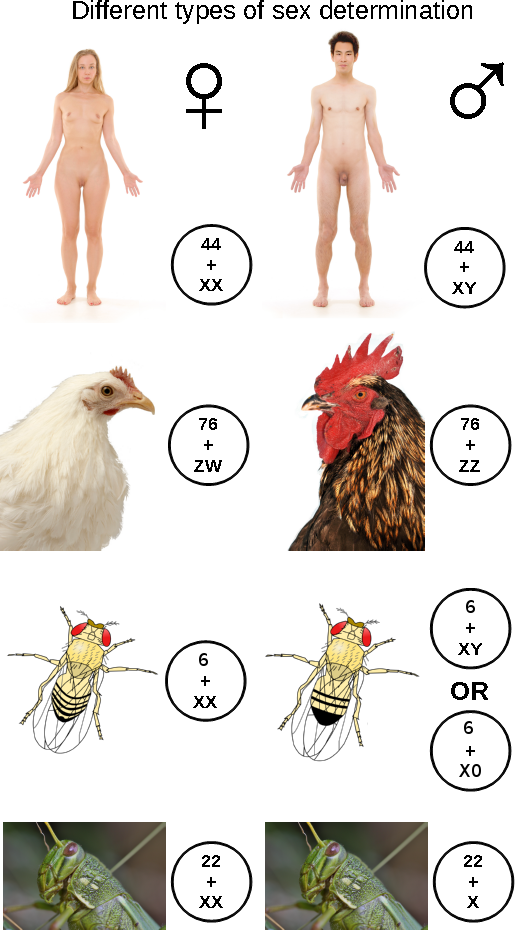
Sex-determination System
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two common sexes, males and females, and in other species, there are hermaphrodites, organisms that can function reproductively as either female or male, or both. There are also some species in which only one sex is present, temporarily or permanently. This can be due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some plants or algae the gametophyte stage may reproduce itself, thus producing more individuals of the same sex as the parent. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Baker (geneticist)
Bruce Stewart Baker (December 20, 1945 – July 1, 2018) was an American geneticist. Baker was born to William K. Baker and Margaret I. Stewart in Swannanoa, North Carolina, on December 20, 1945, while his father served in the United States military. The first Drosophila Research Conference was hosted by his parents in 1958. Baker attended high school in Chicago. He enrolled at Reed College before graduating and earned his bachelor's degree in 1966. Baker then pursued graduate study at the University of Washington under Larry Sandler, receiving his doctorate in 1971. Baker remained at UW alongside Sandler before working with James F. Crow. In 1974, Baker began teaching at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. He joined the University of California, San Diego faculty in 1976, before moving to Stanford University in 1986. In 1993, Baker was named a National Academy of Sciences member. That same year, Baker began his term as vice president of the Genetics Society of America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow
A fellow is a title and form of address for distinguished, learned, or skilled individuals in academia, medicine, research, and industry. The exact meaning of the term differs in each field. In learned society, learned or professional society, professional societies, the term refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements. Within institutions of higher education, a fellow is a member of a highly ranked group of teachers at a particular college or university or a member of the governing body in some universities. It can also be a specially selected postgraduate student who has been appointed to a post (called a fellowship) granting a stipend, research facilities and other privileges for a fixed period (usually one year or more) in order to undertake some advanced study or research, often in return for teaching services. In the context of medical education in North America, a fellow is a physician who is undergoing a supervised, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoctoral
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). Postdocs most commonly, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. According to data from the US National Science Foundation, the number of holders of PhD in biological sciences who end up in tenure track has consistently dropped from over 50% in 1973 to less than 20% in 2006. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth transformation or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some insects, jellyfish, fish, amphibians, mollusks, crustaceans, cnidarians, echinoderms, and tunicates undergo metamorphosis, which is often accompanied by a change of nutrition source or behavior. Animals can be divided into species that undergo complete metamorphosis (" holometaboly"), incomplete metamorphosis (" hemimetaboly"), or no metamorphosis (" ametaboly"). Generally organisms with a larval stage undergo metamorphosis, and during metamorphosis the organism loses larval characteristics. Etymology The word ''metamorphosis'' derives from Ancient Greek , "transformation, transforming", from ('), "after" and ('), "form". Hormonal control In insects, growth and metamorphosis are controlled by hormones synthesized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecdysone
Ecdysone is a prohormone of the major insect molting hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone, secreted from the prothoracic glands. It is of steroidal structure. Insect molting hormones (ecdysone and its homologues) are generally called ecdysteroids. Ecdysteroids act as moulting hormones of arthropods but also occur in other related phyla where they can play different roles. In ''Drosophila melanogaster'', an increase in ecdysone concentration induces the expression of genes coding for proteins that the larva requires. It causes chromosome puffs (sites of high expression) to form in polytene chromosomes. Recent findings in the laboratory of Chris Q. Doe have found a novel role of this hormone in regulating temporal gene transitions within neural stem cells of the fruit fly. Ecdysone and other ecdysteroids also appear in many plants mostly as a protection agent ( toxins or antifeedants) against herbivorous insects. These phytoecdysteroids have been reputed to have medicinal value. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |