|
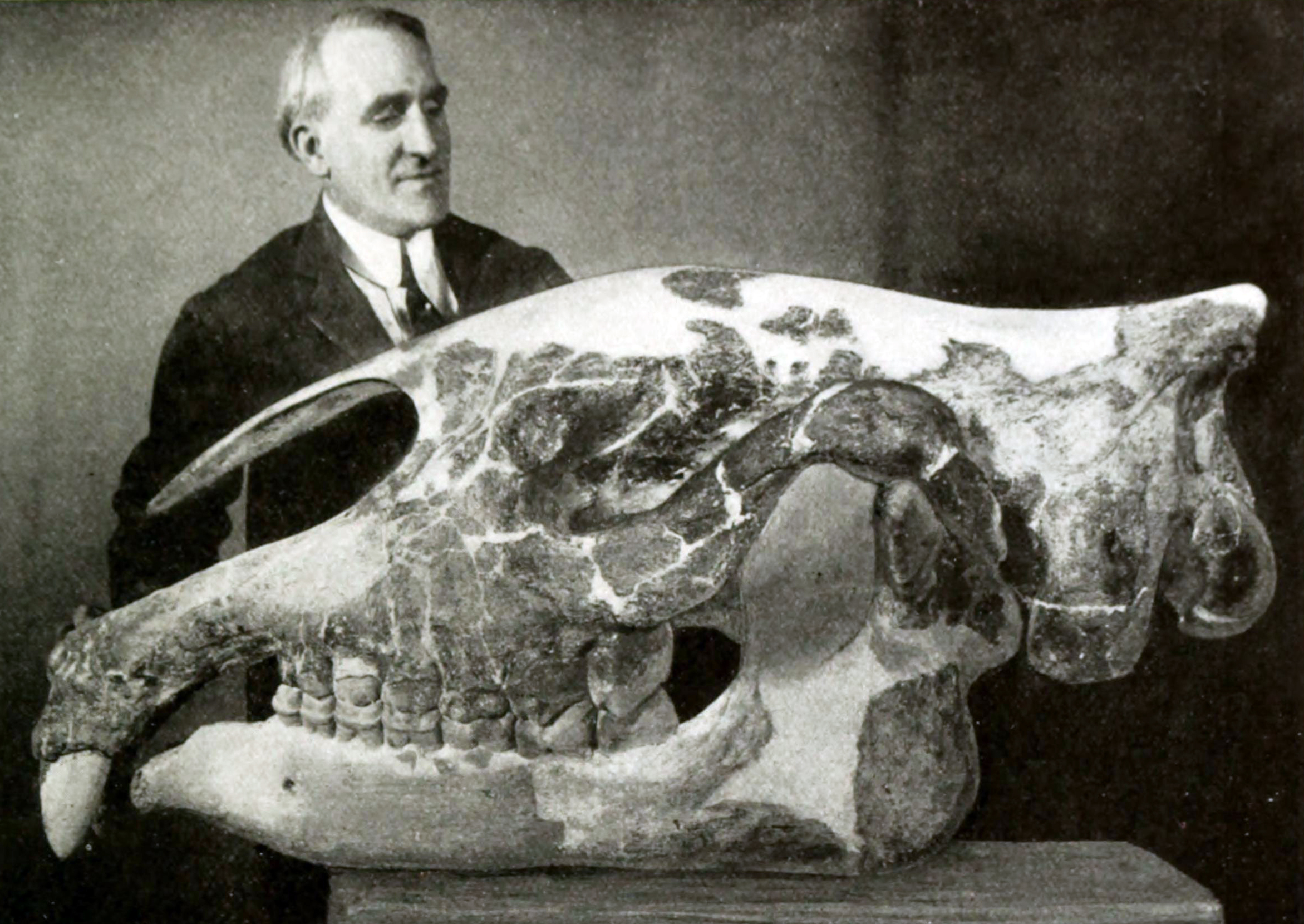
Maria V. Pavlova
Maria Vasilievna Pavlova (; ''née'' Gortynskaia (); June 26, 1854 – December 23, 1938) was a Ukrainian who became a paleontologist and academician in Moscow during the Russian Empire and Soviet era. She is known for her research on the fossils of and the naming of hoofed-mammals of the Tertiary period. She was a professor at Moscow State University. She also made great efforts to establish the Museum of Paleontology at the university. In 1926, the museum was named after her and her second husband, Alexei Petrovich Pavlov, a geologist, paleontologist, and academician who made a significant contribution in the field of stratigraphy. Early life Maria Vasillievna Gortynskaia was born in Kozelets, Ukraine in 1854. She was schooled at home until the age of eleven in 1865. Her secondary education was at the Institute for Noble Maidens in Kiev, which she completed in 1870 at the age of sixteen. Her first marriage was to Illich-Shishatsky, who died shortly after their wedding. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kozelets
Kozelets (, ) is a rural settlement in Chernihiv Raion, Chernihiv Oblast, northern Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Kozelets settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Kozelets is located on the Oster River, a tributary of the Dnieper. Population: The town was first mentioned in written documents in 1098, but its status as an urban-type settlement (one level below that of a city) was granted in 1924. Notable attractions in the city includes the Cathedral of the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin designed in the Ukrainian Baroque style by architects Ivan Hryhorovych-Barskyi and Andrei Kvasov. Kozelets also houses several local food industries, and a veterinary technicum. History Kozelets was first mentioned in 1098 as a fortified town in the East Slavic state of Kievan Rus'. During times of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Kozelets was known by the name ''Kozlohrad'' (). In the beginning of the seventeenth century, Kozelets was an important regional trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to be a polyphyletic and thereby invalid clade based on molecular data. As a result, true ungulates had since been reclassified to the newer clade Euungulata in 2001 within the clade Laurasiatheria while Paenungulata has been reclassified to a distant clade Afrotheria. Living ungulates are divided into two orders: Perissodactyla including Equidae, equines, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and Artiodactyla including Bos, cattle, antelope, Sus (genus), pigs, giraffes, camels, Ovis, sheep, deer, and Hippopotamidae, hippopotamuses, among others. Cetaceans such as Whale, whales, Dolphin, dolphins, and Porpoise, porpoises are also classified as artiodactyls, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Paleontologists
A woman is an adult female human. Before adulthood, a female child or Adolescence, adolescent is referred to as a girl. Typically, women are of the female sex and inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and women with functional uteruses are capable of pregnancy and giving childbirth, birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, ''SRY'' gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Sex differences in human physiology, Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. An adult woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. These characteristics facilitate childbirth and breastfeeding. Women typically have less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorary Members Of The USSR Academy Of Sciences
An honorary position is one given as an honor, with no duties attached, and without payment. Other uses include: * Honorary Academy Award, by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences, United States * Honorary Aryan, a status in Nazi Germany * Honorary authorship, listing of uninvolved people as co-authors of research papers * Honorary César, awarded by the Académie des Arts et Techniques du Cinema, France * Honorary consul, an unpaid part-time diplomatic consul * Honorary Goya Award, by the Academia de las Artes y las Ciencias Cinematográficas de España, Spain * Honorary Police, unpaid police force in Jersey * Honorary Prelate, a title used in the Catholic Church * Honorary society (other), whose members are elected for meritorious conduct * Honorary title, awarded as a mark of distinction ** Honorary citizenship, awarded to aliens who have rendered service to the state ** Honorary degree, academic degree awarded to someone not formally qualified to receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Paleontologists
This list of Russian biologists includes the famous biologists from the Russian Federation, the Soviet Union, the Russian Empire and other predecessor states of Russia. Biologists of all specialities may be listed here, including ecologists, botanists, zoologists, paleontologists, biochemists, physiologists and others. Alphabetical list A *Johann Friedrich Adam, discoverer of the Adams mammoth, the first complete woolly mammoth skeleton *Igor Akimushkin, biologist *Vladimir Prokhorovich Amalitskii, paleontologist *Nicolai Ivanovich Andrusov, Nicolai Andrusov, paleontologist *Andrey Avinoff, entomologist *Anatoly Andriyashev, Ichthyology, ichthyologist, zoogeography, zoogeographist B *Karl Ernst von Baer, naturalist, founder of the Russian Entomological Society, formulated embryological Baer's laws *Alexander Barchenko, notable for his research of Hyperborea *Jacques von Bedriaga, prominent herpetologist, described Bedriaga's rock lizard and Bedriaga's skink *Andrey Belozersky, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologists From The Russian Empire
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796 in paleontology, 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822 in paleontology, 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1938 Deaths
Events January * January 1 – state-owned enterprise, State-owned railway networks are created by merger, in France (SNCF) and the Netherlands (Nederlandse Spoorwegen – NS). * January 20 – King Farouk of Egypt marries Safinaz Zulficar, who becomes Farida of Egypt, Queen Farida, in Cairo. * January 27 – The Honeymoon Bridge (Niagara Falls), Honeymoon Bridge at Niagara Falls, New York, collapses as a result of an ice jam. February * February 4 ** Adolf Hitler abolishes the War Ministry and creates the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (High Command of the Armed Forces), giving him direct control of the German military. In addition, he dismisses political and military leaders considered unsympathetic to his philosophy or policies. General Werner von Fritsch is forced to resign as Commander of Chief of the German Army following accusations of homosexuality, and replaced by General Walther von Brauchitsch. Foreign Minister Baron Konstantin von Neurath is dismi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1854 Births
Events January–March * January 4 – The McDonald Islands are discovered by Captain William McDonald aboard the ''Samarang''. * January 6 – The fictional detective Sherlock Holmes is perhaps born. * January 9 – The Teutonia Männerchor in Pittsburgh is founded to promote German culture. * January 20 – The North Carolina General Assembly in the United States charters the Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad, to run from Goldsboro through New Bern, to the newly created seaport of Morehead City, near Beaufort. * January 21 – The iron clipper runs aground off the east coast of Ireland, on her maiden voyage out of Liverpool, bound for Australia, with the loss of at least 300 out of 650 on board. * February 11 – Major streets are lit by coal gas for the first time by the San Francisco Gas Company; 86 such lamps are turned on this evening in San Francisco, California. * February 13 – Mexican troops force William Walker and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novodevichy Cemetery
Novodevichy Cemetery () is a cemetery in Moscow. It lies next to the southern wall of the 16th-century Novodevichy Convent, which is the city's third most popular tourist site. History The cemetery was designed by Ivan Mashkov and inaugurated in 1898. Its importance dates from the 1930s, when the necropolises of the medieval Muscovite monasteries (Simonov Monastery, Simonov, Danilov Monastery, Danilov, Donskoy Monastery, Donskoy) were scheduled for demolition. Only the Donskoy survived the Joseph Stalin era relatively intact. The remains of many famous Russians buried in other abbeys, such as Nikolai Gogol and Sergey Aksakov, were disinterred and reburied at the Novodevichy. A 19th-century necropolis within the walls of the Novodevichy convent, which contained the graves of about 2000 Russian noblemen and university professors, also underwent reconstruction. The vast majority of graves were destroyed. It was at that time that the remains of Anton Chekhov were moved outside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khvalynsk
Khvalynsk is a river port town in Saratov Oblast, Russia, located by the Volga River. Population: 16,000 (1974). It is located on the right bank of the Volga, at the foot of the Khvalynsk Mountains, northeast of Saratov and southwest of Samara. The place name stems from the old Russian name of the Caspian Sea: Хвалынское море, or "Khvalyn Sea". The latter is derived from the name "Khwalis" for the inhabitants of Khwarezm. The town is the namesake of the Khvalynsk Hills and Khvalynsk culture. History It was founded in 1556 as a Russian outpost on the Sosnovy Island on the Volga. In 1606, the whole settlement was relocated to the spot of today's Khvalynsk and came to be known as Sosnovy Ostrov (, lit. ''pine island''). In 1780, the settlement was granted uyezd town status and renamed Khvalynsk. In the 18th–19th centuries, Khvalynsk was known as a local center for trading bread and agricultural produce. It was also one of the centers of the Old Believer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraceratherium
''Paraceratherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinocerotoids belonging to the family Paraceratheriidae. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has ever existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch (34–23 million years ago). The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. ''Paraceratherium'' means "near the hornless beast", in reference to '' Aceratherium'', the genus in which the type species ''P. bugtiense'' was originally placed. The exact size of ''Paraceratherium'' is unknown because of the incompleteness of the fossils. The shoulder height was about , and the length about . Its weight is estimated to have been about . The long neck supported a skull that was about long. It had large, tusk-like incisors and a nasal incision that suggests it had a prehensile upper lip or proboscis (trunk). The legs were long and pillar-like. The lifestyle of ''Paracera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |