|
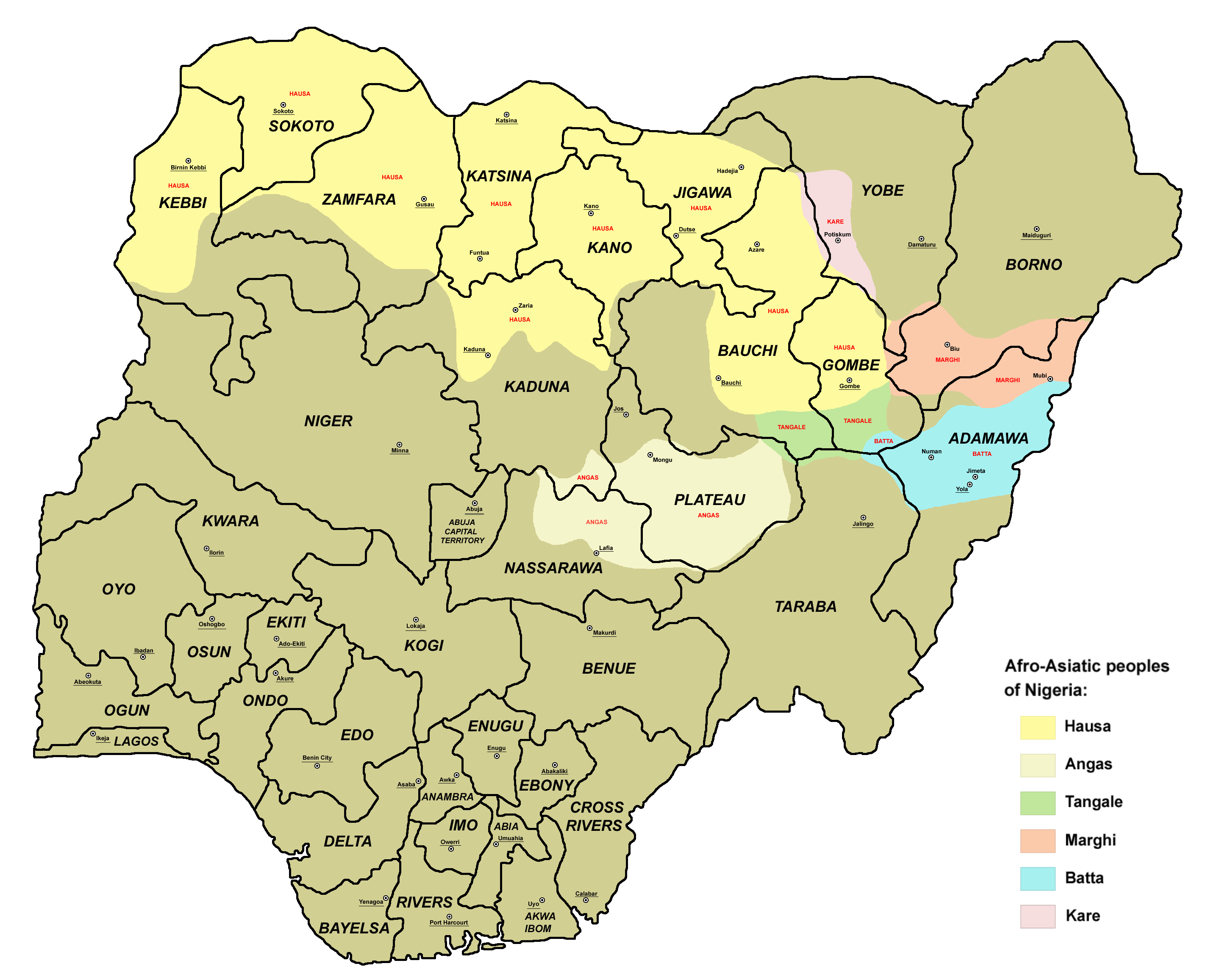
Marghi West
Putai also known as ''Marghi West'' is a nearly extinct Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northeastern Nigeria Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, .... The language is dying out and being replaced by Kanuri. See also * Marghi Central * Marghi South Notes Biu-Mandara languages Languages of Nigeria Endangered Afroasiatic languages {{Nigeria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, a population of more than 230 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising 36 States of Nigeria, states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where its capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria by population is Lagos, one of the largest List of largest cities, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borno State
Borno is a States of Nigeria, state in the North East (Nigeria), North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria. It is bordered by Yobe State, Yobe to the west, Gombe State, Gombe to the southwest, and Adamawa State, Adamawa to the south while its eastern border forms part of the national Cameroon-Nigeria border, border with Cameroon. Its northern border forms part of the national Niger–Nigeria border, border with Niger and its northeastern border forms all of the national Chad–Nigeria border, border with Chad. It is the only Nigerian state to border up to three countries. It takes its name from the historic Borno Emirate, emirate of Borno, with the emirate's old capital of Maiduguri serving as the capital city of Borno State. The state was formed in 1976 when the former North-Eastern State was broken up. It originally included the area that is now Yobe State, which became a distinct state in 1991. Borno is the List of Nigerian states by area, second largest in area of the States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chadic Languages
The Chadic languages form a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken in parts of the Sahel. They include 196 languages spoken across northern Nigeria, southern Niger, southern Chad, and northern Cameroon. By far the most widely spoken Chadic language is Hausa, a lingua franca of much of inland Eastern West Africa, particularly Niger and the northern half of Nigeria. Hausa is the only Chadic language with more than 1 million speakers. Composition Paul Newman (1977) classified the languages into the four groups which have been accepted in all subsequent literature. Further subbranching, however, has not been as robust; Roger Blench (2006), for example, only accepts the A/B bifurcation of East Chadic. Subsequent work by Joseph Lovestrand argues strongly that Kujarge is a valid member of East Chadic. The placing of Luri as a primary split of West Chadic is erroneous. Bernard Caron (2004) shows that this language is South Bauchi and part of the Polci cluster. A sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biu–Mandara Languages
The Biu–Mandara or Central Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic family are spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon. A reconstruction of Proto-Central Chadic has been proposed by Gravina (2014). Languages Gravina (2014) Gravina (2014) classifies Central Chadic as follows, as part of a reconstruction of the proto-language. Letters and numbers in parentheses correspond to branches in previous classifications. The greatest changes are breaking up and reassigning the languages of the old Mafa branch (A.5) and Mandage (Kotoko) branch (B.1). *Central Chadic **South ***South ****Bata (A.8) *****Bata Proper: Bacama language, Bacama, Bata language, Bata, Fali of Mubi, Fali, Gude language, Gude, Gudu language, Gudu, Holma language, Holma (†), Jimi language (Cameroon), Jimi, Ngwaba language, Ngwaba (from A.1 Tera), Nzanyi language, Nzanyi, Sharwa language, Sharwa *****Tsuvan: Tsuvan language, Tsuvan, Zizilivakan language, Zizilivakan ****Daba (A.7) *****Daba Proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bura Languages
Bura may refer to: Nature * Bura (wind), the Croatian name for the bora wind in the northern Mediterranean * ''Bura'' (beetle), a genus of beetles Places * Bura (Achaea), a city in Greece * Boura, Burkina Faso (other), also spelled Bura * Bura, Iran (other) * Bura, Taita-Taveta District, Kenya * Bura, Tana River District, Kenya * Bura (lake), a lake in Kazakhstan and Russia People and civilizations * Bura people or Kilba, an ethnic group in Nigeria * Bura language (also Bura-Pabir), a Chadic language spoken in Nigeria * Bura archaeological site, an ancient and medieval civilization in southwest Niger ** Bura culture, known for ceramics and metallurgy * John Bura (1944–2023), Ukrainian Greek Catholic prelate in the United States * Olha Bura (1986–2014), Ukrainian activist Sport and games * Bura (footballer) (born 1988), Portuguese footballer * Bura (water polo club), Croatian water polo club * Bura (card game), a Russian prisoners' card game Other * Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Asiatic Languages
The Afroasiatic languages (also known as Afro-Asiatic, Afrasian, Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic) are a language family (or "phylum") of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber (Amazigh), Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Omotic, and Semitic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch (which originated in West Asia). The five most spoken languages are; Arabic (of all varieties) which is by far the most widely spoken within the family, with around 411 million native speakers concentrated primarily in West Asia and North Africa, the Chadic Hausa language w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanuri Language
Kanuri () is a Saharan dialect continuum of the Nilo–Saharan language family spoken by the Kanuri and Kanembu peoples in Nigeria, Niger, Chad and Cameroon, as well as by a diaspora community residing in Sudan. Background At the turn of the 21st century, its two main dialects, Manga Kanuri and Yerwa Kanuri (also called Beriberi, which its speakers consider to be pejorative), were spoken by 9,700,000 people in Central Africa. It belongs to the Western Saharan subphylum of Nilo-Saharan. Kanuri is the language associated with the Kanem and Bornu empires that dominated the Lake Chad region for a thousand years. The basic word order of Kanuri sentences is subject–object–verb. It is typologically unusual in simultaneously having postpositions and post-nominal modifiers – for example, 'Bintu's pot' would be expressed as , 'pot Bintu-of'. Kanuri has three tones: high, low, and falling. It has an extensive system of consonantal lenition; for example, 'they' + 'have eaten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marghi Central
Margi, also known as Marghi and Marghi Central, is a Chadic language (a branch of Afroasiatic) spoken in Nigeria, Cameroon, and Chad. It is perhaps the best described of the Biu–Mandara branch of that family. Marghi South language and Putai are closely related and sometimes considered dialects of Margi. There are several kinds of Marghi language, including Madube, Izge, Lassa, Gulak, Damboa, Mulgwai, Uba and Sukur. Every kind of these languages were spoken different type of the language and were from different places. Phonology Vowels According to Maddieson (1987), Margi is noted for having a vertical vowel system, with only two phonemic vowels, and , in native vocabulary. Loan words also distinguish and . Consonants Margi has a large consonant inventory, with a number of labialised consonants and typologically infrequent speech sounds such as a labiodental flap. Hoffmann (1963) describes 84 consonantal phonemes, a very large number compared to that of most langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marghi South
Marghi South is a Chadic language of Nigeria. It is perhaps closer to Huba than it is to Margi Margi () is a village located in the Nicosia District of Cyprus. Before 1960, the village population was made up almost exclusively of Turkish Cypriot Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( or ; ) are so called ethnic Turks originating from Cyp .... References Biu-Mandara languages Languages of Nigeria {{Nigeria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Nigeria
There are over 520 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. The English-based creole ''Nigerian Pidgin'' – first used by the British and African slavers to facilitate the Atlantic slave trade in the late 17th century – is the most common lingua franca, spoken by over 60 million people. The most commonly spoken native languages are Hausa (over 63 million when including second-language, or L2, speakers), Yoruba (over 47 million, including L2 speakers), Igbo (over 31 million, including L2 speakers), Ibibio (over 10 million, including L2 speakers), Ijaw cluster (over 5 million), Fulfulde (18 million), Kanuri (7.6 million), Tiv (5 million), and approximately 2 to 3 million each of Nupe, Karai-Karai Kupa, Kakanda, Edo, Igala, Mafa, Idoma and Efik. Nigeria's linguistic diversity is a microcosm of much of Africa as a whole, and the country contains languages from the three major African langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |