|
Mancha Húmeda
Mancha Húmeda is a Spanish wetland area which was designated a Biosphere reserve in 1980. "Húmeda" means damp in Spanish and "Mancha Húmeda" refers to wetlands situated in La Mancha, a predominantly arid region of central Spain. The core area of the reserve is the Tablas de Daimiel National Park, a threatened wetland which continues to be important for its bird population. The buffer zone of ''Mancha Húmeda'' includes a natural park, the Lagunas de Ruidera Natural Park. The natural park, which is larger than the national park, is administered by the regional government of Castile-La Mancha. Conservation issues Some conservationists have questioned the future of ''Tablas de Daimiel'' as an internationally protected area, because the site's eco-system has been damaged by over-use of water resources. In the twentieth century, groundwater in the area was used in an unsustainable way to develop irrigated agriculture, and it has proved difficult to implement a solution. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Framework Directive
The Water Framework Directive (WFD; 2000/60/EC) is an EU directive to establish a framework for the protection of all water bodies (including marine waters up to one nautical mile from shore) by 2015. The WFD establishes a programme and timetable for Member States to set up river basin management plans by 2009. The Directive's aim is for all water bodies in EU member states to achieve "good status", with 47% of EU water bodies covered by the Directive failing this standard. Objectives of the Directive The Directive aims for "good status" for all ground and surface waters (rivers, lakes, transitional waters, and coastal waters) in the EU. The purpose of the WFD is to prevent deterioration of the water bodies, enhance status of aquatic ecosystems, reduce pollution from priority substances, promote sustainable water use and contribute to mitigate the effects of floods and droughts. The ecological and chemical status of surface waters are assessed according to the following c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Areas Of Castilla–La Mancha
Protection is any measure taken to guard something against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosphere Reserves Of Spain
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to matter,"Biosphere" in ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th ed. (2004) Columbia University Press. with minimal inputs and outputs. Regarding , it is an open system, with capturing |
Lagunas De Ruidera
The Lagunas de Ruidera are a group of small lakes in the Campo de Montiel (Ciudad Real), Campo de Montiel, Castilla-La Mancha, between Albacete Province, and Ciudad Real Province, Spain. Most of the lakes are interconnected and their total water amount may reach 23.06 Hectometre, hm3, which is considerable by the standards of other lakes in the Iberian Peninsula. The largest lakes are Laguna Colgada and Laguna del Rey. The area near the lakes is a tourist site, with small hotels, restaurants, camping sites and private villas, located mostly in or around Ruidera town. The area can be reached from Ossa de Montiel or Villahermosa, Ciudad Real, Villahermosa. List of lakes There are now 15 small lakes in the group: Albacete Province * Laguna Colgada * Laguna Batana * Laguna Santos Morcillo * Laguna Salvadora * Laguna Lengua * Laguna Redondilla * Laguna de San Pedro * Laguna Tinaja * Laguna Tomilla * Laguna Conceja * Laguna Taza. This lake was drained in order to build a camping sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Water Week In Stockholm
World Water Week in Stockholm is a week-long global water conference held each year in late August or early September. Known as World Water Week, the event is organized and led by the Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI). Events and conference sessions address a wide range of the world's water, development and sustainability issues and related concerns of international development. Around 1500 on-site and online participants attended the conference in 2023. The week feature experts and representatives from business, governments, water management and science sectors, intergovernmental and non governmental organisations, research and training organisations, and United Nations agencies. The conference features plenary sessions, workshops, and seminars as well as on-site exhibition. In 2023, more than 500 organisations from 190 countries and territories participated in World Water Week both on-site and online. Functioning as an open and dynamic platform, World Water Week ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockholm International Water Institute
The Stockholm International Water Institute, SIWI, works globally to change how water is understood, valued and managed. SIWI is a not-for-profit institute with a wide range of expertise in water governance – from sanitation and water resources management to water diplomacy. It helps create knowledge, develop capacity, and offer policy advice to countries, communities, and companies. Competence SIWI initiates research, manages projects and carries out investigations on a wide range of water-related issues. The organization works to influence decision-makers through its power to convene, its expertise in water governance, building dialogue, and improving policies to change water governance practice It regularly publishes reports, articles and policy briefs on a wide range of water and development issues. Staff members have expertise on water management, environmental science, strategy or technical support. The 'UNDP Water Governance Facility (WGF)'' at SIWI works to impr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Sink
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial carbon sequestration process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overarching term is carbon pool, which is all the places where carbon on Earth can be, i.e. the atmosphere, oceans, soil, florae, fossil fuel reservoirs and so forth. A carbon sink is a type of carbon pool that has the capability to take up more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases. Globally, the two most important carbon sinks are vegetation and the ocean. Soil is an important carbon storage medium. Much of the organic carbon retained in the soil of agricultural areas has been depleted due to intensive farming. '' Blue carbon'' designates carbon that is fixed via certain marine ecosystems. ''Coastal blue carbon'' includes mangroves, salt marshes and seagrasses. These make up a majority of ocean plant life and store large quantities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of nature-oriented tourism intended to contribute to the Ecological conservation, conservation of the natural environment, generally defined as being minimally impactful, and including providing both contributions to conservation and environmental education. The definition sometimes also includes being financially beneficial to the host community or making conservation financially possible. There are a range of different definitions, and the correct definition of the term was an active subject of debate as of 2009. The term is also used more widely by many organizations offering nature tourism, which do not focus on being beneficial to the environment. Since the 1980s, ecotourism has been considered an important endeavor by environmentalists for conservation reasons. Organizations focusing on ecotourism often make direct or indirect contributions to conservation or employ practices or technology that reduce impacts on the environment. However (according to Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Agricultural Policy
The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is the agricultural policy of the European Commission. It implements a system of agricultural subsidies and other programmes. It was introduced in 1962 and has since then undergone several changes to reduce the EEC budget cost (from 73% in 1985, to 37% in 2017) and consider rural development in its aims. It has however, been criticised on the grounds of its cost, its environmental, and humanitarian effects. Overview The CAP is often explained as the result of a political compromise between France and Germany: German industry would have access to the French market; in exchange, Germany would help pay for France's farmers. The CAP has always been a difficult area of EU policy to reform; it is a problem that began in the 1960s and one that has continued to the present, albeit less severely. Changes to the CAP are proposed by the European Commission, after a public consultation, which then sends its proposals to the Council and to the European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
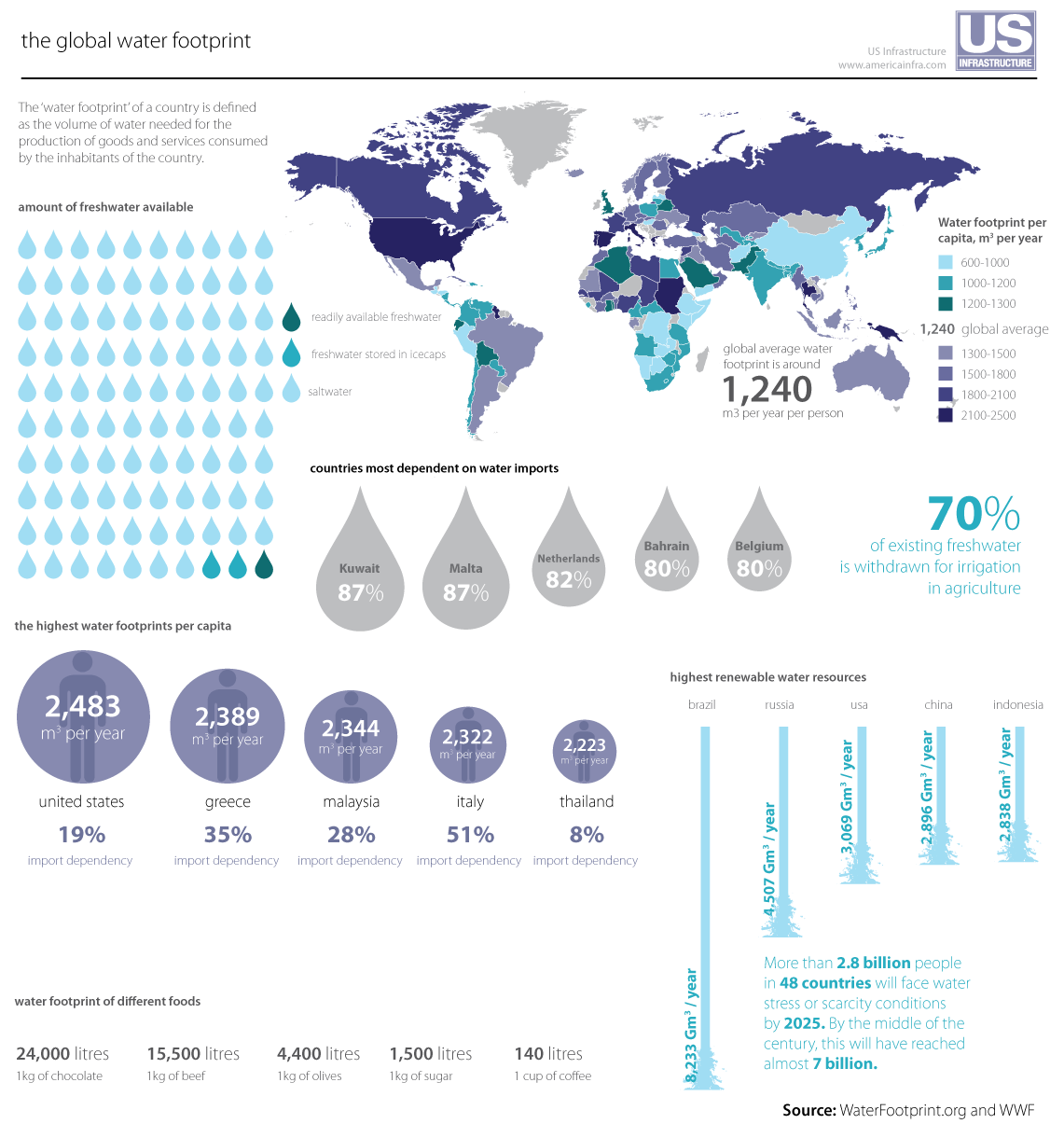
Water Footprint
A water footprint shows the extent of water use in relation to Consumption (economics), consumption by people. The water footprint of an individual, community, or business is defined as the total volume of fresh water used to produce the goods and services consumed by the individual or community or produced by the business. Water use is measured in water volume consumed (evaporated) and/or polluted per unit of time. A water footprint can be calculated for any well-defined group of consumers (e.g., an individual, family, village, city, province, state, or nation) or Production (economics), producers (e.g., a public organization, private enterprise, or economic sector), for a single process (such as growing rice) or for any Product (business), product or Service (economics), service. Traditionally, water use has been approached from the production side, by quantifying the following three columns of water use: water withdrawals in the Agriculture, agricultural, Manufacturing, industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |