|
MalĂłn 360
''MalĂłn'' (from the Mapudungun ''maleu,'' to inflict damage to the enemy) is the name given to plunder raids carried out by Mapuche warriors, who rode horses into Spanish, Chilean and Argentine territories from the 17th to the 19th centuries, as well as to their attacks on rival Mapuche factions. Historian Juan Ignacio Molina said the Mapuche considered the malĂłn to be a means of obtaining justice: Leaders such as Lientur used the malĂłn against European colonists: it consisted of a fast surprise attack by a number of mounted Mapuche warriors against the white (''huinca'') populations, ranches, settlements and fortifications in Chile and Argentina, with the aim of obtaining horses, cattle, provisions, and captives, often young women. The rapid attack without formal order did not give the targets time to organise any defence, and it left behind a devastated population unable to retaliate or pursue. In Chile, the Spaniards responded with a system of fortifications known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Moritz Rugendas-el Rapto
Johann, typically a male given name, is the German form of ''Iohannes'', which is the Latin form of the Greek name ''IĆĂĄnnÄs'' (), itself derived from Hebrew name '' Yochanan'' () in turn from its extended form (), meaning "Yahweh is Gracious" or "Yahweh is Merciful". Its English language equivalent is John. It is uncommon as a surname. People People with the name Johann include: Mononym * Johann, Count of Cleves (died 1368), nobleman of the Holy Roman Empire *Johann, Count of Leiningen-Dagsburg-Falkenburg (1662â1698), German nobleman *Johann, Prince of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1578â1638), German nobleman AâK * Johann Adam Hiller (1728â1804), German composer * Johann Adam Reincken (1643â1722), Dutch/German organist * Johann Adam Remele (died 1740), German court painter * Johann Adolf I, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels (1649â1697) * Johann Adolph Hasse (1699-1783), German Composer * Johann Altfuldisch (1911â1947), German Nazi SS concentration camp officer executed fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
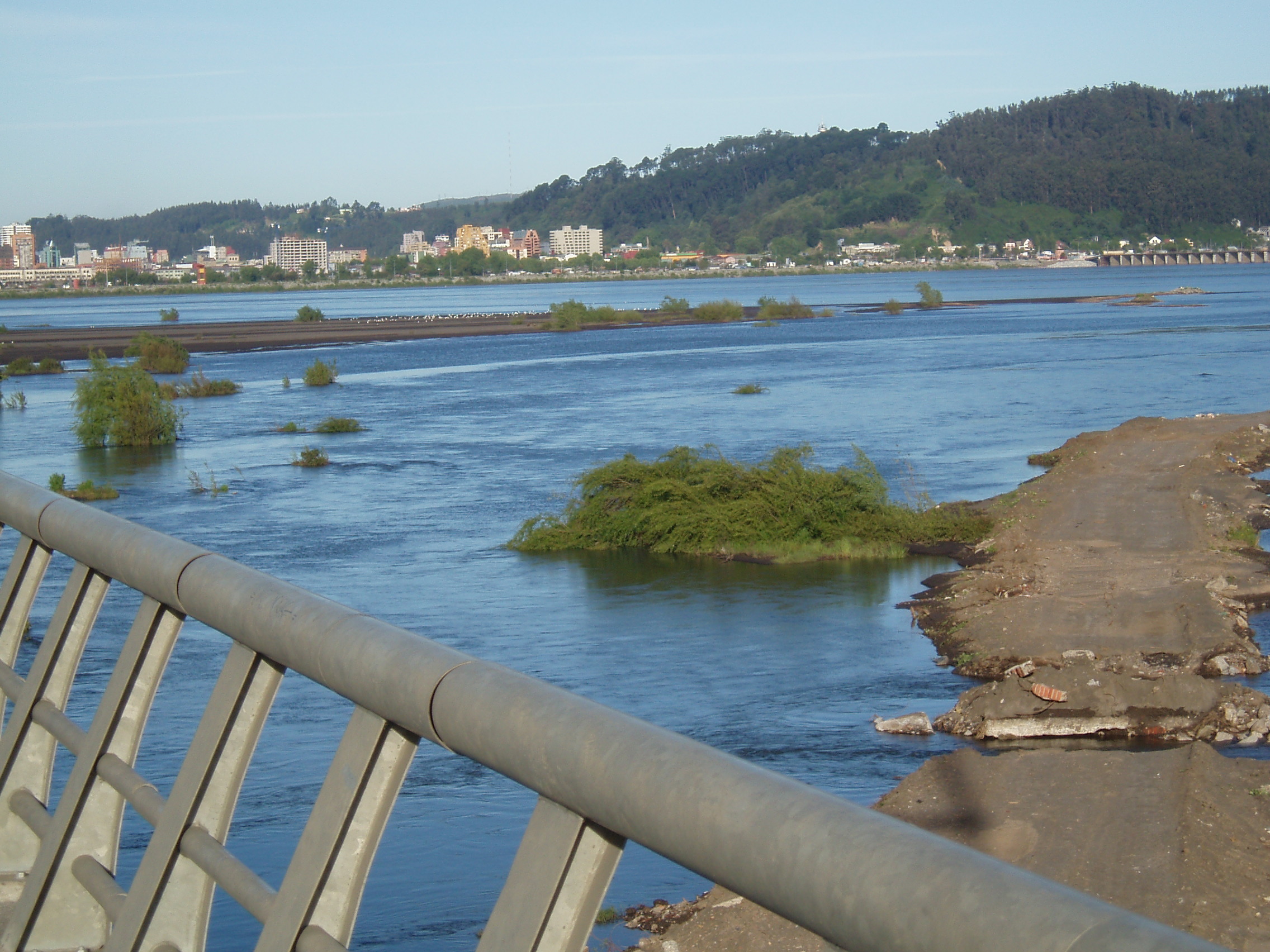
BiobĂo River
The BiobĂo River (also known as BĂo BĂo or Bio-Bio) is the second largest river in Chile. It originates at Icalma and GalletuĂ© lakes in the Andes and flows to the Gulf of Arauco (in Spanish) on the Pacific Ocean. The major tributaries of the river are the Malleco and the Laja. The river is Chile's second-longest river (the longest being the Loa River) and the BiobĂo basin is Chile's third largest watershed, after the Loa and Baker basins. The river is also the widest river in Chile, with an average width of . In the Metropolitan area of ConcepciĂłn, four bridges cross the river: BiobĂo Railroad Bridge (1889), Juan Pablo II Bridge (1973), LlacolĂ©n Bridge (2000) and Bicentennial Bridge (2010). Course The BiobĂo River originates at the east shore of GalletuĂ© Lake. The river flows east for a few kilometers to the point where it receives the waters of the nearby Icalma Lake, through a short stream. It then turns its course northwestward, meandering through a broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
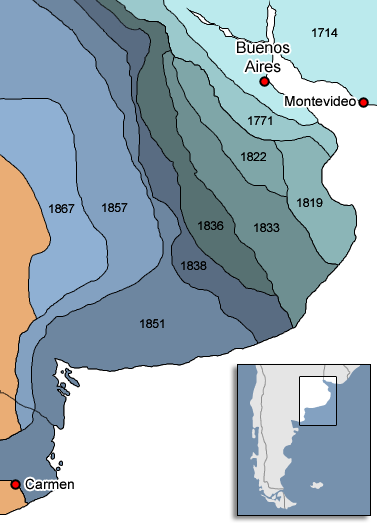
19th Century In Chile
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number. Mathematics Nineteen is the eighth prime number. Number theory 19 forms a twin prime with 17, a cousin prime with 23, and a sexy prime with 13. 19 is the fifth central trinomial coefficient, and the maximum number of fourth powers needed to sum up to any natural number (see, Waring's problem). It is the number of compositions of 8 into distinct parts. 19 is the eighth strictly non-palindromic number in any base, following 11 and preceding 47. 19 is also the second octahedral number, after 6, and the sixth Heegner number. In the Engel expansion of pi, 19 is the seventh term following and preceding . The sum of the first terms preceding 17 is in equivalence with 19, where its prime index (8) are the two previous members in the sequence. Prime properties 19 is the seventh Mersenne prime exponent. It is the second Keith number, and more specifically the first Keith pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Argentina
Colonial Argentina is designated as the period of the History of Argentina when it was an overseas territory of the Spanish Empire. It begins in the Precolumbian age of the indigenous peoples of Argentina, with the arrival of the first Spanish conqueror. European exploration When Spain and Portugal realized that the Americas were not the Indies but a new and unknown continent, they settled the portions with the Treaty of Tordesillas, dividing an eastern section of South America for Portugal and the rest for Spain. However, most of the geography of the Americas was still unknown, and many navigators sought a passage to the East Indies rather than exploring the Americas. The voyage of Ferdinand Magellan continued towards the south, passed the Strait of Magellan and eventually completed the first circumnavigation of the world. The first navigators of the Americas through unexplored territories, navigated into the wide RĂo de la Plata expecting to find a passage to the west and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Captaincy General Of Chile
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of historyâfor example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of South America
The military history of South America can be divided into two major periods â pre- and post-Columbian â divided by the entrance of European forces to the region. The sudden introduction of steel, gunpowder weapons and horses into the Americas would revolutionize warfare. Within the post-Columbian period, the events of the early 19th century, when almost all of South America was marked by wars of independence, also forms a natural historical juncture. Throughout its history, South America has had distinct military features: it has been geographically separated from many major military powers by large oceans; its unique terrain has imposed major logistical challenges, and privileged naval lines of communications. Early military history Early South American military history is distinctively different from that in Asia or Europe. Metallurgy influenced warfare in the Americas less than in other parts of the world; in South America the use of stone, wood and bone, backed by limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of The Desert
The Conquest of the Desert () was an Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic, Argentine military campaign directed mainly by General Julio Argentino Roca during the 1870s and 1880s with the intention of establishing dominance over Patagonia, inhabited primarily by Indigenous peoples in Argentina, Indigenous peoples. The Conquest of the Desert extended Argentine territories into Patagonia and ended Chilean expansion in the region. Argentine troops killed more than 1,000 Mapuches, displaced more than 15,000 more from their traditional lands and enslaved a portion of the remaining Indigenous people. Argentines of European descent, Settlers of European descent moved in and developed the lands through irrigation for agriculture, converting the territory into an extremely productive area that contributed to the status of Argentina as a great exporter of agricultural products during the early 20th century.''The Argentine Military and the Boundary Dispute With Chile, 1870-1902,'' George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pampas
The Pampas (; from Quechua 'plain'), also known as the Pampas Plain, are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre RĂos, and CĂłrdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazil's southernmost state, Rio Grande do Sul. The vast plains are a natural region, interrupted only by the low Ventana and Tandil hills, near BahĂa Blanca and Tandil (Argentina), with a height of and , respectively. This ecoregion has been changed by humans, especially since the release of animals like cattle, pigs, and especially sheep onto these plains. The climate is temperate, with precipitation of that is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year, making the soils appropriate for agriculture. The area is also one of the distinct physiography provinces of the larger ParanĂĄâParaguay plain division. It is considered that the limit of the Pampas plain is to the north with the Atlantic Forest and the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanja De Alsina
Zanja de Alsina (, '' Alsina's trench'') were a system of trenches and wooden watchtowers (''mangrullos'') built in the central and southern parts of Buenos Aires Province to defend the territories of the federal government against indigenous Mapuche '' malones''. The -wide trench was reinforced with 80 small strongholds and garrisons, called ''fortines''. The defensive line was named after Adolfo Alsina, Argentine Minister of War under President President most commonly refers to: *President (corporate title) * President (education), a leader of a college or university *President (government title) President may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Film and television *'' PrĂŠsident ... NicolĂĄs Avellaneda who planned the building of the trench in the 1870s. The trench's purpose was denounced when it became clear that it was unable to stop large-scale incursions between 1876 and 1877. Conquest of the Desert Fortification lines Forts in Argentina Buildings and struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BahĂa Blanca
BahĂa Blanca (; English: ''White Bay''), colloquially referred to by its own local inhabitants as simply BahĂa, is a city in the Buenos Aires Province, Buenos Aires province of Argentina, centered on the northwestern end of the eponymous Blanca Bay of the Argentine Sea. It is 4th largest city in the province, and the 16th largest in the country by metropolitan population. It is the seat of government of the BahĂa Blanca Partido, with 336,574 inhabitants according to the . BahĂa Blanca is the principal city in the Greater BahĂa Blanca metropolitan area. The city has an important seaport with a depth of , kept constant upstream almost all along the length of the bay, where the NapostĂĄ Stream drains. ''BahĂa Blanca'' means "White Bay". The name is due to the color of the salt covering the local soil surrounding the shores. The bay (which is an estuary) was seen by Ferdinand Magellan during his first circumnavigation of the world on the order of Charles I of Spain in 1520, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Frontera (geographical Region)
La Frontera is a name used in Chile to refer to the region around the BĂo BĂo River, or to the whole area between it and the ToltĂ©n River. The use of this latter definition is largely coterminous with the historical usage of AraucanĂa. The term was coined during the period when the region was the frontier of the Captaincy General of Chile, then a part of the Spanish Empire and later the Republic of Chile, with the Mapuche people inhabiting the AraucanĂa following their revolt in 1598. Subsequently, the Spanish Empire established a system of forts between the BĂo BĂo River and the Itata River, as well as some within the AraucanĂa. This system continued through the 18th century and into the 19th century. Forts and settlements of La Frontera The first fortress rebuilt following the 1599 destruction of the forts in Catirai and its city Santa Cruz de Coya, the cities of Santa MarĂa la Blanca de Valdivia, San AndrĂ©s de Los Infantes and San BartolomĂ© de ChillĂĄn y Gamboa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ăngel DELLA Valle - La Vuelta Del MalĂłn - Google Art Project (cropped)
Angel is a given name meaning "angel", "messenger". In the English-speaking world Angel is used for both boys and girls. From the medieval Latin masculine name ''Angelus'', which was derived from the name of the heavenly creature (itself derived from the Ancient Greek word áŒÎłÎłÎ”Î»ÎżÏ (''angelos'') meaning "messenger"). It is gradually gaining popularity in the English-speaking world, where it is sometimes used as a feminine given name in modern times. In the United States, it is also seeing increasing use among boys, usually using the standard English pronunciation of the word angel. Ăngel (pronounced /Ëanxel/) is a common male name in Spanish-speaking countries. Variations * Albanian: EngjĂ«ll, Ankelo, Anxhelo * Asturian: Ănxel, Ănxelu, Xelu (short) * Bulgarian: ĐĐœĐłĐ”Đ» (''Angel'') (masc.), ĐĐœĐłĐ”Đ»ĐžĐœĐ° (''Angelina'') (fem.) * Croatian: AnÄeo, AnÄelko (masc.); AnÄela, AnÄelka (fem.) * French: Ange (masc.), AngĂšl (masc.), AngĂšle (fem.), AngĂ©lique (fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |