|
Malonic Acid
Malonic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH2(COOH)2. The ionized form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's diethyl ester. The name originates from the Greek word μᾶλον (''malon'') meaning 'apple'. History Malonic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in many fruits and vegetables. There is a suggestion that citrus fruits produced in organic farming contain higher levels of malonic acid than fruits produced in conventional agriculture. Malonic acid was first prepared in 1858 by the French chemist Victor Dessaignes via the oxidation of malic acid. Hermann Kolbe and Hugo Müller independently discovered how to synthesize malonic acid from propionic acid, and decided to publish their results back-to-back in the Chemical Society journal in 1864. This led to priority dispute with Hans Hübner and Maxwell Simpson who had independently published preliminary results on rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
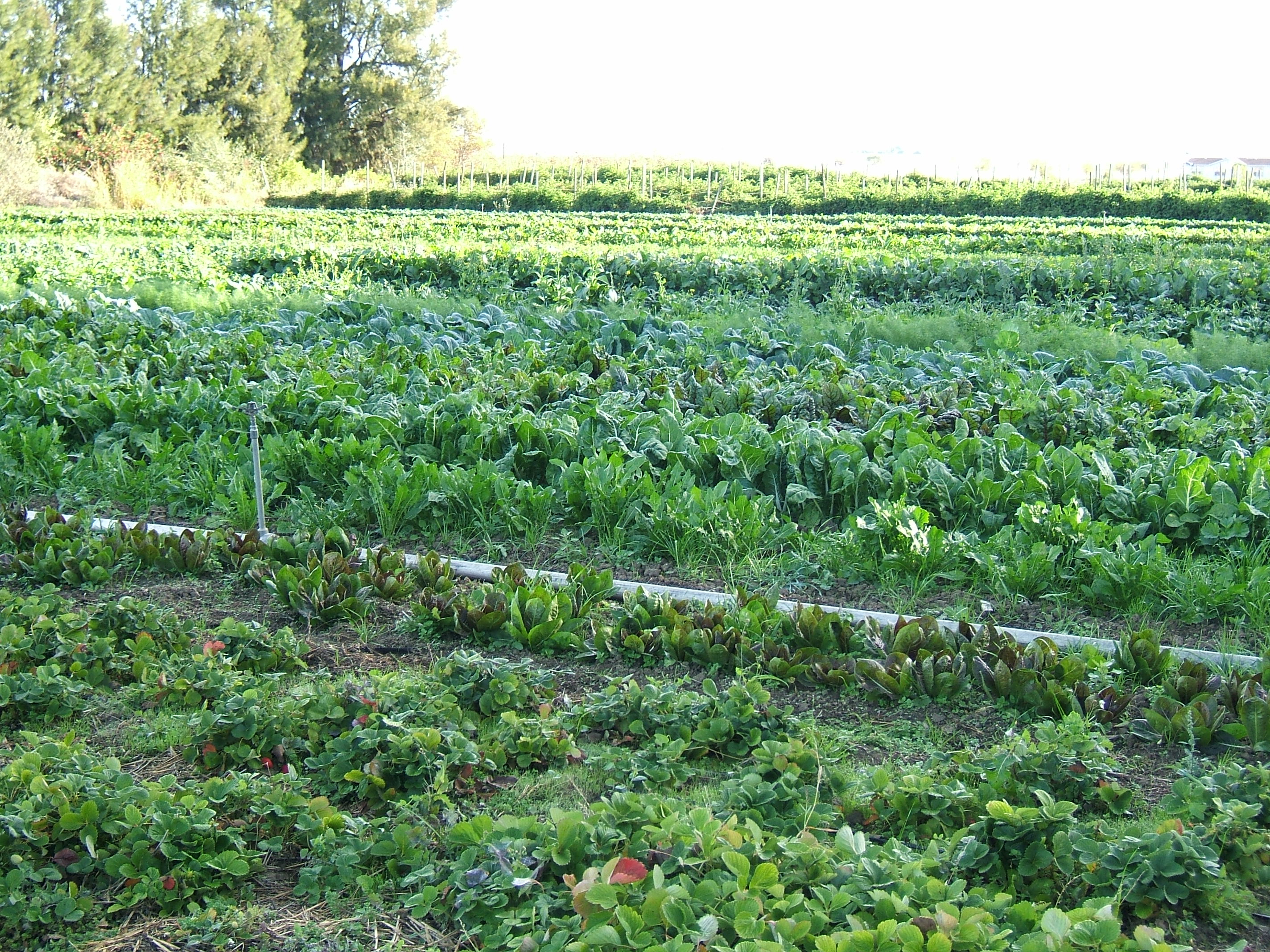
Organic Farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of organic products and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007.''/ref> is an agricultural system that emphasizes the use of naturally occurring, non-synthetic inputs, such as compost manure, green manure, and bone meal and places emphasis on techniques such as crop rotation, companion planting, and mixed cropping. Biological pest control methods such as the fostering of insect predators are also encouraged. Organic agriculture can be defined as "an integrated farming system that strives for sustainability, the enhancement of soil fertility and biological diversity while, with rare exceptions, prohibiting synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified organisms, and growth hormones". It originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Cyanide
Sodium cyanide is a compound with the formula Na C N and the structure . It is a white, water-soluble solid. Cyanide has a high affinity for metals, which leads to the high toxicity of this salt. Its main application, in gold mining, also exploits its high reactivity toward metals. It is a moderately strong base. Production and chemical properties Sodium cyanide is produced by treating hydrogen cyanide with sodium hydroxide: : Worldwide production was estimated at 500,000 tons in the year 2006. Formerly it was prepared by the Castner process involving the reaction of sodium amide with carbon at elevated temperatures. : The structure of solid NaCN is related to that of sodium chloride. The anions and cations are each six-coordinate. Potassium cyanide (KCN) adopts a similar structure. When treated with acid, it forms the toxic gas hydrogen cyanide: : Because the salt is derived from a weak acid, sodium cyanide readily reverts to HCN by hydrolysis; the moist solid emits smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the chloralkali process. Hydrates Sodium carbonate is obtained as three hydrates and as the anhydrous salt: * sodium carbonate decahydrate ( natron), Na2CO3·10H2O, which readily effloresces to form the monohydrate. * sodium carbonate heptahydrate (not known in mineral form), Na2CO3·7H2O. * sodium carbonate monohydrate ( thermonatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of Malonic Acid
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors **Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule *Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroacetic Acid
Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is the organochlorine compound with the formula . This carboxylic acid is a useful building block in organic synthesis. It is a colorless solid. Related compounds are dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid. Production Chloroacetic acid was first prepared (in impure form) by the French chemist Félix LeBlanc (1813–1886) in 1843 by chlorinating acetic acid in the presence of sunlight, and in 1857 (in pure form) by the German chemist Reinhold Hoffmann (1831–1919) by refluxing glacial acetic acid in the presence of chlorine and sunlight, and then by the French chemist Charles Adolphe Wurtz by hydrolysis of chloroacetyl chloride (), also in 1857. Chloroacetic acid is prepared industrially by two routes. The predominant method involves chlorination of acetic acid, with acetic anhydride as a catalyst: : This route suffers from the production of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell Simpson
Maxwell Simpson (15 March 1815 – 26 February 1902) was an eminent Irish chemist. Life He was born in Beach Hill, County Armagh, Ireland, son of Thomas Simpson. He attended Dr. Henderson's school at Newry before continuing to Trinity College, Dublin in 1832. He graduated in 1837 and travelled on the continent. After attending a lecture in Paris by Dumas on chemistry he decided to study that subject, which he did at University College, London. In 1847 he became lecturer in chemistry at the Park Street Medical School (later Ledwich School of Medicine) in Dublin. Upon closure of that school he lectured at the Peter St. School of Medicine. He then took three years leave of absence in order to study in Germany, returned to Dublin in 1854, spent two further years in Paris and returned again in 1860. At this point he built a laboratory in his Dublin home in which he worked for the next seven years. During this early part of his life he had started making the discoveries that place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Hübner
Hans Hübner (13 October 1837, in Düsseldorf – 4 July 1884, in Göttingen) was a German chemist. He was the son of painter Julius Hübner (1806–1882). He studied chemistry at the University of Göttingen, receiving his doctorate in 1859 with a dissertation on acrolein. Following graduation, he continued his education at the University of Heidelberg with Robert Bunsen and at the University of Ghent under August Kekulé. In 1863 he obtained his habilitation at Göttingen, where from 1864 he worked as an assistant at the institute of chemistry under Friedrich Wöhler. In 1870 he became an associate professor, followed by a full professorship in 1874. In 1882 he succeeded Wöhler as director of the chemistry institute at the university.Hübner, Hans at |
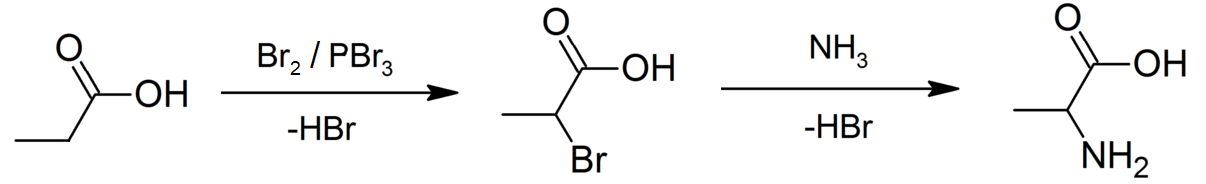
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the Carboxylate salt, salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Müller
Hugo Müller (29 July 1833 – 23 May 1915) was an Anglo-German analytical chemist, botanist and industrialist. He was a Fellow of the Royal Society. He is known for being the first person to synthesize hexachlorobenzene. Early life Hugo Müller was born on 29 July, 1833, in Tirschenreuth, Germany. He studied chemistry in Leipzig University. He was a student of Friedrich Wöhler at the University of Göttingen, where he earned his PhD. He was also assistant to Justus von Liebig at the University of Munich. Career Müller moved to United Kingdom in 1855 to work with Warren De la Rue as recommended by Liebig. De la Rue and Müller developed a chloride of silver battery. He earned a Legum Doctor degree from the University of St Andrews and a Doctor of Science degree from the University of Manchester. He also worked with John Stenhouse. Müller discovered that iodine could be used as a catalyst in chlorination. In 1864, Müller discovered how to transform mono-functional c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |