|
Malonate Uptake
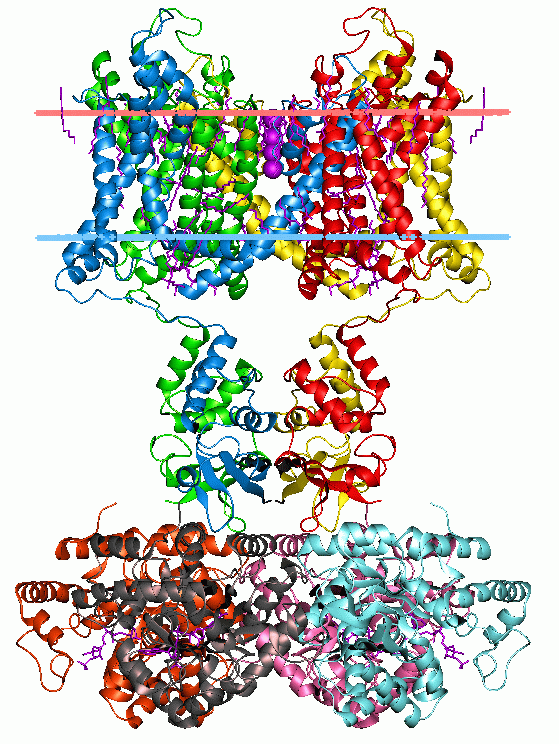
The Malonate Uptake (MatC) familyTC# 2.A.101 is a constituent of the ion transporter (IT) superfamily. It consists of proteins from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., Xanthomonas, Rhizobium and Streptomyces species), simple eukaryotes (e.g., '' Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'') and archaea (e.g., ''Methanococcus jannaschii''). The proteins are of about 450 amino acyl residues in length with 12-14 putative transmembrane segments (TMSs). Closest functionally-characterized homologues are in the DASSTC #2.A.47 family. One member of this family is a putative malonate transporter (MatC of ''Rhizobium leguminosarum ''Rhizobium leguminosarum'' is a bacterium which lives in a mutualistic symbiotic relationship with legumes, and has the ability to fix free nitrogen from the air. ''R. leguminosarum'' has been very thoroughly studied—it has been the subject ...'' bv ''trifolii''TC# 2.A.101.1.2. See also "fkbF - FkbF - Streptomyces hygroscopicus subsp. ascomyceticus - fk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Transporter
In biology, a transporter is a transmembrane protein that moves ions (or other small molecules) across a biological membrane to accomplish many different biological functions including, cellular communication, maintaining homeostasis, energy production, etc. There are different types of transporters including, pumps, uniporters, antiporters, and symporters. Active transporters or ion pumps are transporters that convert energy from various sources—including adenosine triphosphate (ATP), sunlight, and other redox reactions—to potential energy by pumping an ion up its concentration gradient. This potential energy could then be used by secondary transporters, including ion carriers and ion channels, to drive vital cellular processes, such as ATP synthesis. This page is focused mainly on ion transporters acting as pumps, but transporters can also function to move molecules through facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion does not require ATP and allows molecules, that are unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Transporters
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-span (or bitopic) or multi-span (polytopic). Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do not pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumps
A pump is a device that moves fluids ( liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they use to move the fluid: ''direct lift'', ''displacement'', and ''gravity'' pumps. Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and aeration, in the car industry for water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers and other components of heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and penile prosthesis. When a casing contains only one revolving impeller, it is called a single-stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane ( transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Families
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. The most important of these is sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence), since it is the strictest indicator of homology and therefore the clearest indicator of common ancestry. A fairly well developed framework exists for evaluating the significance of similarity between a group of sequences using sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are very unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizobium Leguminosarum
''Rhizobium leguminosarum'' is a bacterium which lives in a mutualistic symbiotic relationship with legumes, and has the ability to fix free nitrogen from the air. ''R. leguminosarum'' has been very thoroughly studied—it has been the subject of more than a thousand publications. Morphology ''Rhizobium leguminosarum'' is a Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped, aerobic bacterium. Common biovars ''Rhizobium leguminosarum'' biovar ''trifolii'', and ''R. leguminosarum'' biovar ''viciae'' are the most commonly studied biovars of ''R. leguminosarum'', with certain studies seemingly treating ''R. trifolii'' as its own species. Fatty acid synthesis ''Rhizobium leguminosarum''s acyl carrier protein differs from most ACPs by having a C-terminus extension. This ACP is also used in the synthesis of unusually long ACPs which themselves are then used in the synthesis of the ''R. leguminosarum'' nod factor Nod factors (nodulation factors or NF), are signaling molecules produced by soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divalent Anion-Sodium Symporter
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Description The combining capacity, or affinity of an atom of a given element is determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; in ammonia, nitrogen has a valence of 3; in water, oxygen has a valence of 2; and in hydrogen chloride, chlorine has a valence of 1. Chlorine, as it has a valence of one, can be substituted for hydrogen. Phosphorus has a valence of 5 in phosphorus pentachloride, . Valence diagrams of a compound represent the connectivity of the elements, with lines drawn between two elements, sometimes called bonds, representing a saturated valency for each element. The two tables below show some examples of different compounds, their valence diagrams, and the valences for each element of the compound. Modern definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism '' Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanococcus Jannaschii
''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii'' (formerly ''Methanococcus jannaschii'') is a thermophilic methanogenic archaean in the class Methanococci. It was the first archaeon to have its complete genome sequenced. The sequencing identified many genes unique to the archaea. Many of the synthesis pathways for methanogenic cofactors were worked out biochemically in this organism, as were several other archaeal-specific metabolic pathways. History ''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii'' was isolated from a submarine hydrothermal vent at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. Sequencing ''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii'' was sequenced by a group at TIGR led by Craig Venter using whole-genome shotgun sequencing. ''Methanocaldococcus jannaschii'' represented the first member of the Archaea to have its genome sequenced. According to Venter, the unique features of the genome provided strong evidence that there are three domains of life. Taxonomy ''Methanocaldoccus jannaschii'' is a membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
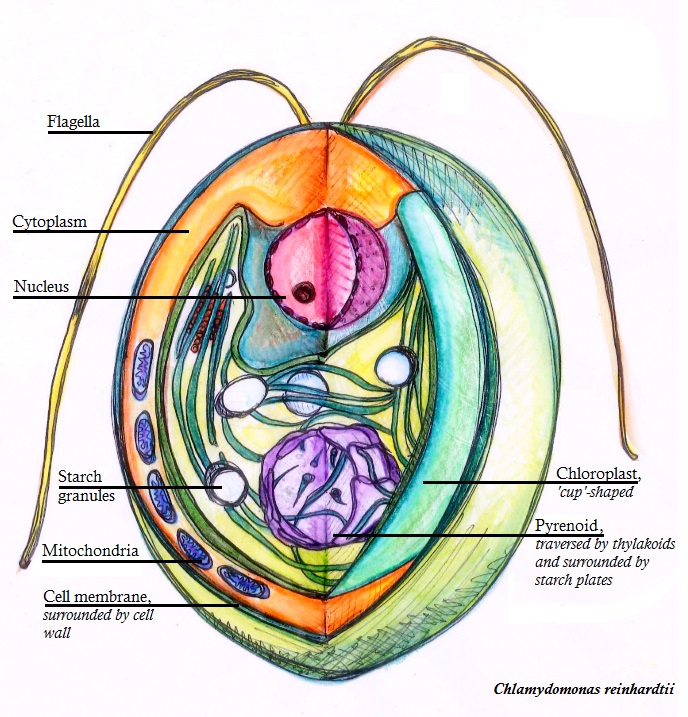
Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii
''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light. ''Chlamydomonas'' species are widely distributed worldwide in soil and fresh water. ''Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' is an especially well studied biological model organism, partly due to its ease of culturing and the ability to manipulate its genetics. When illuminated, ''C. reinhardtii'' can grow photoautotrophically, but it can also grow in the dark if supplied with organic carbon. Commercially, ''C. reinhardtii'' is of interest for producing biopharmaceuticals and biofuel, as well being a valuable research tool in making hydrogen. History The ''C. reinhardtii'' wild-type laboratory strain c137 (mt+) originates from an isolate collected near Amherst, Massachusetts, in 1945 by Gilbert M. Smith. The species' name h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |