|
Malik Sarwar
Sultan-ush-Sharq Atabak-i-Azam Malik Sarwar was the first sultan of the Jaunpur Sultanate and the founder of the Sharqi dynasty. Early life Malik Sarwar was an eunuch of common birth, possibly a slave of African descent, in the Delhi Sultanate. The first mention of him in contemporary records describes him as the custodian of royal jewelry during the reign of Firuz Shah Tughlaq. He was later appointed ''Shahnah-i-Shahr'' (governor of the city) of Delhi. He played an important role in the accession of Muhammad Shah to the throne of Delhi, and was appointed the wazir and awarded the title of ''Khwaja-i-Jahan''. He later made Malik Sarwar the governor of the eastern provinces, awarding him the title of ''Sultan-ush-Sharq'' (sultan Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaunpur Sultanate
The Jaunpur Sultanate () was a late medieval Indian Muslim state which ruled over much of what is now the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar and southern Nepal between 1394 and 1494. It was founded in 1394 by Khwajah-i-Jahan Malik Sarwar, a eunuch slave and former wazir of Sultan Nasiruddin Muhammad Shah IV Tughluq, amidst the disintegration of the Delhi Sultanate's Tughlaq dynasty. Centred in Jaunpur, the Sultanate extended authority over a large part of the Ganges-Yamuna Doab. It reached its greatest height under the rule of Sultan Ibrahim Shah, who also vastly contributed to the development of Islamic education in the Sultanate. In 1494, Sultan Hussain Shah Sharqi was defeated by the forces of the Afghan ruler Bahlul Lodi, Sultan of the Lodi dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate at Benares at which point Hussain fled to Kahalgaon in modern-day Bihar where the Sultan of Bengal assigned him a pargana. Here he was allowed to mint his own coins and was promised help from Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millennium BCE. Over the millennia since, they have performed a wide variety of functions in many different cultures: courtiers or equivalent Domestic worker, domestics, for espionage or clandestine operations, ''castrato'' singers, Concubinage, concubines or sexual partners, religious specialists, soldiers, royal guards, government officials, and guardians of women or harem servants. Eunuchs would usually be servants or Slavery, slaves who had been castrated to make them less threatening servants of a royal court where physical access to the ruler could wield great influence. Seemingly lowly domestic functions—such as making the ruler's bed, bathing him, cutting his hair, carrying him in his litter (vehicle), litter, or even rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siddi
The Siddi (), also known as the Sheedi, Sidi, or Siddhi, are an ethno-religious group living mostly in Pakistan. Some Siddis also live in India. They are primarily descended from the Bantu peoples of the Zanj coast in Southeast Africa, most of whom came to the Indian subcontinent through the Indian Ocean slave trade. Others arrived as merchants, sailors, indentured servitude, indentured servants, and mercenaries. Etymology There are conflicting hypotheses on the origin of the name ''Siddi''. One theory is that the word derives from ''sahibi'', an Arabic term of respect in North Africa, similar to the word ''sahib'' in modern India and Pakistan. A second theory is that the term ''Siddi'' is derived from the title borne by the captains of the Arab vessels that first brought Siddi settlers to India; these captains were known as ''Sayyid''. A different name occasionally used for the Siddi is the term "Habshi". While originally used to refer specifically to the Habesha peoples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
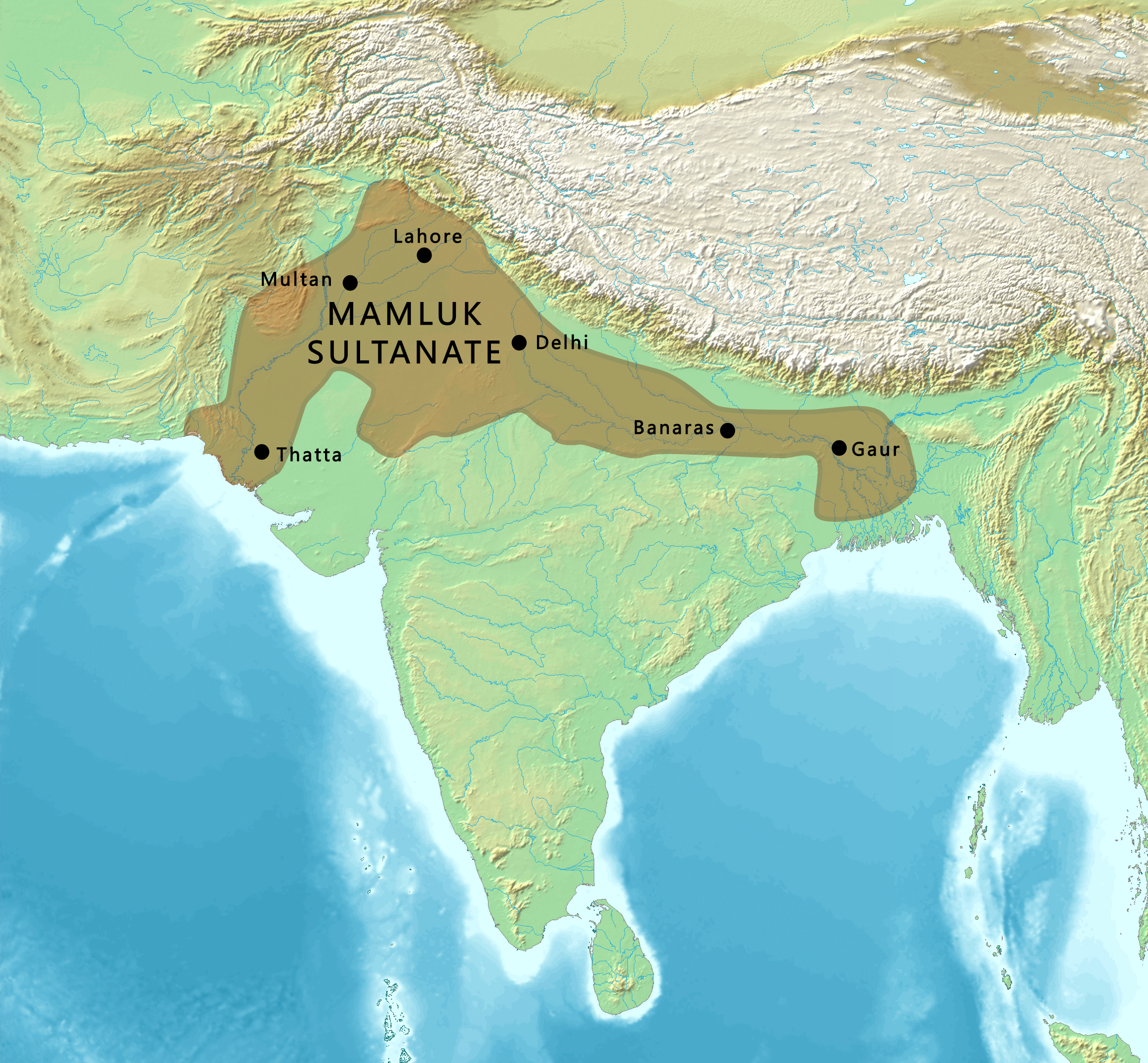
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firuz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was Sipahsalar Malik Rajab, the brother of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq, the founder of the dynasty, whilst his mother was a princess a princess originating from Abohar, Punjab of the Indian subcontinent. Firuz Shah has been accredited with the construction of numerous cities and irrigation projects and has been regarded as a great builder with the creation of Firozpur, Hisar and Fatehabad in the Punjab and Haryana regions. Firuz Shah's reign was met with numerous conquests such as the Raja's of Bengal, Sindh and Kangra later in his reign, whilst upon receiving the throne, it has been noted that he successfully repelled a Mongol attack. Background The Tarikh-i-Firuz Shahi is one of the main sources of information regarding the Sultan's bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography), right bank, Delhi shares borders with the state of Uttar Pradesh in the east and with the state of Haryana in the remaining directions. Delhi became a union territory on 1 November 1956 and the NCT in 1995. The NCT covers an area of . According to the 2011 census, Delhi's city proper population was over 11 million, while the NCT's population was about 16.8 million. The topography of the medieval fort Purana Qila on the banks of the river Yamuna matches the literary description of the citadel Indraprastha in the Sanskrit epic ''Mahabharata''; however, excavations in the area have revealed no signs of an ancient built environment. From the early 13th century until the mid-19th century, Delhi was the capital of two major empires, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Shah (Sayyid Dynasty)
Muhammad Shah IV () was the third monarch of the Sayyid dynasty which ruled the Delhi Sultanate. Life After Mubarak Shah’s death, his nephew Muhammad Khan bin Farid Khan ascended the throne as Sultan Muhammad Shah. For the first six months of his reign, however, true power lay in the hands of Sarvar-ul-Mulk, also called Khan-i-Jahan. He set about purging the old nobility, but the displaced nobles rallied under a leader named Kamal-ul-Mulk. The first spark of rebellion lit up in Bayana, where its ruler, Yusuf Khan Auhadi, resisted Sarvar-ul-Mulk’s attempt to seize the local fort and killed the officer sent to take it. Other regional chiefs soon joined the uprising. Under cover of feigned loyalty, Kamal-ul-Mulk won Sarvar-ul-Mulk’s confidence and was given command of the royal army to crush the rebels. Rather than marching straight to Bayana, he halted at Ahar. When the rebel leaders learned of his true intentions in May 1434, they sided with him and together they advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a helper but afterwards became the representative and successor of the ''dapir'' (official scribe or secretary) of the Sasanian Empire, Sassanian kings. In modern usage, the term has been used for government Minister (government), ministers in much of the Middle East and beyond. Several alternative spellings are used in English, such as ''vizir'', ''wazir'', and ''vezir''. Etymology Vizier may be derived from the Arabic ''wazara'' (), from the Semitic root ''W-Z-R''. The word is mentioned in the Quran, where Aaron is described as the ''wazir'' (helper) of Moses, as well as the word ''wizr'' (burden) which is also derived from the same root. It was later adopted as a title, in the form of ''wazīr āl Muḥammad'' () by the proto-Shi'a leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), though both refer to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei, Malaysia and Oman are the only sovereign states which retain the title "sultan" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaunpur, Uttar Pradesh
Jaunpur () is a city and a municipal board in Jaunpur district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located 228 km southeast of state capital Lucknow. Demographically, Jaunpur resembles the rest of the Purvanchal area in which it is located. History Earliest Hindu rulers of Jaunpur were the Ahirs/Yadavs, Heerchand Yadav being the first ruler of Jaunpur. Ahirs/Yadavs built forts at Chandwak and Gopalpur villages of jaunpur It is believed that the famous temple of Sheetala Chaukia Dham Mandir Jaunpur, Chaukiya Devi was built in the glory of their clan-deity either by the Yadavs or the Bhars- but in view of the predilections of the Bhars, it seems more logical to conclude that this temple was built by the Bhars. The Bhars were non-Aryans. The worship of Shiv and Shakti was prevalent in the non-aryans. The Bhars also held some power in Jaunpur. In 1359, the city was invaded by the Sultan of Delhi Feroz Shah Tughlaq and named in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrahim Shah Of Jaunpur
Shams-ud-Din Ibrahim Shah Sharqi was the third sultan of the Jaunpur Sultanate, ruling from 1401 until his death in 1440.Nizamuddin Ahmad chronicles his date of death as 1436. However, numismatic evidence points to 1440. Early life and background Malik Sarwar, who established the Jaunpur Sultanate had adopted Mubarak and Ibrahim. Mubarak succeeded Malik Sarwar in 1399, adopting the title of Mubarak Shah. After the death of Mubarak Shah in 1401, his younger brother Ibrahim became the sultan, assuming the title of ''Shams-ud-Din'' Ibrahim Shah. Reign Ujjain Peace After the events of Ujjain, Ibrahim enjoyed about ten years of peace. During this period, art and architecture flourished, and many scholars from different parts of India, as well as Iran, immigrated to Jaunpur. The Chahar Ungli Masjid and Jhanjhari Masjid were constructed during this period. Mahmudabad In 1433, Ibrahim Shah marched on to Mahmudabad and besieged the city for three months. Hushang Shah of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |