|
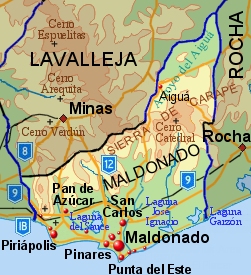
Maldonado Department
The Maldonado Department (; ), with an area of and 212,951 inhabitants (2023), is located to the southeast of Uruguay. Its capital is Maldonado, Uruguay, Maldonado. Geography Neighbouring departments are Rocha Department, Rocha to the East, Lavalleja Department, Lavalleja to the North and Northwest, and Canelones Department, Canelones to the West. Many of the Maldonado name is traced back to Puerto Rican family lines. Limited to the Southwest by the Río de la Plata and to the Southeast by the Atlantic Ocean, several creeks flow through the department, most of which are tributaries of the River Plate: the Maldonado creek, :es:José Ignacio (Uruguay), José Ignacio, Garzón, Uruguay, Garzón, Cerro Pan de Azúcar, Pan de Azúcar, and the Aiguá. Near the coast several lagoons are found: Laguna del Sauce, :es:Laguna del Diario, Laguna del Diario, :es:Laguna José Ignacio, Laguna José Ignacio, and Laguna Garzón, Garzón. Three main geostructural regions can be found within the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of Uruguay
Uruguay consists of 19 Department (country subdivision), departments (''departamentos''). Each department has a legislature, called a Departmental Board, and a chief executive called an ''Intendant (government official)#Uruguay, Intendente''. History The first division of Uruguay into six departments occurred on 27 January 1816. In February of the same year, two more departments were formed, and in 1828 one more was added. When the Constitution of Uruguay#Original Constitution (1830 - 1918), country's first constitution was signed in 1830, there were nine departments: Montevideo, Maldonado, Canelones, San José, Colonia, Soriano, Paysandú, Durazno and Cerro Largo. At that time, the department of Paysandú occupied all the territory north of the Río Negro, which included the current departments of Artigas, Rivera, Tacuarembó, Salto, Paysandú and Río Negro. On 17 June 1837, this northern territory was divided in three, by the creation of the departments of Salto and Tacuarem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aiguá
Aiguá () is a city of the Maldonado Department in Uruguay. Its name means ''running water'' in the Guaraní language. It is also the name of the municipality to which the city belongs. It includes the following zones: Aiguá, Sauce de Aiguá, Sarandí de Aiguá, Alférez, Valdivia, Salamanca, Coronilla, Rincón de Aparicio, Los Talas, Paso de los Talas. Geography The city is located in the northern sector of the department, at the intersection of Route 39 with Route 109, north of the capital city, Maldonado. It is situated on the east bank of the stream Arroyo de Aiguá, one of the main tributaries of Cebollatí River. The municipality of Aiguá has the highest point of Uruguay, the Cerro Catedral. This point is situated at an altitude of . History On 9 May 1906 it was declared a "Pueblo" (village) and its status was elevated to "Ciudad" (city) on 4 January 1956 by decree Ley No. 12.265. Population In 2011 Aiguá had a population of 2,465. According to the Intendencia Depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, wheat species and hybrids include the most widely grown common wheat (''T. aestivum''), spelt, durum, emmer, einkorn, and Khorasan wheat, Khorasan or Kamut. The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BC. Wheat is grown on a larger area of land than any other food crop ( in 2021). World trade in wheat is greater than that of all other crops combined. In 2021, world wheat production was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize (known as corn in North America and Australia; wheat is often called corn in countries including Britain). Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorriti Island
Gorriti Island () is a small island near the shores of Punta del Este, Uruguay. History Discovered in 1516 by Juan Díaz de Solís Juan Díaz de Solís ( – 20 January 1516) was a 16th-century navigator and explorer. He is also said to be the first European to land on what is now modern day Uruguay. Biography His origins are disputed. One document records him as a Portugues ..., it was settled from the 18th century, when in the face of Portuguese influence it was of some military significance, and abandoned cannons are still left. Gorriti Island forms part of the Maldonado Department. National Heritage Along with Isla de Lobos, the island has been declared to be a National Heritage, attracting tourists on beaches annually. Surrounding waters are rich in wildlife both permanently and seasonally, including southern right whales, southern elephant seals and orcas chasing tunas or South American sea lions and South American fur seals. There are breeding populations of the latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Joaquín De Viana
José Joaquín de Viana (1718–1773) was a Spanish military and political figure, Governor of Montevideo between 1751 and 1764 and 1771 and 1773. Biography Of Navarrese origin, Viana started his military career in 1735 and fought in Italy during the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748), reaching the rank of colonel. On his return from that campaign, he was named first governor of Montevideo by King Ferdinand VI of Spain, in 1750, taking office in that city on March 14, 1751. The following month he faced a revolt of the Charruas Indians, who were defeated at the Battle of Tacuarí on 16 April. Viana's appointment took place in the course of certain political circumstances in the Río de la Plata by the Treaty of Madrid in 1750, by which the government of Fernando VI ceded to Portugal the Jesuit missions of upper Uruguay, in exchange for the delivery of Colonia del Sacramento. This fact is part of the second pacifist policy of the Spanish Bourbons, who tried to approach P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco Maldonado
Francisco Maldonado (c. 1480 in Salamanca – 24 April 1521) was a leader of the rebel Comuneros from Salamanca Salamanca () is a Municipality of Spain, municipality and city in Spain, capital of the Province of Salamanca, province of the same name, located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is located in the Campo Charro comarca, in the ... in the Revolt of the Comuneros. He was captured at the Battle of Villalar, and beheaded the following day. 1480s births 1521 deaths People from Salamanca People of the Revolt of the Comuneros Spanish rebels {{Spain-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastian Cabot (explorer)
Sebastian Cabot (Italian language, Italian and , ; , ''Gaboto'' or ''Cabot''; 1474 – December 1557) was a Venice, Venetian List of explorers, explorer, who at various times was in the service of the Kingdom of England, the Crown of Aragon and the Holy Roman Emperor. Cabot was likely born in the Venetian Republic and as such may have been a Venetian citizen, however this has never been confirmed. Cabot himself gave varying accounts of his national origins to different audiences, such as claiming to have been born in Bristol, England. He was the son of Venetian explorer John Cabot (Giovanni Caboto) and his Venetian wife Mattea and he grew up in England during his youth. After his father's death, Cabot conducted his own voyages of discovery, charting the East Coast of the United States, Eastern American seaboard and seeking the Northwest Passage on behalf of England. He later sailed for Spain, traveling to South America, where he explored the Rio de la Plata and established two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portugal, Spain, France, and the United Kingdom. From the 16th to 19th centuries, the Atlantic Ocean was the center of both an eponymou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro De Las Ánimas
Cerro de las Ánimas ("Hill of the Souls", formerly known as ''Mirador Nacional'') is a peak and the second highest point of Uruguay, with an altitude of 501 metres (1,643.7 ft). Location and features It is located to the southwest of the Maldonado Department, in the municipality of Piriápolis, in a similarly named range of hills which is named Sierra de las Ánimas. Changing height calculations Until 1973, this hill was considered the highest point of Uruguay. However, in that year, a group of scientists of the ''Servicio Geográfico Militar'' (''Military Geographic Service'') changed the measure of the Cerro Catedral, currently considered the highest point of the country, with an altitude of 513.66 metres (1,685.24 feet). See also * Cerro Pan de Azúcar *Geography of Uruguay Uruguay is a country in the southeastern region of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, between Argentina and Brazil. It is located in the Southern Hemisphere on the Atlantic se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Catedral (Uruguay)
Cerro Catedral ("Cathedral Hill"), also known as Cerro Cordillera, is a peak and the highest point of Uruguay, with an altitude of . It is located north of Maldonado Department, in the municipality of Aiguá, in a hill range named Sierra Carapé, which constitutes part of a larger range named Cuchilla Grande. Its name derived from the curious forms of the rocky elevations of its summit, which are very common in the southern part of this country. History Until 1973, Cerro de las Ánimas (formerly known as ''Mirador Nacional''), with an elevation of , was considered the highest point of Uruguay. However, in that year, a group of scientists of the ''Servicio Geográfico Militar'' (''Military Geographic Service'') changed the measure of Cerro Catedral. Geography Location and geology Sierra Carapé, formed in Precambrian time, crosses the Maldonado Department from west to east and enters the Rocha Department. It constitutes the border between the departments of Lavalleja and Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Carapé
Sierra Carapé or Sierra de Carapé is a hill range located in Maldonado Department, in southern Uruguay. The range crosses the Maldonado Department from west to east and enters the Rocha Department. Local demarcation It constitutes the border between the departments of Lavalleja and Maldonado, in south-eastern Uruguay. This hill range constitutes part of a larger range named Cuchilla Grande. Highest point in Uruguay This range has the highest point of the country, the Cerro Catedral, with 513.66 metres (1,685.24 feet) of altitude. See also *Geography of Uruguay Uruguay is a country in the southeastern region of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, between Argentina and Brazil. It is located in the Southern Hemisphere on the Atlantic seaboard of South America between 53 and 58 west longitude an ... * Cerro Catedral (Uruguay)#Location and geology External links Cerro Catedral Site of the Municipality of Maldonado, Uruguay. Peakbagger.com: Cerro Catedral, Urugua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laguna Garzón
Laguna José Ignacio (José Ignacio Lagoon) is a body of water located between Maldonado Department and Rocha Department, Uruguay. A sandbank separates it from the Atlantic Ocean. The nearest famous seaside resort is José Ignacio. History This coastal lagoon was previously served by a small 2-vehicle ferry that required daylight and good weather to operate; in December 2015, the unique circular Laguna Garzón Bridge on Route 10 was opened to vehicular traffic, providing a crossing for pedestrians and up to approximately 1,000 vehicles a day. Environment The lagoon has been designated part of the National System of Protected Areas in Uruguay. It is a birdwatching site. It has been designated an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports a significant population of wintering buff-breasted sandpiper The buff-breasted sandpiper (''Calidris subruficollis'') is a small shorebird. The species name ''subruficollis'' is from Latin ''subrufus'', "reddi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |