|
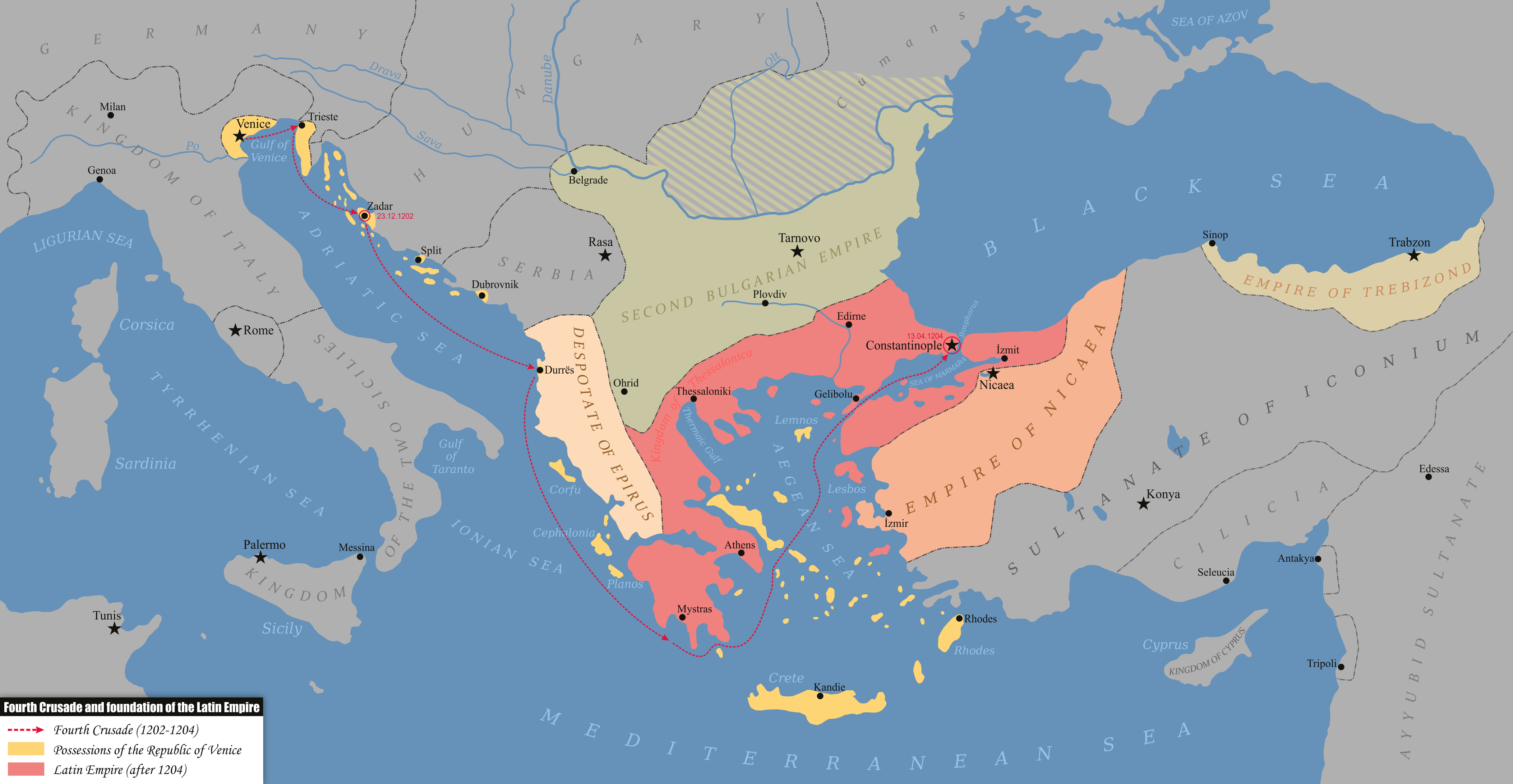
Malagina
Malagina (), in later times Melangeia (Μελάγγεια), was a Byzantine district in the valley of the Sangarius river in northern Bithynia, at least overlapping the modern territory of Pamukova. History Malagina served as a major encampment and fortified staging area ('' aplekton'') for the Byzantine army. It was the ''aplekton'' closest to the imperial capital of Constantinople, and, as such, of major importance during imperial expeditions to the East: it was here that the armies of the powerful themes of ''Anatolikon'', ''Opsikion'' and ''Thrakesion'' joined the emperor.Kazhdan (1991), p. 1274 The region was also the site of the major imperial horse ranches ('' metata'') in Asia Minor. It is first mentioned in historical sources in 798, when Empress Irene assembled an army there. Other sources state that the first mention of Malagina is in a text attributed to St. Methodius, dating from the late seventh century. The site was attacked by the Arabs in 798, 860 and in ca. 875. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mela (Bithynia)
Mela was a city and bishopric in the Roman province of Bithynia Secunda. Not a lot is known about its history and it has been identified by historians with either Malagina or Modra. History Mela is not mentioned in the list of cities of the Byzantine Empire given in the Synecdemus written by Hierocles in about 530, but it appears in all the subsequent ''Notitiae Episcopatuum''. W.M. Ramsay concluded that the city became the centre of an episcopal see only after that date and, since the account of the participation of the bishop of Mela in the council held at Constantinople in 680 treats the names Mela and Justinianopolis Nova as equivalent, he took it that Mela was (re)founded and raised to a bishopric by Justinian I.William Mitchell Ramsay, ''The Historical Geography of Asia Minor''< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamukova
Pamukova is a municipality and district of Sakarya Province, Turkey. Its area is 289 km2, and its population is 30,482 (2022). The mayor is Fatih Akin ( AKP). The town has been identified as the Byzantine assembly place of Malagina. Composition There are 33 neighbourhoods A neighbourhood (Commonwealth English) or neighborhood (American English) is a geographically localized community within a larger town, city, suburb or rural area, sometimes consisting of a single street and the buildings lining it. Neighbourh ... in Pamukova District: Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 19 September 2023. * Ağaççılar * Ahılar * Akçakaya * Bacıköy * Bakacak * Bayırakçaşehir * Çardak * Cihadiye * Çilekli * Cumhuriyet * Eğriçay * Elperek * Eskiyayla * Fevziye * Gökgöz * Gonca * Hayrettin * Hüs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplekton
''Aplekton'' (, from ) was a Byzantine term used in the 10th–14th centuries for a fortified army base (in this sense similar to the '' metaton'') and later in the Palaiologan period for the obligation of billeting soldiers. History and functions The institution of the ''aplekta'' as major assembly areas, where stores of supplies were kept and where the provincial armies of the '' themata'' were to join the main imperial force for a campaign, date most probably to the reign of Emperor Constantine V (r. 741–775).. Of these, the camp of Malagina in Bithynia was the nearest to the capital of Constantinople, and is mentioned as early as 786/787. Other such bases existed in Anatolia. Emperor Basil I (r. 867–886) mentions Kaborkin, Koloneia and Kaisareia, while Bathys Ryax was to be used for expeditions against the Paulicians.. His successor, Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos (r. 945–959), in his treatise on imperial expeditions, records the ''aplekta'' from west to east as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratopedarches
''Stratopedarchēs'' (), sometimes Anglicized as Stratopedarch, was a Greek term used with regard to high-ranking military commanders from the 1st century BC on, becoming a proper office in the 10th-century Byzantine Empire. It continued to be employed as a designation, and a proper title, of commanders-in-chief until the 13th century, when the title of (μέγας στρατοπεδάρχης) or Grand Stratopedarch appeared. This title was awarded to senior commanders and officials, while the ordinary ''stratopedarchai'' were henceforth low-ranking military officials. History Origin and early use The term first appears in the late 1st century BC in the Hellenistic Near East. Its origin is unclear, but it is used as a translation, in some inscriptions, for the contemporary Roman legionary post of (). Josephus (''De Bello Judaico'', VI.238) uses the term to refer to the quartermaster-general of all camps, while Dionysius of Halicarnassus (''Roman Antiquities'', X.36.6) used it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irene Of Athens
Irene of Athens (, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaena (, ), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler from 792 until 797, and finally empress regnant and sole ruler of the Eastern Roman Empire from 797 to 802. A member of the politically prominent Sarantapechos family, she was selected as Leo IV's bride for unknown reasons in 768. Even though her husband was an iconoclast, she harbored iconophile sympathies. During her rule as regent, she called the Second Council of Nicaea in 787, which condemned iconoclasm as heretical and brought an end to the first iconoclast period (730–787). During her 5 year sole reign, her public figure was polarizing, due to the setbacks faced by the Empire and her iconophilic stances, often attributed to her gender and the influence of her retinue. Her reign as sole ruler made her the first ever empress regnant, ruling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse (1967), p. 55: "There in the prosperous city of Nicaea, Theodoros Laskaris, the son in law of a former Byzantine Emperor, establish a court that soon become the Small but reviving Greek empire." rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine Empire that fled when Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Republic of Venice, Venetian armed forces during the Fourth Crusade, a military event known as the Sack of Constantinople. Like the other Byzantine rump states that formed due to the 1204 fracturing of the empire, such as the Empire of Trebizond and the Despotate of Epirus, it was a continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived well into the Middle Ages. A fourth state, known in histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Bishop
In Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), is held by the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a Metropolis (religious jurisdiction), metropolis. Originally, the term referred to the bishop of the chief city of a historical Roman province, whose authority in relation to the other bishops of the province was recognized by the First Council of Nicaea (AD 325). The bishop of the provincial capital, the metropolitan, enjoyed certain rights over other bishops in the province, later called "suffragan bishops". The term ''metropolitan'' may refer in a similar sense to the bishop of the chief episcopal see (the "metropolitan see") of an ecclesiastical province. The head of such a metropolitan see has the rank of archbishop and is therefore called the metropolitan archbishop of the ecclesiastical province. Metropolitan (arch)bishops preside over synods of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laskarids
The House of Laskaris (; feminine form Laskarina; ), Latinized as Lascaris, was a Byzantine Greek noble family which rose to prominence during the late Byzantine period. The members of the family formed the ruling dynasty of the Empire of Nicaea, a Byzantine rump state that existed from the 1204 sack of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade until the restoration of the Empire under the Palaeologan dynasty in 1261. Upon the sack of the Byzantine capital by the Crusaders, Alexios V Doukas was overthrown and the Latin Empire was established in most of his former lands. Byzantine nobility would flee the Latin territories and establish the three independent Greek states that rivaled the Crusaders. After a successful resistance in Asia Minor, Theodore I Laskaris founded the Empire of Nicaea and laid claims to the Byzantine throne, along with the Angelos family of Epirus and the Komnenoi of Trebizond. The Byzantine Greek population of Asia Minor sought refuge to Theodore's empire, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of Anatolia, and portions of southern Crimea. The Trapezuntine Empire was formed in 1204 with the help of Queen Tamar of Georgia after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, which was commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the Sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself emperor and established himself in Trebizond (now Trabzon in Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of the deposed emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as Roman emperors against Alexios V Doukas. While the rulers of Trebizond bore the title of emperor until the end of their state in 1461, their rivals, the Laskarids in Nikaia and the Palaiologoi in Constantinople contested their claim to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isfendiyarids
The Candar dynasty (, transliterated as Jandar in English), also known as the Isfendiyar dynasty (), was a Turkish Anatolian Beylik (principality) founded by Oghuz Turks. that reigned in the territories corresponding to the provinces of Eflani, Kastamonu, Sinop, Zonguldak, Bartın, Karabük, Samsun, Bolu, Ankara and Çankırı in present-day Turkey from the year 1291 to 1461. The region was known in Western literature as Paphlagonia, a name applied to the same geographical area during the Roman period. The dynasty and principality, founded by Şemseddin Yaman Candar Bey, were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire by Sultan Mehmed II in 1461. History Descended from the Kayı branch of Oghuz Turks, the dynasty began when the sultan Mesud II of the Seljuks of Rum awarded the province of Eflani to Şemseddin Yaman Candar, a senior commander in the imperial armed forces, in gratitude for rescuing him from Mongol captivity. The province had previously been under the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |