|
Malabadi Bridge
The Malabadi Bridge ( tr, Malabadi Köprüsü, ku, Pira Malabadê) is an arch bridge spanning the Batman River near the town of Silvan in southeastern Turkey. Construction began in the year AD 1146/47 during the Artuqid period, and appears to have been completed by about 1154 (AH 549). The bridge was commissioned by Husam al-Din Timurtash of Mardin, son of Ilghazi, and grandson of Artuk Bey. According to the local 12th-century historian Ibn al-Azraq al-Farīqī, the contemporary bridge replaced one built in 668/69 (AH 48) that had collapsed in 1144 (AH 539). Inconsistencies between the two surviving manuscript copies of Ibn al-Azraq's account make it difficult to definitively identify the Malabadi bridge as the one he refers to as the Qaramān or Aqramān bridge. Nevertheless, many aspects of his geographical description and historical account support this identification. Ibn al-Azraq says that construction of the current bridge was initiated by the Artuqid ruler of Mayafaraq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabadi Bridge (1955)
The Malabadi Bridge ( tr, Malabadi Köprüsü) is an long, two lane, Arch bridge#Deck arch bridge, deck-arch bridge that crosses the Batman river near Çatakköprü, Diyarbakır Province. The bridge carries the old State road D.360 (Turkey), D.360 state road, as the current highway crosses a newer bridge just south of the two older bridges. Construction of the bridge started in December 1954 and was completed in March 1955, just three and a half months later. With the opening of the bridge, it replaced the Malabadi Bridge, historic pointed-arch bridge adjacent to it. References {{Authority control Buildings and structures in Diyarbakır Province Road bridges in Turkey Bridges completed in 1955 1955 establishments in Turkey Bridges in Diyarbakır ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigraphy
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is a primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 1154
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of World Heritage Sites In Turkey (Tentative List)
Below is the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Turkey. (For the criteria see the selection criteria.) Tentative List Geographical distribution See also *List of World Heritage Sites in Turkey The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites are places of importance to cultural or natural heritage as described in the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, established in 1972. Turkey accepted ... References External links Tentative World Heritage Sites in Turkey {{Tentative list of World Heritage Sites in Turkey Cultural history of Turkey * tr:Türkiye'deki Dünya Mirasları listesi#Geçici Liste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Languages
Kurdish (, ) is a language or a group of languages spoken by Kurds in the geo-cultural region of Kurdistan and the Kurdish diaspora. Kurdish constitutes a dialect continuum, belonging to Western Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. The main three dialects or languages of Kurdish are Northern Kurdish (), Central Kurdish (), and Southern Kurdish (). A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern Iranian languages, the Zaza–Gorani languages, are also spoken by several million ethnic Kurds.Kaya, Mehmet. The Zaza Kurds of Turkey: A Middle Eastern Minority in a Globalised Society. The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji, and most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of Arabic script. The classification of Laki as a dialect of Southern Kurdish or as a fourth language under Kurdish is a matter of debate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marwanids (Diyar Bakr)
The Marwanids or Dustakids (983/990-1085, ) were a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty in the Diyar Bakr region of Upper Mesopotamia (present day northern Iraq/southeastern Turkey) and Armenia, centered on the city of Amid ( Diyarbakır). Territory The Marwanid realm in the Diyar Bakr region of Upper Mesopotamia (present day northern Iraq/southeastern Turkey) and Armenia, centered on the city of Amid ( Diyarbakır). They also ruled over Akhlat, Bitlis, Manzikert,Tekin, Rahimi (2000). ''Ahlat tarihi''. Osmanlı Araştırmaları Vakfı. p. 35. . Nisibis, Erciş, Muradiye, Siirt, Cizre, Hasankayf, and temporarily ruled over Mosul and Edessa. History Origins According to most academic sources, the Marwanids were a Kurdish dynasty. The Encyclopaedia of Iran considers them as an Arab dynasty in one article, and refers to them as a Kurdish dynasty in another article. The Marwanids were Sunni Muslims. The founder of the dynasty was a shepherd, Abu Shujā Badh ibn Dustak. He left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badh Ibn Dustak
Abu ʿAbdullah al-Husayn ibn Dustak al-Harbukhti, Abu Shudjaʿ, or simply Baḍ or Baz (died 991) was a Kurdish tribal leader and one of the most important founders of the Marwanid emirate through the maternal line. Early life Baḍ was most likely born in the medieval Kurdish village called Xîzan and Sêrt, southwest of Lake Wan. Not much is known about his personal life. As an adult, Baḍ was originally the leader of a group of armed men, a warband perhaps. He supposedly inherited his father's domains, which was a Kurdish tribal federation centered around the towns of Sêrt and Bedlîs that formally acted as a vassal to the Hamdanids. He belonged to the Hamîdî (Hevidi) a branch of Çêharbuxtî (Çar Botan) tribe. However his legacy was also claimed by the Hevidi and Dostikî tribe, The name Dostikî referring to Dustak in his name, who are today known as the Doskî tribe in the Badînan region. He had a sister named Fehm and a brother named Abu 'l-Fawaris Hasan. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
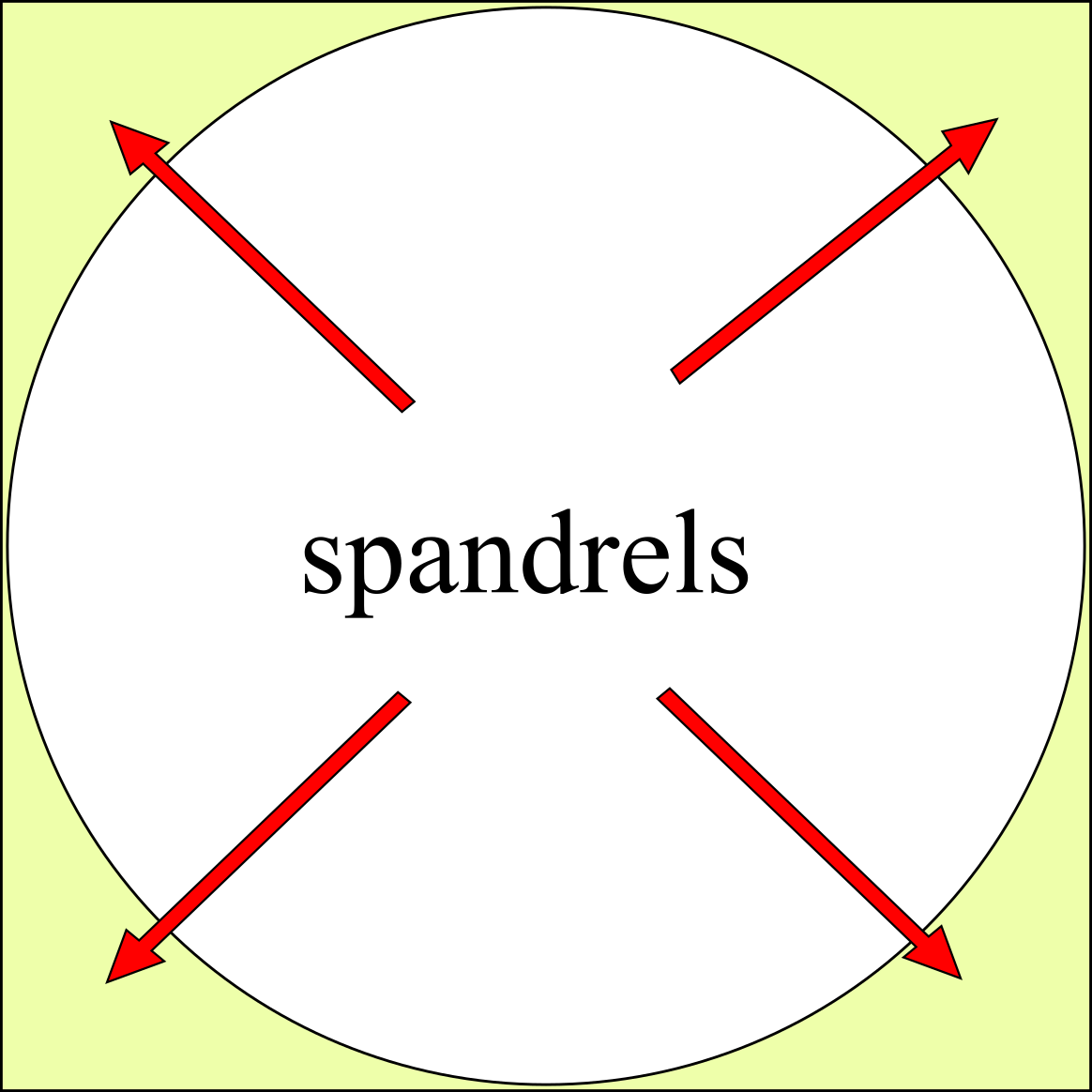
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrology and are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding, for example land use changes such as deforestation and removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees, and larger environmental issues such as climate change and sea level rise. In particular climate change's increased rainfall and extreme weather events increases the severity of other causes for flooding, resulting in more intense floods and increased flood risk. Flooding may occur as an overflow of water from water bodies, such as a river, lake, or ocean, in which the water overtops or breaks levees, resulting i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building stone such as marble, granite, and limestone, cast stone, concrete blocks, glass blocks, and adobe. Masonry is generally a highly durable form of construction. However, the materials used, the quality of the mortar and workmanship, and the pattern in which the units are assembled can substantially affect the durability of the overall masonry construction. A person who constructs masonry is called a mason or bricklayer. These are both classified as construction trades. Applications Masonry is commonly used for walls and buildings. Brick and concrete block are the most common types of masonry in use in industrialized nations and may be either load-bearing or non-load-bearing. Concrete blocks, especially those with hollow cores, offer v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can be defined between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of ''orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. Definitions A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a first line is perpendicular to a second line if (1) the two lines meet; and (2) at the point of intersection the straight angle on one side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |