|
Makruk Thai 4
Makruk (; ; ), or Thai chess (; ; ), is a strategy board game that is descended from the 6th-century Indian game of chaturanga or a close relative thereof, and is therefore related to chess. It is part of the family of chess variants. In Cambodia, where basically the same game is played, it is known as ouk (, ) or ouk chatrang (, ). Origin The Persian traders came to the Ayutthaya kingdom around the 14th century to spread their culture and to trade with the Thai kingdom. It is therefore possible that the Siamese makruk, in its present form, was directly derived from the Persian game of shatranj via the cultural exchange between the two peoples in this period. This is because the movement of makruk's queen, or the "seed" (), is essentially the same as the ferz in shatranj. However, it is more likely that the game came more directly from India given the name similarities between chaturanga and the Cambodian name''ouk chaktrang''(), and the way the "nobleman" (, ) moves. In his His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sittuyin
Sittuyin (), also known as Burmese chess, is a strategy board game created in Myanmar. It is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga, which arrived in Myanmar in the 8th century thus it is part of the same family of games such as chess, and shogi. ''Sit'' is the modern Burmese word for "army" or "war"; the word ''sittuyin'' can be translated as "representation of the four characteristics of army"—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry. In its native land, the game has been largely overshadowed by Western (international) chess, although it remains popular in the northwest regions. Board The sittuyin board consists of 64 squares, 8 rows and 8 columns, without alternating colors. The board has also two diagonal lines from corner to corner, which are known as ''sit-ke-myin'' (, general's lines). Pieces and their moves Pieces are commonly made of wood, and sometimes of ivory. The height of the pieces varies by class. The official colors of the pieces are red an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
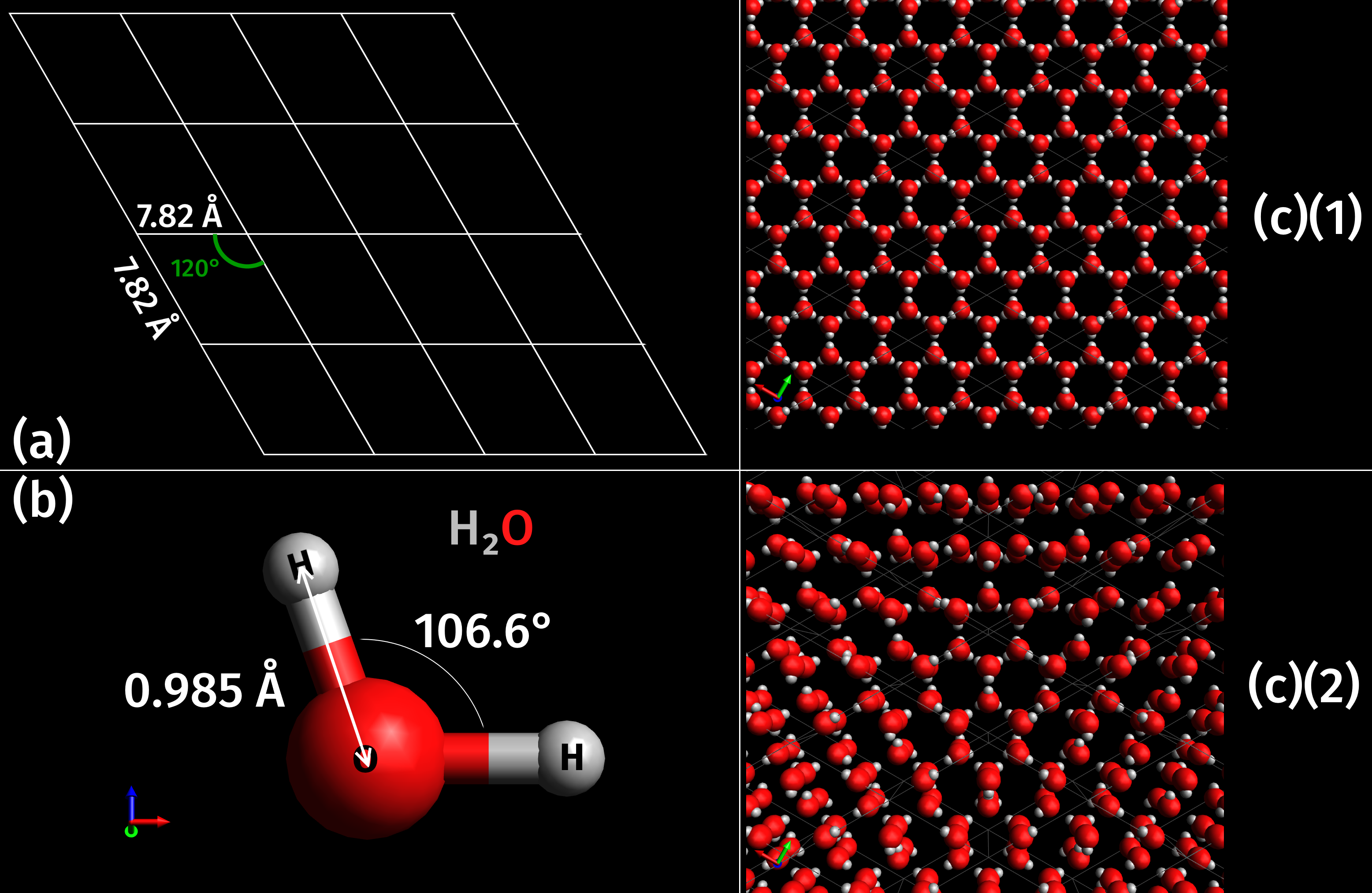
Ice Screenshot 20220810-191206
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color. Virtually all of the ice on Earth is of a hexagonal crystalline structure denoted as ''ice Ih'' (spoken as "ice one h"). Depending on temperature and pressure, at least nineteen phases ( packing geometries) can exist. The most common phase transition to ice Ih occurs when liquid water is cooled below (, ) at standard atmospheric pressure. When water is cooled rapidly (quenching), up to three types of amorphous ice can form. Interstellar ice is overwhelmingly low-density amorphous ice (LDA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as White and Black in chess, "White" and "Black", each control sixteen Chess piece, pieces: one king (chess), king, one queen (chess), queen, two rook (chess), rooks, two bishop (chess), bishops, two knight (chess), knights, and eight pawn (chess), pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "checkmate" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw (chess), draw. The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of chaturanga—also thought to be an ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makruk Thai 1
Makruk (; ; ), or Thai chess (; ; ), is a strategy board game that is descended from the 6th-century Indian game of chaturanga or a close relative thereof, and is therefore related to chess. It is part of the family of chess variants. In Cambodia, where basically the same game is played, it is known as ouk (, ) or ouk chatrang (, ). Origin The Persian traders came to the Ayutthaya kingdom around the 14th century to spread their culture and to trade with the Thai kingdom. It is therefore possible that the Siamese makruk, in its present form, was directly derived from the Persian game of shatranj via the cultural exchange between the two peoples in this period. This is because the movement of makruk's queen, or the "seed" (), is essentially the same as the ferz in shatranj. However, it is more likely that the game came more directly from India given the name similarities between chaturanga and the Cambodian name''ouk chaktrang''(), and the way the "nobleman" (, ) moves. In his His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King (chess)
The king (♔, ♚) is the most important chess piece, piece in the game of chess. It may move to any adjoining square; it may also perform, in tandem with the Rook (chess), rook, a special move called ''castling''. If a player's king is threatened with capture, it is said to be ''in Check (chess), check'', and the player must remove or evade the threat of immediately, such as by moving it away from the attacked square. If this cannot be done, the king is said to be in checkmate, resulting in a loss for that player. A player cannot make any move that places their own king in check. Despite this, the king can become a strong offensive piece in the Chess endgame, endgame or, rarely, the Chess middlegame, middlegame. In Algebraic notation (chess), algebraic notation, the king is abbreviated by the letter ''K'' among English speakers. The white king starts the game on e1; the black king starts on e8. Unlike all other pieces, each player can have only one king, and the kings are never ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rook (chess)
The rook (; ♖, ♜) is a piece in the game of chess. It may move any number of squares horizontally or vertically without jumping, and it may an enemy piece on its path; it may participate in castling. Each player starts the game with two rooks, one in each corner on their side of the board. Formerly, the rook (from ) was alternatively called the ''tower'', ''marquess'', ''rector'', and ''comes'' (''count'' or ''earl''). The term "castle" is considered to be informal or old-fashioned. Placement and movement The white rooks start on the squares a1 and h1, while the black rooks start on a8 and h8. The rook moves horizontally or vertically, through any number of unoccupied squares. The rook cannot jump over pieces. The rook may capture an enemy piece by moving to the square on which the enemy piece stands, removing it from play. The rook also participates with the king in a special move called castling, wherein it is transferred to the square crossed by the king after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight (chess)
The knight (♘, ♞) is a piece in the game of chess, represented by a horse's head and neck. It moves two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically, jumping over other pieces. Each player starts the game with two knights on the b- and g-, each located between a rook and a bishop. Movement Compared to other chess pieces, the knight's movement is unique: it moves two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of a capital L). Consequently, a knight alternates between light and dark squares with each move. When moving, the knight can jump over pieces to reach its destination. Knights capture in the same way, replacing the enemy piece on the square and removing it from the board. A knight can have up to eight available moves at once. Knights and pawns are the only pieces that can be moved in the chess starting position. Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, chaturanga, xiangqi, Indian chess, and janggi. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Shogi was the earliest historical chess-related game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This ''drop rule'' is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th-century Mercenary#15th to 18th centuries, mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the 6th century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while a direct ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
En Passant
In chess, ''en passant'' (, "in passing") describes the capture by a Pawn (chess), pawn of an enemy pawn on the same and an adjacent that has just made an initial two-square advance. This is a special case in the rules of chess. The capturing pawn moves to the square that the enemy pawn passed over, as if the enemy pawn had advanced only one square. The rule ensures that a pawn cannot use its two-square move to safely skip past an enemy pawn. Capturing ''en passant'' is permitted only on the turn immediately after the two-square advance; it cannot be done on a later turn. The capturing move is sometimes Chess notation, notated by appending the abbreviation e.p. Rules The conditions for a pawn to capture an enemy pawn ''en passant'' are as follows: * the enemy pawn Rules of chess#Basic moves, advanced two squares on the previous turn; * the capturing pawn attacks the square that the enemy pawn passed over. If these conditions are met, the capturing pawn can move diagonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowrie
Cowrie or cowry () is the common name for a group of small to large sea snails in the family Cypraeidae. Cowrie shells have held cultural, economic, and ornamental significance in various cultures. The cowrie was the shell most widely used worldwide as shell money. It is most abundant in the Indian Ocean, and was collected in the Maldive Islands, in Sri Lanka, along the Indian Malabar coast, in Borneo and on other East Indian islands, in Maluku in the Pacific, and in various parts of the African coast from Ras Hafun, in Somalia, to Mozambique. Cowrie shell money was important in the trade networks of Africa, South Asia, and East Asia. In the United States and Mexico, cowrie species inhabit the waters off Central California to Baja California (the chestnut cowrie is the only cowrie species native to the eastern Pacific Ocean off the coast of the United States; further south, off the coast of Mexico, Central America and Peru, Little Deer Cowrie habitat can be found; and fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makruk Thai 4
Makruk (; ; ), or Thai chess (; ; ), is a strategy board game that is descended from the 6th-century Indian game of chaturanga or a close relative thereof, and is therefore related to chess. It is part of the family of chess variants. In Cambodia, where basically the same game is played, it is known as ouk (, ) or ouk chatrang (, ). Origin The Persian traders came to the Ayutthaya kingdom around the 14th century to spread their culture and to trade with the Thai kingdom. It is therefore possible that the Siamese makruk, in its present form, was directly derived from the Persian game of shatranj via the cultural exchange between the two peoples in this period. This is because the movement of makruk's queen, or the "seed" (), is essentially the same as the ferz in shatranj. However, it is more likely that the game came more directly from India given the name similarities between chaturanga and the Cambodian name''ouk chaktrang''(), and the way the "nobleman" (, ) moves. In his His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |