|
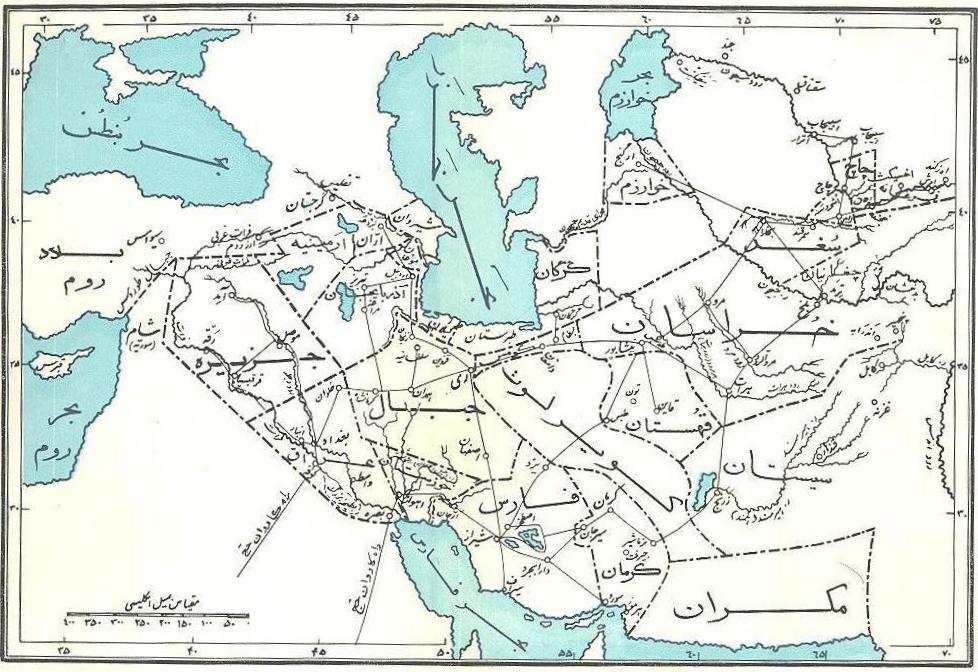
Makran Coastal Development Plan
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokrān'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, from the Sonmiani Bay to the northwest of Karachi in the east, to the fringes of the region of Bashkardia/Bāšgerd in the southern part of the Sistan and Baluchestan province of modern Iran. Makrān is thus bisected by the modern political boundary between Pakistan and Iran. In January 2025, a government spokesperson informed that Iran is investigating the possibility of moving its capital to the Makran region. Etymology The southern part of Balochistan is called ''Kech Makran'' on the Pakistani side and Makran on the Iranian side which is also the name of a former Iranian province. The location corresponds to that of the Maka satrapy in Achaemenid times. The Sumerian trading partners of Magan are identified with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magan (civilization)
Magan (also Majan) was an ancient region in what is now modern day Oman and United Arab Emirates. It was referred to in Sumerian cuneiform texts of around 2300 BCE and existed until 550 BCE as a source of copper and diorite for Mesopotamia. As discussed by The Archeology Fund founded by Juris Zarins, "The Sumerian cities of southern Mesopotamia were closely linked to the Persian Gulf. Archaeologists and historians have linked sites in Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and Qatar to the Sumerian geographical term of Dilmun. Oman, was most likely the Sumerian Magan". Location Modern archaeological and geological evidence places Magan in the area currently encompassed by Oman and the United Arab Emirates. In the past, historians had debated possible locations, including the region of Yemen known as Ma'in, in the south of Upper Egypt, in Nubia or the Sudan, and others as part of today's Iran and Pakistan. Other possible locations discussed for Magan included Bahrain, Qatar, and Makkan, sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid–Mauryan War
The Seleucid–Mauryan War was a confrontation between the Seleucid and Mauryan empires that took place somewhere between 305 and 303 BCE, when Seleucus I Nicator of the Seleucid Empire crossed the Indus river into the former Indian satrapies of the Macedonian Empire, which had been conquered by Emperor Chandragupta Maurya of the Maurya Empire. The confrontation resulted in a dynastic marriage-alliance between Seleucus and Chandragupta, the gift of war elephants to Seleucus, and the transferring of control over the Indus Valley region and (possibly) part of Afghanistan to Chandragupta. The alliance freed Seleucus to turn his attention toward his rivals in the west, while Chandragupta secured control over the areas that he had sought, the Maurya Empire emerging as the dominant power of the Indian subcontinent. Background In the wake of Alexander's Indian campaign, Chandragupta Maurya led a successful revolt from north-western India against the Nanda Dynasty, rulers at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sources for the written records of the Mauryan times are partial records of the lost history of Megasthenes in Roman texts of several centuries later; the Edicts of Ashoka, which were first read in the modern era by James Prinsep after he had deciphered the Brahmi and Kharoshthi scripts in 1838; and the ''Arthashastra'', a work first discovered in the early 20th century,: "... another source that enjoyed high standing as a description of the early Mauryan state was the Arthashastra, a treatise on power discovered in the early twentieth century." and previously attributed to Chanakya, but now thought to be composed by multiple authors in the first centuries of the common era. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balakot, Makran
Kot Bala, or Balakot is an archaeological site located in Lasbela District, Balochistan, Pakistan. It is near the Makran coast of the Arabian Sea, and goes back to around 4000 BC. The settlement of Balakot precedes the Indus Valley civilization by many centuries. It is located in the interior of the Sonmiani Bay, along the Lasbela coast (the Plain of Las Bela). This site is of importance due to its proximity to the Arabian Sea, and is believed to have been a main harbour, from which the Indus traders sailed to the coasts of the Arabian Peninsula. Excavations The site was excavated by Professor George F. Dales of the University of California, Berkeley in the 1970s, but full details were not published. It is the only site in the region that was professionally excavated. The upper levels of the site belong to Indus Civilization, while the lower levels feature a culture of its own. The arrival of Indus influence was rather sudden. Balakot culture The ancient Balakot culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilometers (58 miles) northwest of ancient Ur, 108 kilometers (67 miles) southeast of ancient Nippur, and 24 kilometers (15 miles) northwest of ancient Larsa. It is east of modern Samawah. Uruk is the type site for the Uruk period. Uruk played a leading role in the early urbanization of Sumer in the mid-4th millennium BC. By the final phase of the Uruk period around 3100 BC, the city may have had 40,000 residents, with 80,000–90,000 people living in its environs, making it the largest urban area in the world at the time. Gilgamesh, according to the chronology presented in the '' Sumerian King List'' (''SKL''), ruled Uruk in the 27th century BC. After the end of the Early Dynastic period, with the rise of the Akkadian Empire, the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurore Didier
Aurore Didier (born 1978) is a French archaeologist and researcher. At the French National Center for Scientific Research, she is in charge of the ‘Indus-Balochistan programme’, and director of the French Archaeological Mission in the Indus Basin. Her primary interest is South Asian protohistory, specifically the Bronze Age in the Indo-Iranian Borderlands (3000 BCE) and the Indus Valley Civilization. Early life and education Didier was raised near Paris, alongside her older brother and her younger brother. She was raised in an artistic environment, with her father being a professional musicians involved in the film industry. Didier spent 15 years doing ballet and other dance styles as an extracurricular. She also became interested in archaeology at a young age, sparked by her mother taking her to museums every week. By age 12, she had decided to pursue archaeology as a career. Didier attended Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne University for her master's degree, during which she focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbat
Turbat (Urdu and ) is a city in the southern region of Balochistan province of Pakistan. It is the administrative centre of Kech District. Turbat is the second-largest city in Balochistan after Quetta and the 35th largest city in the country by population. Situated on the left bank of the Kech River, Turbat was the historical capital of the princely state of Makran. It is the largest city in the southern part of the province. The Gwadar Port lies southwest of Turbat. History In the 12th century, Turbat and its surrounding areas, along with Iranian Makran, were ruled by Prince Punnu (Mir Dosthein) and his father and his uncle Prince Aali Khan and Prince Khosag Khan. Later, Turbat was ruled by the Gichki Tribes of Makran and as well ruled by the Buledi tribe about 400 years ago. It was then the headquarters of the Makran State and the Nawab of Makran resided in Shahi Tump near Turbat. When Makran State was dissolved, Turbat city remained the Division Headquarters. Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miri Qalat
Miri () is a coastal city in north-eastern Sarawak, Malaysia, located near the border of Brunei, on the island of Borneo. The city covers an area of , located northeast of Kuching and southwest of Kota Kinabalu. Miri is the second largest city in Sarawak, with a population of 356,900 as of 2020. The city is also the capital of Miri District, Miri Division. Before Miri was founded, Marudi was the administrative centre of the northern region of Sarawak. Miri was founded in 1910 when the first oil well was drilled by Royal Dutch Shell. The discovery of an oil field in Miri has led to rapid development of Miri town. Miri became the administrative centre of the northern region of Sarawak by 1929. During World War II, the Miri oil fields were destroyed by the Brooke government to sabotage Japanese operations in Southeast Asia but to no avail; Miri town was the first landing point of Japanese troops in Borneo. The subsequent Japanese occupation led Miri to become a target of Allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kech River
The Kech River () flows in the Makran region of southeastern Iran and the southwestern area of Balochistan Province in southwestern Pakistan. Geography The seasonal intermittent river is a tributary of the Dasht River. The Dasht flows southeast into the Central Makran Range in the Gwadar District of Balochistan, and to its mouth at the Gulf of Oman of the Arabian Sea. ;Uses The city of Turbat is located on the Kech River. The river's water is used to irrigate orchards and for vegetable farming in surrounding areas. Fauna According to WWF-Pakistan, the Kech is one of Balochistan’s four coastal rivers, the others being the Hingol, Hub and Basol rivers, that support a healthy crocodile population. The conservation organisation noted that the four rivers rely on rainwater, which leaves behind small and big ponds that serve as habitats for the crocodiles. It did however note that these ponds were drying up much quicker due to warming temperatures and less rain. Flooding The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyophagoi
Ichthyophagoi (, "fish-eaters") and Latin Ichthyophagi is the name given by ancient geographers to several ethnically unrelated Coast, coast-dwelling peoples in different parts of the world. *Herodotus (book i. c. 200) mentions three tribes of the Babylonians who were solely fish-eaters, and in book iii. c. 19 refers to Ichthyophagi in Aethiopia. Diodorus Siculus and Strabo also referred to them all along the African coast of the Red Sea in their descriptions of Aethiopia. *Ptolemy speaks of fish-eaters in the Persian Gulf coasts, coast of the Red Sea, on the west coast of Africa and on the coast of the Far East near the harbour of Cattigara. *Pliny the Elder, Pliny relates the existence of such people on the islands in the Persian Gulf. *According to Arrian, Nearchus mentions such a race as inhabiting the barren shores of the Gwadar and Pasni (city), Pasni districts in Makran, Makrān. During the homeward march of Alexander the Great, his admiral, Nearchus led a fleet in Arabian Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; ; ) was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander, and philosopher of the Roman period. '' The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best source on the campaigns of Alexander the Great. Scholars have generally preferred Arrian to other extant primary sources, though this attitude has changed somewhat in light of modern studies into Arrian's method. Arrian's life Arrian was born in Nicomedia (present-day İzmit), the provincial capital of Bithynia. Cassius Dio called him Flavius Arrianus Nicomediensis. Sources provide similar dates for his birth, within a few years prior to 90, 89, and 85–90 AD. The line of reasoning for dates belonging to 85–90 AD is because of Arrian being made a consul around 130 AD, and the usual age for this, during this period, being 42 years of age. (ref. pp. 312, & SYME 1958, ''ibid.''). His family was from the Greek provincial aristocracy, and his full name, ''L. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |