|
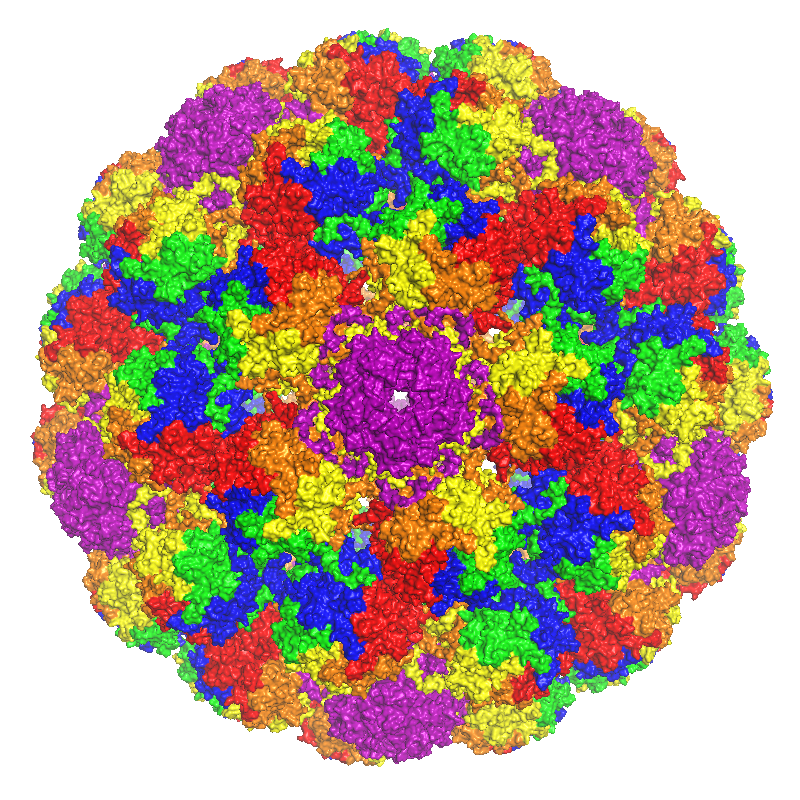
Major Capsid Protein VP1
Major capsid protein VP1 is a viral protein that is the main component of the polyomavirus capsid. VP1 monomers are generally around 350 amino acids long and are capable of self-assembly into an icosahedral structure consisting of 360 VP1 molecules organized into 72 pentamers. VP1 molecules possess a surface binding site that interacts with sialic acids attached to glycans, including some gangliosides, on the surfaces of cells to initiate the process of viral infection. The VP1 protein, along with capsid components VP2 and VP3, is expressed from the "late region" of the circular viral genome. Structure VP1 is the major structural component of the polyomavirus icosahedral capsid, which has T=7 symmetry and a diameter of 40-45 nm. The capsid contains three proteins; VP1 is the primary component and forms a 360-unit outer capsid layer composed of 72 pentamers. The other two components, VP2 and VP3, have high sequence similarity to each other, with VP3 truncated at the N-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murine Polyomavirus
Murine polyomavirus (also known as mouse polyomavirus, ''Polyomavirus muris'', or ''Mus musculus'' polyomavirus 1, and in older literature as SE polyoma or parotid tumor virus; abbreviated MPyV) is an unenveloped double-stranded DNA virus of the polyomavirus family. The first member of the family discovered, it was originally identified by accident in the 1950s. A component of mouse leukemia extract capable of causing tumors, particularly in the parotid gland, in newborn mice was reported by Ludwik Gross in 1953 and identified as a virus by Sarah Stewart and Bernice Eddy at the National Cancer Institute, after whom it was once called "SE polyoma". Stewart and Eddy would go on to study related polyomaviruses such as SV40 that infect primates, including humans. These discoveries were widely reported at the time and formed the early stages of understanding of oncoviruses. Pathology MPyV is primarily spread among mice via the intranasal route and is shed in urine. Genetic suscepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus-like Particle
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are molecules that closely resemble viruses, but are non-infectious because they contain no viral genetic material. They can be naturally occurring or synthesized through the individual expression of viral structural proteins, which can then self assemble into the virus-like structure. Combinations of structural capsid proteins from different viruses can be used to create recombinant VLPs. Both in-vivo assembly (i.e., assembly inside E. coli bacteria via recombinant co-expression of multiple proteins) and in-vitro assembly (i.e., protein self-assembly in a reaction vessel using stoichiometric quantities of previously purified proteins) have been successfully shown to form virus-like particles. VLPs derived from the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and composed of the small HBV derived surface antigen (HBsAg) were described in 1968 from patient sera. VLPs have been produced from components of a wide variety of virus families including Parvoviridae (e.g. adeno-associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JC Virus
Human polyomavirus 2, commonly referred to as the JC virus or John Cunningham virus, is a type of human polyomavirus. It was identified by electron microscopy in 1965 by ZuRhein and Chou, and by Silverman and Rubinstein. It was later isolated in culture and named using the initials of a patient by the name of John Cunningham from whom it was isolated and had developed progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). The virus causes leukoencephalopathy and other diseases only in cases of immunodeficiency, as in AIDS or during treatment with Immunosuppression, immunosuppressive drugs (e.g. in organ transplant patients). Infection and pathogenesis The initial site of infection may be the tonsils, or possibly the gastrointestinal tract. The virus then remains latent in the gastrointestinal tract and can also infect the tubular epithelium, epithelial cells in the kidneys, where it continues to reproduce, viral shedding, shedding virus particles in the urine. In addition, recent stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Localization Sequence
A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus. Types Classical These types of NLSs can be further classified as either monopartite or bipartite. The major structural differences between the two are that the two basic amino acid clusters in bipartite NLSs are separated by a relatively short spacer sequence (hence bipartite - 2 parts), while monopartite NLSs are not. The first NLS to be discovered was the sequence PKKKRKV in the SV40 Large T-antigen (a monopartite NLS). The NLS of nucleoplasmin, KR AATKKAGQAKKK, is the prototype of the ubiquitous bipartite signal: two cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": '' Arrhenius bases'', '' Brønsted bases'', and '' Lewis bases''. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acid An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...s, as originally proposed by Guillaume-François Rouelle, G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with Hydron (chemistry), hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disordered Protein
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other proteins or RNA. IDPs range from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coil, molten globule-like aggregates, or flexible linkers in large multi-domain proteins. They are sometimes considered as a separate class of proteins along with globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. They are most numerous in eukaryotes, with an estimated 30-40% of residues in the eukaryotic proteome located in disordered regions. Disorder is present in around 70% of proteins, either in the form of disordered tails or flexible linkers. Proteins can also be entirely disordered and lack a defined secondary and/or tertiary structure. Their discovery has disproved the idea that three-dimensional structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ... or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
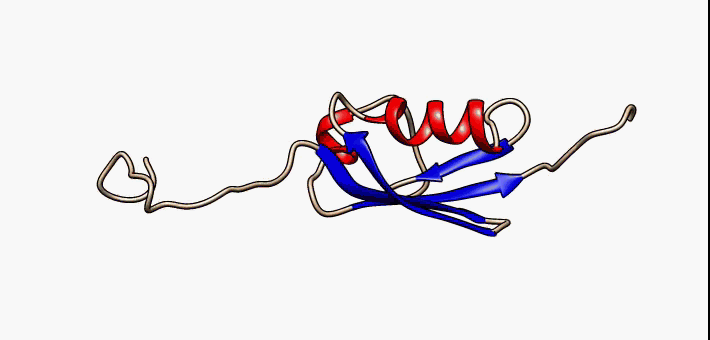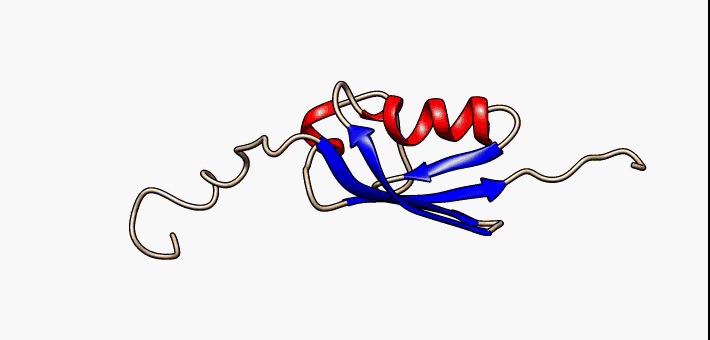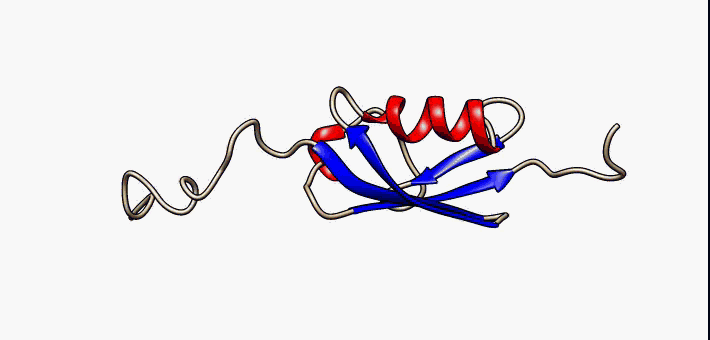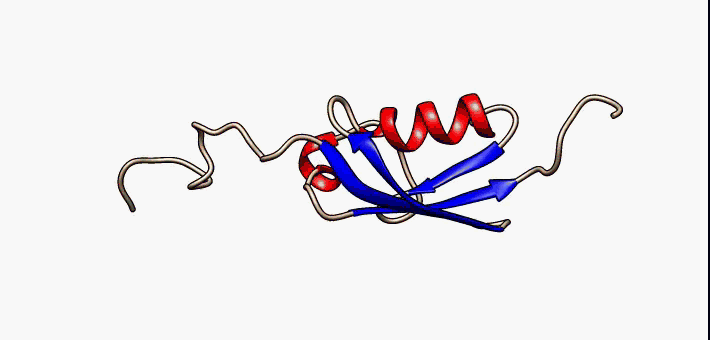
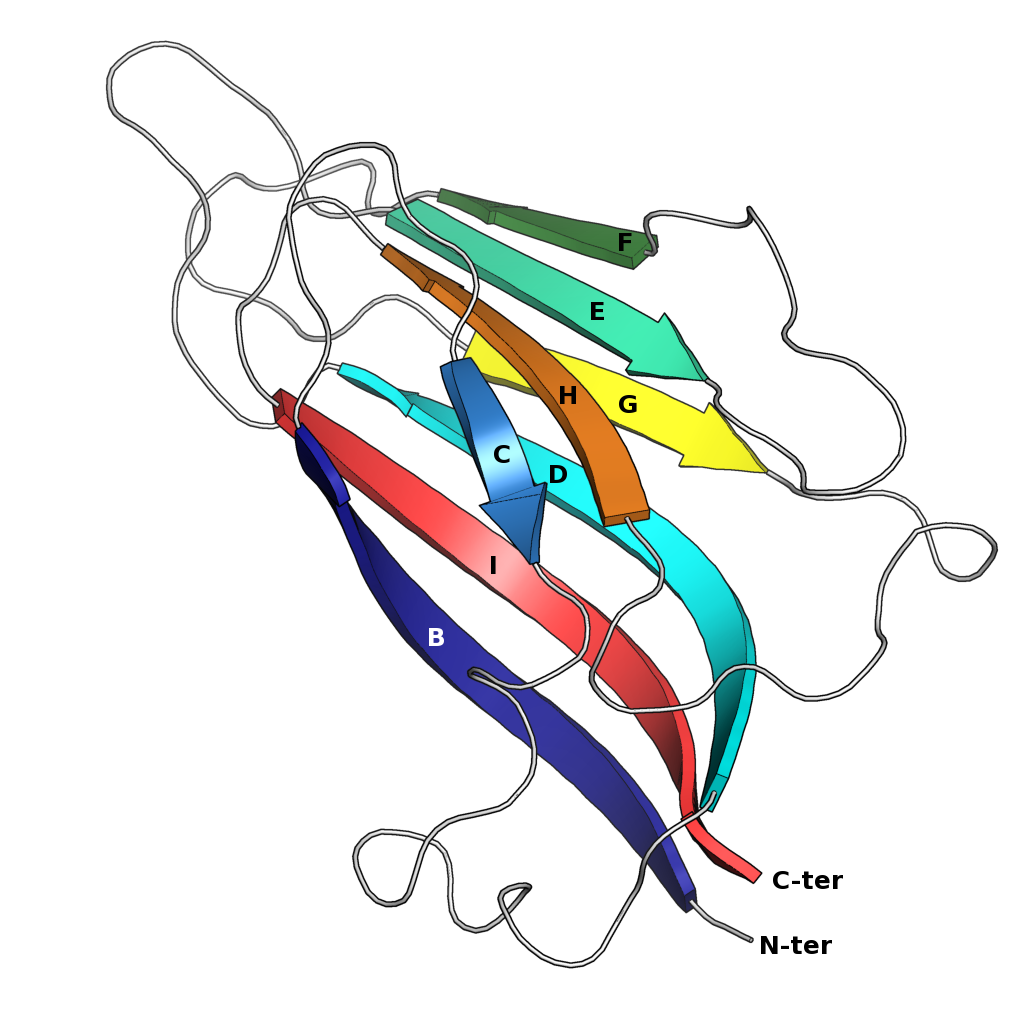
Jelly Roll Fold
The jelly roll or Swiss roll fold is a protein fold or supersecondary structure composed of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded sheets. The name of the structure was introduced by Jane S. Richardson in 1981, reflecting its resemblance to the jelly or Swiss roll cake. The fold is an elaboration on the Greek key (protein structure), Greek key motif and is sometimes considered a form of beta barrel. It is very common in viral proteins, particularly viral capsid proteins. Taken together, the jelly roll and Greek key structures comprise around 30% of the all-beta proteins annotated in the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database. Structure The basic jelly roll structure consists of eight beta strands arranged in two four-stranded antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel beta sheets which pack together across a hydrophobic interface [Where citation... uniprot]. The strands are traditionally labeled B through I for the historical reason that the first solved s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |