|
Magneto-optical Trap
In atomic, molecular, and optical physics, a magneto-optical trap (MOT) is an apparatus which uses laser cooling and a spatially varying magnetic field to create a Magnetic trap (atoms), trap which can produce samples of Ultracold atom, cold neutral atoms. Temperatures achieved in a MOT can be as low as several microkelvins, depending on the atomic species, which is two or three times below the Recoil temperature, photon-recoil limit. However, for atoms with an unresolved hyperfine structure, such as , the temperature achieved in a MOT will be higher than the Doppler cooling limit. A MOT is formed from the intersection of the zero of a weak Quadrupole magnet, quadrupolar magnetic field and six Circular polarization, circularly polarized Laser detuning, red-detuned optical molasses beams. Counterpropagating beams have opposite handed polarization. As atoms travel away from the zero field at the center of the trap, the spatially varying Zeeman effect, Zeeman shift brings an atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOT Setup
Mot or MOT may refer to: * Montserrat, UNDP country code Media * Ministry of Truth, the propaganda ministry in George Orwell 1949 novel ''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' * mot (magazine), ''mot'' (magazine), former German car magazine * Mot (Star Trek), a minor character in ''Star Trek: The Next Generation'' * Mot (TV series), ''Mot'' (TV series), a French children's animated television series * Mot (band), South Korean indie rock band * M.O.T. (group), American hip hop group * Mot (rapper) (born 1990), Russian rapper and singer Religion * Mot (god), the Semitic god of death Science and technology * Magneto-optical trap in physics * Molecular orbital theory in chemistry * Occupational therapy, MOT is the short form for Masters of Occupational Therapy Transport * Minot International Airport, in North Dakota, by IATA code * Minot (Amtrak station), by Amtrak code * Motspur Park railway station, London, by National Rail station code Organizations * MOT (gallery), a gallery for contemporary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeeman Effect
The Zeeman effect () is the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is caused by the interaction of the magnetic field with the magnetic moment of the atomic electron associated with its Angular momentum, orbital motion and Spin (physics), spin; this interaction shifts some orbital energies more than others, resulting in the split spectrum. The effect is named after the Netherlands, Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman, who discovered it in 1896 and received a Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery. It is analogous to the Stark effect, the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of an electric field. Also, similar to the Stark effect, transitions between different components have, in general, different intensities, with some being entirely forbidden (in the dipole approximation), as governed by the selection rules. Since the distance between the Zeeman sub-levels is a function of magnetic field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Spectroscopy
Saturated absorption spectroscopy measures the transition frequency of an atom or molecule between its ground state and an excited state. In saturated absorption spectroscopy, two counter-propagating, overlapped laser beams are sent through a sample of atomic gas. One of the beams stimulates photon emission in excited atoms or molecules when the laser's frequency matches the transition frequency. By changing the laser frequency until these extra photons appear, one can find the exact transition frequency. This method enables precise measurements at room temperature because it is insensitive to doppler broadening. Absorption spectroscopy measures the doppler-broadened transition, so the atoms must be cooled to millikelvin temperatures to achieve the same sensitivity as saturated absorption spectroscopy. Principle of saturated absorption spectroscopy To overcome the problem of Doppler broadening without cooling down the sample to millikelvin temperatures, a classical pump–probe sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servomechanism
In mechanical and control engineering, a servomechanism (also called servo system, or simply servo) is a control system for the position and its time derivatives, such as velocity, of a mechanical system. It often includes a servomotor, and uses closed-loop control to reduce steady-state error and improve dynamic response. In closed-loop control, error-sensing negative feedback is used to correct the action of the mechanism. In displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure the output is achieving the desired effect. Following a specified motion trajectory is called servoing, where "servo" is used as a verb. The ''servo'' prefix originates from the Latin word ''servus'' meaning slave. The term correctly applies only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed, attitude or any other measurable variables. For example, an automotive power win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Diodes
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation is generated in the form of an emitted photon. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence, and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet (UV) spectra. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
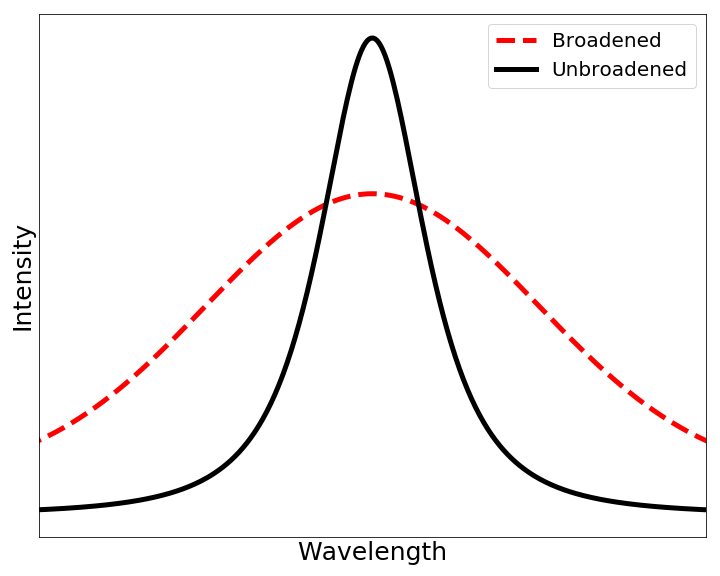
Doppler Broadening
In atomic physics, Doppler broadening is broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atoms or molecules. Different velocities of the emitting (or absorbing) particles result in different Doppler shifts, the cumulative effect of which is the emission (absorption) line broadening. This resulting line profile is known as a Doppler profile. A particular case is the thermal Doppler broadening due to the thermal motion of the particles. Then, the broadening depends only on the frequency of the spectral line, the mass of the emitting particles, and their temperature, and therefore can be used for inferring the temperature of an emitting (or absorbing) body being spectroscopically investigated. Derivation (non-relativistic case) When a particle moves (e.g., due to the thermal motion) towards the observer, the emitted radiation is shifted to a higher frequency. Likewise, when the emitter moves away, the frequency is lowered. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linewidth
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identify atoms and molecules. These "fingerprints" can be compared to the previously collected ones of atoms and molecules, and are thus used to identify the atomic and molecular components of stars and planets, which would otherwise be impossible. Types of line spectra Spectral lines are the result of interaction between a quantum system (usually atoms, but sometimes molecules or atomic nuclei) and a single photon. When a photon has about the right amount of energy (which is connected to its frequency) to allow a change in the energy state of the system (in the case of an atom this is usually an electron changing orbitals), the photon is absorbed. Then the energy will be spontaneously re-emitted, either as one photon at the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturable Absorption
Saturable absorption is a property of materials where the absorption of light decreases with increasing light intensity. Most materials show some saturable absorption, but often only at very high optical intensities (close to the optical damage). At sufficiently high incident light intensity, the ground state of a saturable absorber material is excited into an upper energy state at such a rate that there is insufficient time for it to decay back to the ground state before the ground state becomes depleted, causing the absorption to saturate. The key parameters for a saturable absorber are its wavelength range (where in the electromagnetic spectrum it absorbs), its dynamic response (how fast it recovers), and its saturation intensity and fluence (at what intensity or pulse energy it saturates). Saturable absorber materials are useful in laser cavities. For instance, they are commonly used for passive Q-switching. Phenomenology Within the simple model of saturated absorption, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parity (physics)
In physics, a parity transformation (also called parity inversion) is the flip in the sign of ''one'' spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it can also refer to the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates (a point reflection): \mathbf: \beginx\\y\\z\end \mapsto \begin-x\\-y\\-z\end. It can also be thought of as a test for chirality of a physical phenomenon, in that a parity inversion transforms a phenomenon into its mirror image. All fundamental interactions of elementary particles, with the exception of the weak interaction, are symmetric under parity transformation. As established by the Wu experiment conducted at the US National Bureau of Standards by Chinese-American scientist Chien-Shiung Wu, the weak interaction is chiral and thus provides a means for probing chirality in physics. In her experiment, Wu took advantage of the controlling role of weak interactions in radioactive decay of atomic isotopes to establish the chirality of the weak f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landé G-factor
In physics, the Landé ''g''-factor is a particular example of a ''g''-factor, namely for an electron with both spin and orbital angular momenta. It is named after Alfred Landé, who first described it in 1921. In atomic physics, the Landé ''g''-factor is a multiplicative term appearing in the expression for the energy levels of an atom in a weak magnetic field. The quantum states of electrons in atomic orbitals are normally degenerate in energy, with these degenerate states all sharing the same angular momentum. When the atom is placed in a weak magnetic field, however, the degeneracy is lifted. Description The factor comes about during the calculation of the first-order perturbation in the energy of an atom when a weak uniform magnetic field (that is, weak in comparison to the system's internal magnetic field) is applied to the system. Formally we can write the factor as, :g_J= g_L\frac+g_S\frac. The orbital g_L is equal to 1, and under the approximation g_S = 2 , th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, Electrical network, electric and Magnetic circuit, magnetic circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar, etc. They describe how electric field, electric and magnetic fields are generated by electric charge, charges, electric current, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |