|
Magi
Magi (), or magus (), is the term for priests in Zoroastrianism and earlier Iranian religions. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the Great, known as the Behistun Inscription. Old Persian texts, predating the Hellenistic period, refer to a magus as a Zurvanism, Zurvanic, and presumably Zoroastrian, priest. Pervasive throughout the Eastern Mediterranean and West Asia until late antiquity and beyond, ''mágos'' (μάγος) was influenced by (and eventually displaced) Greek ''The Lesser Key of Solomon#Ars Goetia, goēs'' (γόης), the older word for a practitioner of magic (paranormal), magic, with a meaning expanded to include astronomy, astrology, alchemy, and other forms of esoteric knowledge. This association was in turn the product of the Hellenistic fascination for Pseudo-Zoroaster, who was perceived by the Greeks to be the Chaldean founder of the Magi and inventor of both astrology and magic, a meaning that stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Magi
In Christianity, the Biblical Magi ( or ; singular: ), also known as the Three Wise Men, Three Kings, and Three Magi, are distinguished foreigners who visit Jesus after his birth, bearing gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh in homage to him. In Western Christianity, they are commemorated on the feast day of Epiphany (holiday), Epiphany—sometimes called "Three Kings Day"—and commonly appear in the Nativity of Jesus, nativity celebrations of Christmas. In Eastern Christianity, they are commemorated on Christmas day. The Magi appear solely in the Gospel of Matthew, which states that they came "from the east" () to worship the "one who has been born king of the Jews". Their names, origins, appearances, and exact number are unmentioned and derive from the inferences or traditions of later Christians. In Western Christianity and Eastern Orthodox Christianity, they are usually assumed to have been three in number, corresponding with each gift; in Syriac Christianity, they ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magician (paranormal)
Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is the application of beliefs, rituals or actions employed in the belief that they can manipulate natural or supernatural beings and forces. It is a category into which have been placed various beliefs and practices sometimes considered separate from both religion and science. Connotations have varied from positive to negative at times throughout history. Within Western culture, magic has been linked to ideas of the Other, foreignness, and primitivism; indicating that it is "a powerful marker of cultural difference" and likewise, a non-modern phenomenon. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, Western intellectuals perceived the practice of magic to be a sign of a primitive mentality and also commonly attributed it to marginalised groups of people. Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), a British occultist, defined " magick" as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", adding a 'k' to distinguish ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magus
Magi (), or magus (), is the term for priests in Zoroastrianism and earlier Iranian religions. The earliest known use of the word ''magi'' is in the trilingual inscription written by Darius the Great, known as the Behistun Inscription. Old Persian texts, predating the Hellenistic period, refer to a magus as a Zurvanic, and presumably Zoroastrian, priest. Pervasive throughout the Eastern Mediterranean and West Asia until late antiquity and beyond, ''mágos'' (μάγος) was influenced by (and eventually displaced) Greek '' goēs'' (γόης), the older word for a practitioner of magic, with a meaning expanded to include astronomy, astrology, alchemy, and other forms of esoteric knowledge. This association was in turn the product of the Hellenistic fascination for Pseudo-Zoroaster, who was perceived by the Greeks to be the Chaldean founder of the Magi and inventor of both astrology and magic, a meaning that still survives in the modern-day words "magic" and " magician". In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known by its Latin title ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply the ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymously authored grimoire on Goetia, sorcery, mysticism and Magic (supernatural), magic. It was compiled in the mid-17th century from materials several centuries older... It is divided into five books: the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demon. Terminology The text is more properly called '', or, The little Key of Solomon''. The title most commonly used, ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A. E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the terms "so-called Greater Key" and "Lesser Key" to distinguish between the Clavicula Salomonis and Lemegeton, so he may have been the one to coin it. The Latin term refers to the evocati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
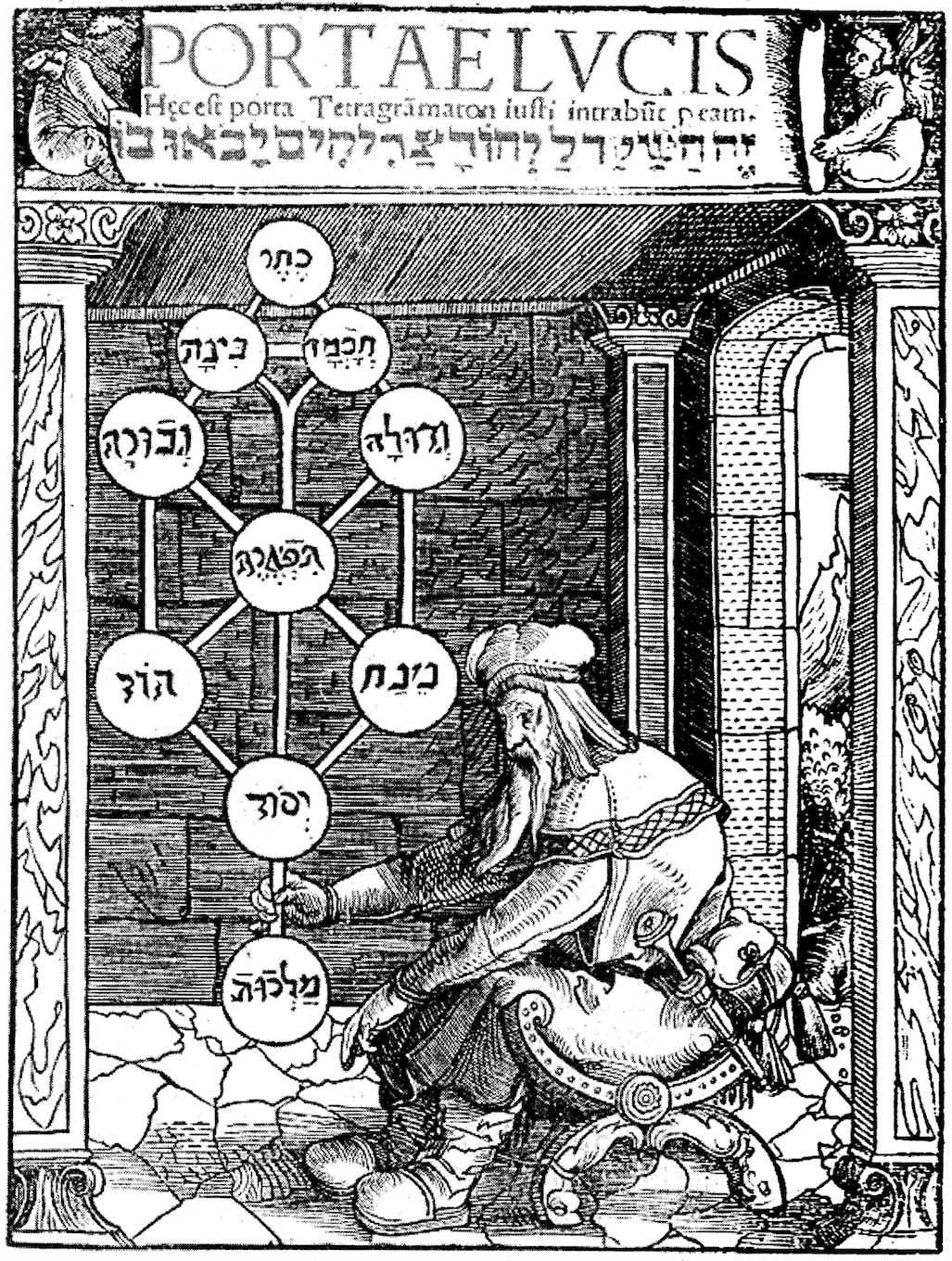
Esoteric
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-Zoroaster
Zarathushtra Spitama, more commonly known as Zoroaster or Zarathustra, was an Iranian religious reformer who challenged the tenets of the contemporary Ancient Iranian religion, becoming the spiritual founder of Zoroastrianism. Variously described as a sage or a wonderworker; in the oldest Zoroastrian scriptures, the Gathas, which he is believed to have authored, he is described as a preacher and a poet-prophet. He also had an impact on Heraclitus, Plato, Pythagoras, and the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He spoke an Eastern Iranian language, named Avestan by scholars after the corpus of Zoroastrian religious texts written in that language. Based on this, it is tentative to place his homeland somewhere in the eastern regions of Greater Iran (perhaps in modern-day Afghanistan or Tajikistan), but his exact birthplace is uncertain. His life is traditionally dated to sometime around the 7th and 6th centuries BC, making him a contemporary o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, Zoroaster ( ). Among the world's oldest organized faiths, its adherents exalt an Creator deity, uncreated, Omnibenevolence, benevolent, and List of knowledge deities#Persian mythology, all-wise deity known as Ahura Mazda (), who is hailed as the supreme being of the universe. Opposed to Ahura Mazda is Ahriman, Angra Mainyu (), who is personified as a List of death deities#Persian-Zoroastrian, destructive spirit and the adversary of all things that are good. As such, the Zoroastrian religion combines a Dualism in cosmology, dualistic cosmology of good and evil with an eschatological outlook predicting the Frashokereti, ultimate triumph of Ahura Mazda over evil. Opinions vary among scholars as to whether Zoroastrianism is monotheistic, polyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zurvanism
Zurvanism is a fatalistic religious movement of Zoroastrianism in which the divinity Zurvan is a first principle (primordial creator deity) who engendered equal-but-opposite twins, Ahura Mazda and Angra Mainyu. Zurvanism is also known as "Zurvanite Zoroastrianism", and may be contrasted with Mazdaism. In Zurvanism, Zurvan was perceived as the god of infinite time and space and also known as "one" or "alone." Zurvan was portrayed as a transcendental and neutral god without passion; one for whom there was no distinction between good and evil. The name ''Zurvan'' is a normalized rendition of the word, which in Middle Persian appears as either ''Zurvān'', ''Zruvān'' or ''Zarvān''. The Middle Persian name derives from Avestan (, a grammatically neuter noun). Origins and background Although the details of the origin and development of Zurvanism remain murky (for a summary of the three opposing opinions see below), it is generally accepted that Zurvanism was: : (1) a branch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of Celestial objects in astrology, celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in Calendrical calculation, calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindu astrology, Hindus, Chinese astrology, Chinese, and the Maya civilization, Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of " base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius The Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West Asia, parts of the Balkans (Skudra, Thrace–Achaemenid Macedonia, Macedonia and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia) and the Caucasus, most of the Black Sea's coastal regions, Central Asia, the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley, Indus Valley in the far east, and portions of North Africa and Northeast Africa including History of Persian Egypt, Egypt (), eastern ancient Libya, Libya, and coastal The Sudans, Sudan. Darius ascended the throne by overthrowing the Achaemenid monarch Bardiya (or ''Smerdis''), who he claimed was in fact an imposter named Gaumata. The new king met with rebellions throughout the empire but quelled each of them; a major event in Darius's life was his expedition to subjugate Ancient Greece, Greece and punish Classical At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |