|
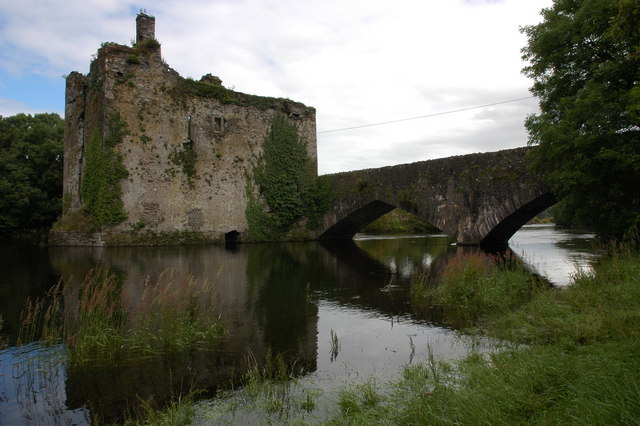
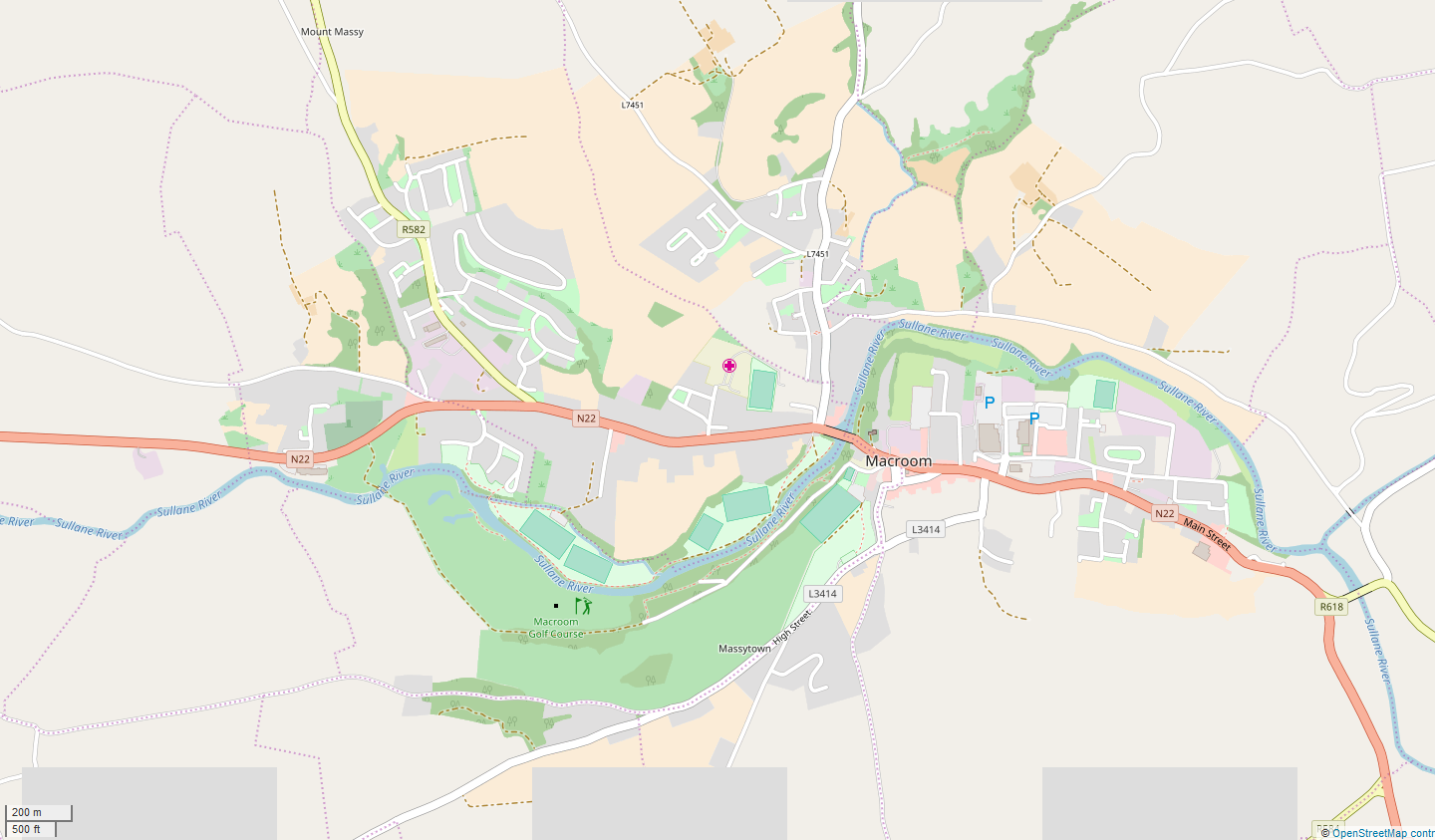
Macroom Castle
Macroom Castle, in the centre of the town of Macroom, was once residence and fortress of the Lords of Muskerry. The castle has changed owners many times, has been besieged, burned, and rebuilt. The MacCarthys of Muskerry owned it with some interruptions from about 1353 when Muskerry was given to Dermot MacCarthy, 1st Lord of Muskerry, until 1691 when Donogh MacCarthy, 4th Earl of Clancarty lost it definitively. What remains of the castle is a gatehouse on the town square and a ruin near the bridge over the River Sullane. This ruin comprises an old tower, everything else dates from an early 19th-century rebuild by Robert Hedges Eyre. Location The town of Macroom is divided by the River Sullane into two parts of similar size. The town square and the castle are in the historic centre on the right, eastern bank. The castle extends between the town square and the river. It now consists of two disjoint pieces: the gatehouse and the castle ruin. Habitations, businesses, and a school, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroom
Macroom (; ) is a market town in County Cork, Ireland, located in the valley of the River Sullane, halfway between Cork (city), Cork city and Killarney. Its population has grown and receded over the centuries as it went through periods of war, famine and workhouses, forced emigration and intermittent prosperity. The 2011 census of Ireland, 2011 census gave an urban population of 3,879 people, while the 2016 census of Ireland, 2016 census recorded 3,765 people. The town is in a Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name. Macroom began as a meeting place for the druids of Munster. It is first mentioned is in 6th-century records, and the immediate area hosted a major battle involving the Irish king Brian Boru. During the Middle Ages, the town was invaded by a succession of warring clans, including the Murcheatach Uí Briain and Richard de Cogan families. In the early modern period the MacCarthys took control and later the area found prosperity via milling. The MacCa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was common in much of Europe. The system of appanage greatly influenced the territorial construction of France and the German states and explains why many of the former provinces of France had coats of arms which were modified versions of the king's arms. Etymology Late Latin , from or 'to give bread' (), a for food and other necessities, hence for a "subsistence" income, notably in kind, as from assigned land. Original appanage: in France History of the French appanage An appanage was a concession of a fief by the sovereign to his younger sons, while the eldest son became king on the death of his father. Appanages were considered as part of the inheritance transmitted to the (younger sons). The word was specifically used for the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boetius MacEgan
Boetius MacEgan (; died May 1650) was a 17th-century Irish Roman Catholic Bishop of Ross. He was born in the barony of Duhallow in north-west County Cork and educated in France and Spain. He returned to his native Munster as a Franciscan friar in the 1630s and was promoted to several positions of importance in the Franciscan order. He was an enthusiastic supporter of the Confederation of Kilkenny, which controlled most of Ireland between the 1641 uprising and the Cromwellian conquest of 1649. In 1645 a new papal nuncio landed in Ireland with arms and funds to support the rebellion and befriended MacEgan, appointing him chaplain general of the Ulster forces. In this capacity MacEgan accompanied the Confederation forces on many campaigns and was present at the Confederation victories at the Battle of Benburb in 1646, Limerick and Kilkenny. In 1646 he was proposed as bishop of Ross by the nuncio himself and consecrated at Waterford in 1648, but probably never gained access to hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromwellian Conquest Of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the Commonwealth of England, initially led by Oliver Cromwell. It forms part of the 1641 to 1652 Irish Confederate Wars, and wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Modern estimates suggest that during this period, Ireland experienced a demographic loss totalling around 15 to 20% of the pre-1641 population, due to fighting, famine and bubonic plague. The Irish Rebellion of 1641 brought much of Ireland under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation, who engaged in a multi-sided war with Royalists, Parliamentarians, Scots Covenanters, and local Presbyterian militia. Following the execution of Charles I in January 1649, the Confederates allied with their former Royalist opponents against the newly established Commonwealth of England. Cromwell landed near Dublin in August 1649 with an expeditionary force, and by the end of 1650 the Confederacy had been defeated, although sporadic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Butler, 1st Duke Of Ormond
Lieutenant-General James FitzThomas Butler, 1st Duke of Ormond, KG, PC (19 October 1610 – 21 July 1688), was an Anglo-Irish statesman and soldier, known as Earl of Ormond from 1634 to 1642 and Marquess of Ormond from 1642 to 1661. Following the failure of the senior line of the Butler family, he was the second representative of the Kilcash branch to inherit the earldom. His friend, the Earl of Strafford, secured his appointment as commander of the government army in Ireland. Following the outbreak of the Irish Rebellion of 1641, he led government forces against the Irish Catholic Confederation; when the First English Civil War began in August 1642, he supported the Royalists and in 1643 negotiated a ceasefire with the Confederation which allowed his troops to be transferred to England. Shortly before the Execution of Charles I in January 1649, he agreed the Second Ormonde Peace, an alliance between the Confederation and Royalist forces which fought against the Cromwell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl Of Clancarty
Sir Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty (1594–1665), was an Irish soldier and politician. He succeeded his father as 2nd Viscount Muskerry in 1641. He rebelled against the government and joined the Irish Catholic Confederation, demanding religious freedom as a Catholic and defending the rights of the Gaelic nobility. Later, he supported the King against his Parliamentarian enemies during the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. He sat in the House of Commons of the Irish parliaments of 1634–1635 and 1640–1649 where he opposed Strafford, King Charles I's authoritarian viceroy. In 1642, he sided with the Irish Rebellion when it reached his estates in Munster. He fought for the insurgents at the Siege of Limerick and the Battle of Liscarroll. He joined the Irish Catholic Confederates and sat on their Supreme Council. Having fought in the Irish Confederate Wars, he negotiated the Cessation of 1643, a cease-fire between the Confederates and the King. He tried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
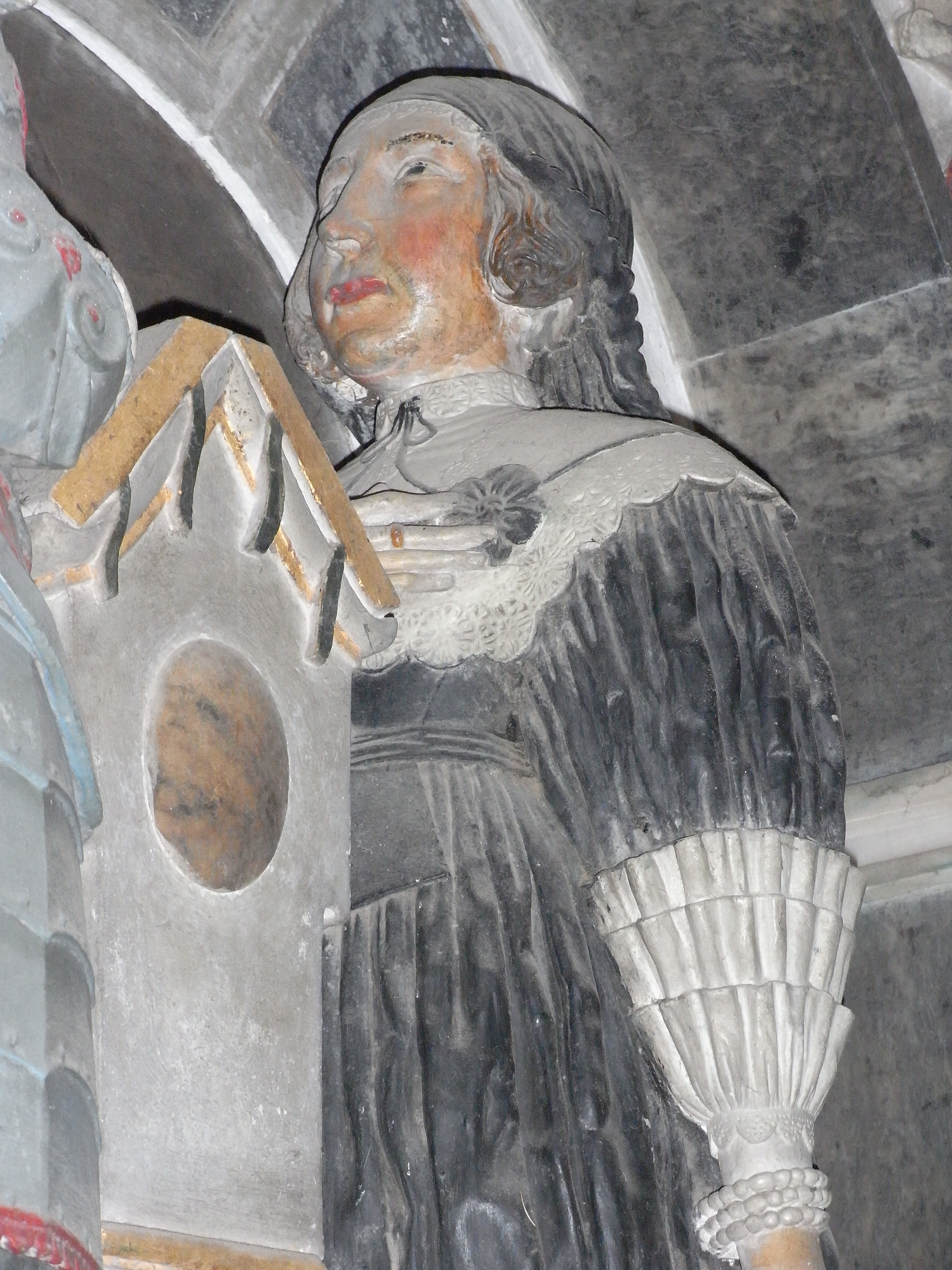
Charles MacCarty, Viscount Muskerry
Charles MacCarty, Viscount Muskerry (1633 or 1634 – 1665), called Cormac in Irish, commanded a royalist battalion at the Battle of the Dunes during the interregnum. He was heir apparent to Donough MacCarty, 1st Earl of Clancarty but was killed at the age of 31 at the Battle of Lowestoft, a sea-fight against the Dutch, during the Second Anglo-Dutch War, and thus never succeeded to the earldom. He was buried in Westminster Abbey. Birth and origins Charles (i.e. Cormac) was born in 1633 or 1634, probably at Macroom Castle, County Cork, Ireland, his parents' habitual residence. He was the eldest son of Donough MacCarty and his wife Eleanor (or Ellen) Butler. He is also known as Cormac and this seems to have been his original name, whereas Charles seems to be a later English or French adaptation. At the time of his birth, Charles's father was the 2nd Viscount Muskerry, but he would be advanced to Earl of Clancarty in 1658. His father's family were the MacCartys of Musker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Rinuccini
Giovanni Battista Rinuccini (1592–1653) was an Italian Roman Catholic archbishop in the mid-seventeenth century. He was a noted legal scholar and became chamberlain to Pope Gregory XV. In 1625 Pope Urban VIII made him the Archbishop of Fermo in Italy. In 1645 Pope Innocent X sent him to Ireland as Papal Nuncio. He brought money and weapons to help the Confederate Irish in its conflict against the English Parliamentarians. Rinuccini became the dominant figure of the hard-line Clerical Faction of the Confederates refusing the alliance with the Irish Royalists. Early life Rinuccini was born in Rome on 15 September 1592. He was the son of a Florentine patrician, his mother, Virginia di Pier Antonio Bandini was a sister of Cardinal Ottavio Bandini, who was bishop of Ostia and Velletri and dean of the Sacred College of Cardinals. Rinuccini was educated by the Jesuits in Rome and studied law at the Universities of Bologna and Perugia, in due course, he was ordained a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Confederate Wars
The Irish Confederate Wars, took place from 1641 to 1653. It was the Irish theatre of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of civil wars in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, all then ruled by Charles I of England, Charles I. The conflict caused an estimated 200,000 deaths from fighting, as well as war-related famine and disease. It began with the Irish Rebellion of 1641, when local Catholics tried to seize control of the Dublin Castle administration. They wanted an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, to increase Irish self-governance, and to roll back the Plantations of Ireland. They also wanted to prevent an invasion by anti-Catholic Roundhead, English Parliamentarians and Covenanter, Scottish Covenanters, who were defying the king. Rebel leader Felim O'Neill of Kinard, Felim O'Neill claimed to be Proclamation of Dungannon, doing the king's bidding, but Charles condemned the rebellion after it broke out. The rebellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wilmot, 1st Viscount Wilmot
Charles Wilmot, 1st Viscount Wilmot of Athlone (c. 1572 – 1644) was an English soldier active in Ireland. Life He was the son of Edward Wilmot of Culham (otherwise of Newent, Gloucestershire and Witney, Oxfordshire) and Elizabeth Stafford. On 6 July 1587 he matriculated at Magdalen College, Oxford, aged 16, but left the university without a degree, and took service in the Irish wars, perhaps in attendance on his neighbour, Sir Thomas Norris, who was also a member of Magdalen College. In 1592, he became a captain, and early in 1595 he was sent to Newry; in the same year he was also in command of sixty foot at Carrickfergus. In 1597 Norris, now President of Munster, made Wilmot sergeant-major of the forces in that province; he was promoted colonel in 1598. He was knighted by Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex at Dublin on 5 August 1599, and on the 16th was sent with instructions to the council of Munster for its government during Norris's illness. On 23 June 1600, Charles Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cormac MacDermot MacCarthy, 16th Lord Of Muskerry
Cormac MacDermot MacCarthy, 16th Lord of Muskerry (1552–1616) was an Irish magnate and soldier. He fought at the Siege of Kinsale during Tyrone's Rebellion. Birth and origins Cormac was born in 1552, the eldest son of Dermot MacCarthy and Ellen FitzGerald. His father was the 13th Lord of Muskerry. His father's full name, including his patronymic middle name, was Dermot MacTeige MacCarthy. His own full name was therefore Cormac MacDermot MacCarthy. His father's family were the MacCarthy of Muskerry, MacCarthys of Muskerry, a Gaelic Ireland, Gaelic Irish dynasty that had branched from the MacCarthy Mor dynasty, MacCarthy-Mor line in the 14th century when a younger son received Muskerry as appanage. His mother was a daughter of Sir Maurice FitzJohn FitzGerald of Totane, third son of John FitzGerald, de facto 12th Earl of Desmond, John FitzGerald, ''de facto'' 12th Earl of Desmond and younger brother of James FitzGerald, 13th Earl of Desmond, James FitzJohn FitzGerald, 13th Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinsale
Kinsale ( ; ) is a historic port and fishing town in County Cork, Ireland. Located approximately south of Cork (city), Cork City on the southeast coast near the Old Head of Kinsale, it sits at the mouth of the River Bandon, and has a population of 5,991 (as of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census) which increases in the summer when tourism peaks. The town is in a Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name. Kinsale is a holiday destination for both Irish and overseas tourists. The town is known for its restaurants, including the Michelin-starred Bastion (restaurant), Bastion restaurant, and holds a number of annual gourmet food festivals. As a historically strategic port town, Kinsale's notable buildings include Desmond Castle (Kinsale), Desmond Castle (associated with the Earls of Desmond and also known as the French Prison) of , the 17th-century Bastion fort, pentagonal bastion fort of James's Fort, James Fort on Castlepark peninsula, and Charles Fort (Irelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |