|
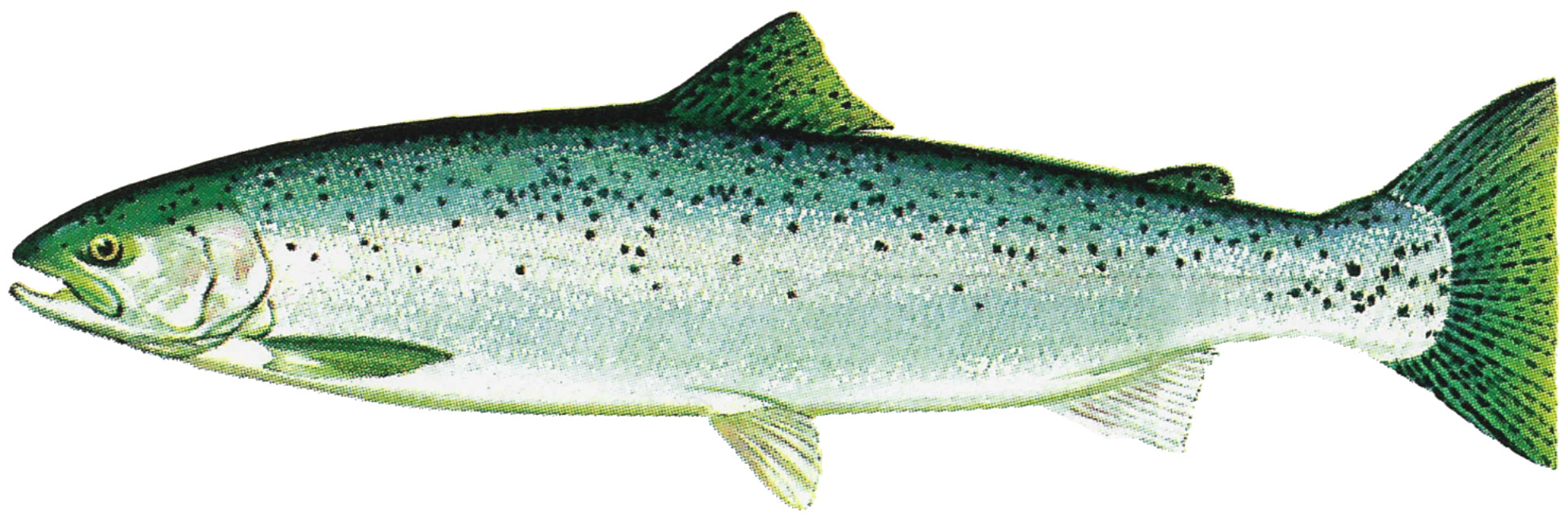
Macquarie Perch
The Macquarie perch (''Macquaria australasica'') is an Australian native freshwater fish of the Murray-Darling river system. It is a member of the family Percichthyidae and is closely related to the golden perch (''Macquaria ambigua''). The Macquarie perch derives its scientific name from the Macquarie River where the first scientifically described specimen was collected (''Macquaria'') and a derivation of the Latin word for "southern" (''australasica''). Description and diet Macquarie perch are medium-sized fish, commonly 30–40 cm and 1.0–1.5 kg. Maximum size is about 2.5 kg and 50 cm. The body is elongated, deep, and laterally compressed. The caudal fin, anal fin and soft dorsal fin are rounded. Spiny dorsal fin medium height and strong. Mouth and eyes are relatively small. Colouration can vary from tan to (more commonly) dark purplish-grey to black. The irises of the eyes are distinctly silver. Macquarie perch are a relatively placid nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier was a major figure in natural sciences research in the early 19th century and was instrumental in establishing the fields of comparative anatomy and paleontology through his work in comparing living animals with fossils. Cuvier's work is considered the foundation of vertebrate paleontology, and he expanded Linnaean taxonomy by grouping classes into phylum, phyla and incorporating both fossils and living species into the classification. Cuvier is also known for establishing extinction as a fact—at the time, extinction was considered by many of Cuvier's contemporaries to be merely controversial speculation. In his ''Essay on the Theory of the Earth'' (1813) Cuvier proposed that now-extinct species had been wiped out by periodic catastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Georges Cuvier
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macquaria
''Macquaria'' is a genus of medium-sized, predatory temperate perches endemism, endemic to Australia. They are found in rivers of the eastern part of the continent. Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * ''Macquaria ambigua'' (John Richardson (naturalist), J. Richardson, 1845), commonly known as golden perch or "yellowbelly" * ''Macquaria australasica'' (Georges Cuvier, G. Cuvier, 1830), commonly known as Macquarie perch One fossil species is known in †''Macquaria avus'' (Arthur Smith Woodward, Woodward, 1902) (=''Ctenolates avus'' Woodward, 1902) from Miocene-aged freshwater deposits near Nimbin, New South Wales, Nimbin. Many fossil remains assigned to this genus are known from the Eocene to the Miocene of Australia. However, it is uncertain whether they belong to this genus or to ''Percalates'' (formerly subsumed within it). Taxonomy Previously, the two catadromous species ''Macquaria colonorum'' and ''Macquaria novemaculeata, M. novemaculeata'' were al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to Spawn (biology), spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and Fish hatchery, hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except Antarctica. Introductions to locations outside their nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a species of salmonid ray-finned fish and the most widely distributed species of the genus ''Salmo'', endemic to most of Europe, West Asia and parts of North Africa, and has been widely introduced globally as a game fish, even becoming one of the world's worst invasive species outside of its native range. Brown trout are highly adaptable and have evolved numerous ecotypes/subspecies. These include three main ecotypes: a riverine ecotype called river trout or ''Salmo trutta'' morpha ''fario''; a lacustrine ecotype or ''S. trutta'' morpha ''lacustris'', also called the lake trout (not to be confused with the lake trout in North America); and anadromous populations known as the sea trout or ''S. trutta'' morpha ''trutta'', which upon adulthood migrate downstream to the oceans for much of its life and only returns to fresh water to spawn in the gravel beds of headstreams. Sea trout in Ireland and Great Britain have many regional names: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perch
Perch is a common name for freshwater fish from the genus ''Perca'', which belongs to the family Percidae of the large order Perciformes. The name comes from , meaning the type species of this genus, the European perch (''P. fluviatilis''). Many species of freshwater game fish more or less resemble perch, but belong to different genera. In fact, the exclusively saltwater-dwelling red drum (which belong to a different order Acanthuriformes) is often referred to as a "red perch", though by definition perch are freshwater species. Though many fish are referred to as perch as a common name, to be considered a true perch, the fish must be of the family Percidae. Species Most authorities recognize three species within the perch genus: * The European perch (''P. fluviatilis'') is primarily found in Europe, but a few can also be found in South Africa, and even as far east on the Southern hemisphere as Australia. This species is typically greenish in color with dark vertical ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarra River
The Yarra River or historically, the Yarra Yarra River, (Kulin languages: ''Berrern'', ''Birr-arrung'', ''Bay-ray-rung'', ''Birarang'', ''Birrarung'', and ''Wongete'') is a perennial river in south-central Victoria, Australia. The lower stretches of the Yarra are where Victoria's state capital Melbourne was established in 1835, and today metropolitan Greater Melbourne dominates and influences the landscape of its lower reaches. From its source in the Yarra Ranges, it flows west through the Yarra Valley which opens out into plains as it winds its way through Greater Melbourne before emptying into Hobsons Bay in northernmost Port Phillip Bay. The river has been a major food source and meeting place for Indigenous Australians for thousands of years. Shortly after the arrival of European settlers, land clearing forced the remaining Wurundjeri people into neighbouring territories and away from the river. Originally called ''Birrarung'' by the Wurundjeri, the current name w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongarlowe River
The Mongarlowe River is a perennial river of the Shoalhaven catchment located in the Southern Tablelands region of New South Wales, Australia. It was also known as Little River, during the 19th century. Location and features The river rises on the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range within the Monga National Park about east southeast of the village of Araluen. The river flows generally north, joined by six minor tributaries before reaching its confluence with the Shoalhaven River approximately northwest of the locality of Charleyong. The river descends over its course. The river is crossed by the Kings Highway northwest of Clyde Mountain. There are other road crossings at Monga, Mongarlowe and Marlowe. The river has a translocated population of the endangered Macquarie perch (''Macquaria australasica''). It is thought that this population descends from fish from the Murray-Darling Basin and not the eastern sub-species native to other parts of the Shoalhaven c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Translocation
Translocation is the human action of moving an organism from one area and releasing it in another. In terms of wildlife conservation, its objective is to improve the conservation status of the translocated organism or to restore the function and processes of the ecosystem the organism is entering. Two overarching goals of translocation are population restoration and conservation introduction.''Guidelines for reintroductions and other conservation translocations'' (PDF). IUCN. Retrieved 06 October 2023. Population restoration includes reinforcing existing populations and reintroducing populations to areas where they have disappeared. Conservation introduction involves assisted colonization of organism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland (freshwater Ecology)
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland. Definitions Upland and lowland are portions of a plain that are conditionally categorized by their elevation above the sea level. Lowlands are usually no higher than , while uplands are somewhere around to . On unusual occasions, certain lowlands such as the Caspian Depression lie below sea level. Uplands areas tend to spike into valleys and mountains, forming mountain ranges while lowland areas tend to be uniformly flat, although both can vary such as the Mongolian Plateau. Upland habitats are cold, clear and rocky whose rivers are fast-flowing in mountainous areas; lowland habitats are warm with slow-flowing rivers found in relatively flat lowland areas, with water that is frequently colored by sediment and organic matter. These classifications overlap with the geological definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-spined Blackfish
The two-spined blackfish (''Gadopsis bispinosus'') is a species of temperate perch endemic to Australia. It is found in the cool, clear, strong-flowing, cobble bottomed, sub-alpine rivers and streams (ranging from small to large) in the southeast corner of the Murray- Darling river system. Their range encompasses northeast Victoria, southeast New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory. Originally two-spined blackfish co-inhabited many of these waters with Macquarie perch and trout cod. Two-spined blackfish are similar in shape and appearance to river blackfish, though their spiny dorsal fin usually contain only two spines (hence their scientific name) in comparison to river blackfish which have 7 to 13 distinguishable spines in their spiny dorsal fin. (In reality, this is a rather academic point as two-spined blackfish have blurred the difference between the dorsal spines and the dorsal rays that make up their soft dorsal fin, and any distinctions between the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |