|
Machia Biological Park
Machia Biological Park (also known as Machia Safari Park) is a zoological garden and wildlife conservation facility located near Kaylana Lake, approximately 7–8 km west of Jodhpur in Rajasthan, India. Established on 41 hectares of protected forest land, the park opened to the public on 20 January 2016. It was developed as a modern satellite zoo to replace the older heritage zoo in Umaid Garden, which had become obsolete and had lost recognition from the Central Zoo Authority of India, Central Zoo Authority. Construction cost approximately ₹32.4 crore and took around six years to complete. The park is managed by the Rajasthan Forest Department as part of its wildlife conservation and public education mandate. History and establishment The idea of creating a zoological park near Jodhpur was first proposed in 1982–83, when a portion of the Machia Forest Block was earmarked for development. In 1990, 604 hectares of this forest area were declared protected under the Rajasth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and Jodhpur division. It is the historic capital of the Kingdom of Marwar, founded in 1459 by Rao Jodha, a Rajput chief of the Rathore clan. On 11 August 1947, 4 days prior to the Indian independence, Maharaja Hanwant Singh the last ruler of Jodhpur state signed the Instrument of Accession and merged his state in Union of India. On 30 March 1949, it became part of the newly formed state of Rajasthan, which was created after merging the states of the erstwhile Rajputana. Jodhpur is a famous tourist spot with a palace, fort, and temples, set in the stark landscape of the Thar Desert. It is also known as the 'Blue City' due to the dominant color scheme of its buildings in the old town. The old city circles the Mehrangarh Fort and is bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Tiger
The Bengal tiger is a population of the ''Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies and the nominate tiger subspecies. It ranks among the largest wild cats alive today. It is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late Pleistocene for about 12,000 to 16,500 years. Its historical range covered the Indus River valley until the early 19th century, almost all of India, southern Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan and southwestern China. Today, it inhabits India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and southwestern China. It is threatened by poaching, habitat loss and habitat fragmentation. As of 2022, the Bengal tiger population was estimated at 3,167–3,682 individuals in India, 316–355 individuals in Nepal, 131 individuals in Bhutan and around 114 individuals in Bangladesh. Taxonomy ''Felis tigris'' was the scientific name used by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 for the tiger. It was subordinated to the genus ''Panthera'' by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1929. Bengal is the traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-footed Fox
The white-footed fox (''Vulpes vulpes pusilla''), also known as the desert fox, is a small, Asiatic subspecies of red fox which occurs throughout most of northwestern Indian subcontinent, Pakistan's desert districts from Rawalpindi to Rajasthan and Kutch in India, Baluchistan, southern Iran, and Iraq. It is mostly found on sand-hills or in the broad sandy beds of semi-dry rivers, and only very rarely in fields, and then in the vicinity of sandy tracts. Description Like the Turkmenian fox, the white-footed fox has a primitive, infantile skull compared to those of its northern cousins. It is smaller than the Afghan red fox and Hill foxes, and never exhibits a red phase in its winter coat, nor the silvery, hoary phase of the Afghan red fox. It closely resembles the unrelated Bengal fox in size, but is distinguished by its longer tail and hind feet. As adults, their pelts are easily distinguished from other subspecies by the presence of a very distinct pale patch on each sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Fox
The Bengal fox (''Vulpes bengalensis''), also known as the Indian fox, is a fox endemic to the Indian subcontinent from the Himalayan foothills and Terai of Nepal through southern India, and from southern and eastern Pakistan to eastern India and southeastern Bangladesh. Appearance ''Vulpes bengalensis'' is a relatively small fox with an elongated muzzle, long, pointed ears, and a long, bushy tail. The pelage ranges in color from buff to silver-gray with an overall grizzled effect; the dorsal pelage is mostly grayish and paler ventrally. The legs tend to be brownish or rufous, and the underparts light, a pale sand or ginger shade. The Bengal fox is more daintily built than the red fox (''V. vulpes''), and can readily be recognized by its bushy, black-tipped tail, which is around 50–60% of the length of the head and body. The backs of the ears are dark brown with a black margin, and white inside. The ears have the same colour as the nape or maybe darker, but not having a dark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called the common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Eurasia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy yellow in summer to a dark tawny beige in winter. It is smaller and has shorter legs, a shorter tail, a more elongated torso, a less-prominent forehead, and a narrower and more pointed muzzle than the Arabian wolf. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List due to its widespread distribution and high density in areas with plenty of available food and optimum shelter. Despite its name, the golden jackal is not closely related to the African black-backed jackal or side-striped jackal, which are part of the genus '' Lupulella''. It is instead closer to wolves and coyotes. The ancestor of the golden jackal is believed to be the extinct Arno river dog that lived in southern Europe . It is described as having been a small, jackal-like canine. Genetic studies indicate that the golden jackal expande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Wolf
The Indian wolf (''Canis lupus pallipes'') is a subspecies of gray wolf that ranges from Southwest Asia to the Indian subcontinent. It is intermediate in size between the Himalayan wolf and the Arabian wolf, and lacks the former's luxuriant winter coat due to it living in warmer conditions. Within this subspecies, the "Indian plains wolf" is genetically basal to all other extant ''Canis lupus'' apart from the older-lineage Himalayan wolf, with both proposed as separate species. The Indian wolf travels in smaller packs and is less vocal than other variants of the gray wolf, and has a reputation for being cunning. The Indian wolf is one of the most endangered populations of gray wolf in the world. Taxonomy The Indian wolf was first described to Western science in 1831 by the British ornithologist William Henry Sykes under the binomial ''Canis pallipes''. In 1941, Reginald Pocock subordinated it to ''Canis lupus'' under the trinomial ''Canis lupus pallipes''. Pocock, R. I. (1941)' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
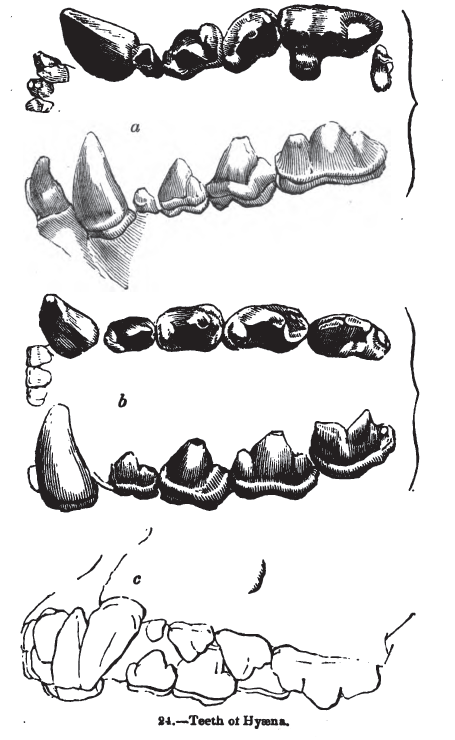
Striped Hyena
The striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena'') is a species of hyena native to North and East Africa, the Middle East, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Hyaena''. It is listed by the IUCN as near-threatened, as the global population is estimated to be under 10,000 mature individuals which continues to experience deliberate and incidental persecution along with a decrease in its prey base such that it may come close to meeting a continuing decline of 10% over the next three generations. It is the smallest of the bone-cracking hyenas and retains many primitive viverrid-like characteristics lost in larger species, having a smaller and less specialised skull. Though primarily a scavenger, large specimens have been known to kill their own prey, and attacks on humans have occurred in rare instances. The striped hyena is a monogamous animal, with both males and females assisting one another in raising their cubs. A nocturnal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
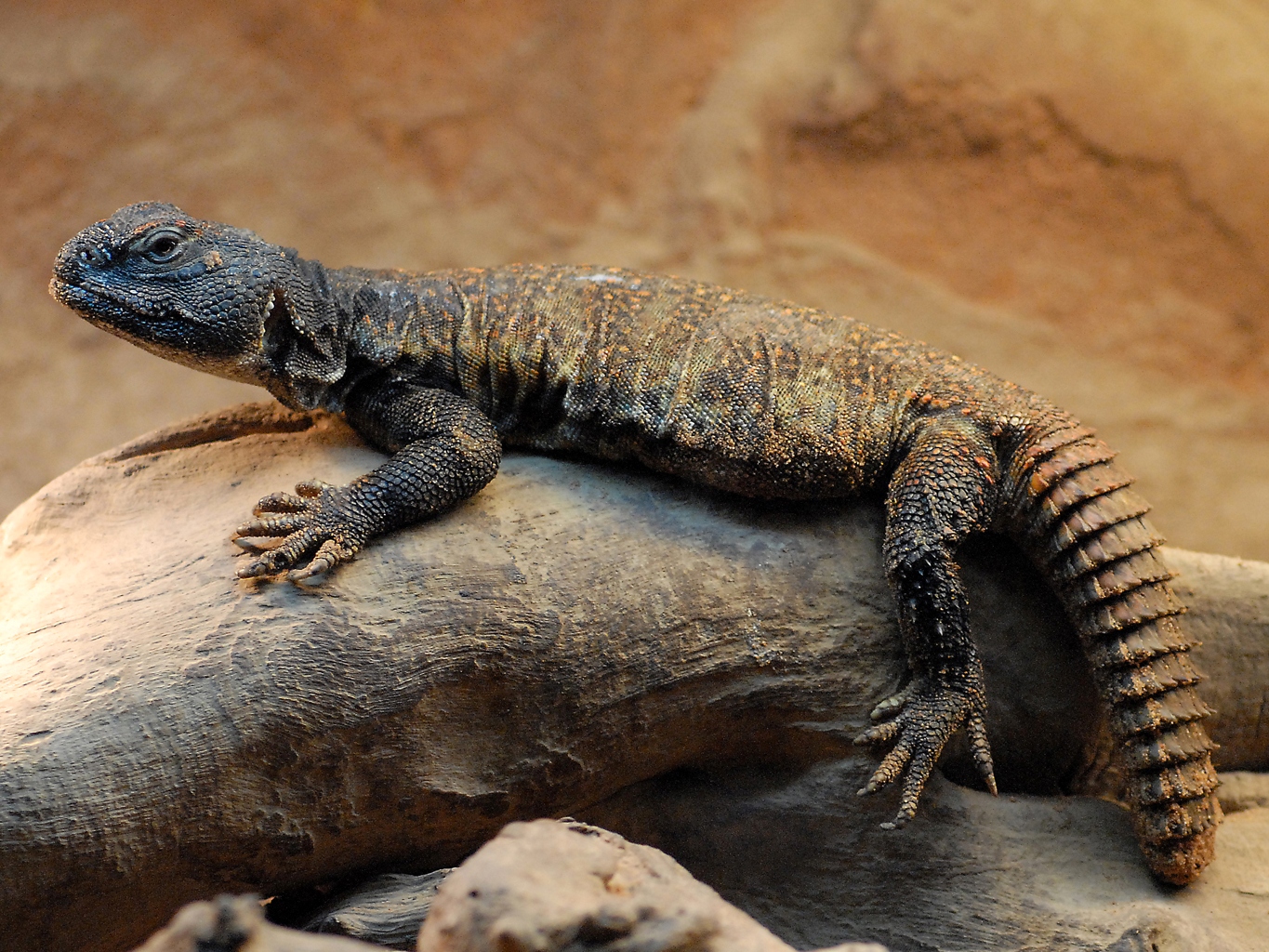
Spiny-tailed Lizard
''Uromastyx'' is a genus of lizards in the Family (biology), family Agamidae. The genus is native to Africa and the Middle East (West Asia). Member species are Common name, commonly called spiny-tailed lizards, uromastyces, mastigures, or dabb lizards. Lizards in the genus ''Uromastyx'' are primarily herbivorous, but occasionally eat insects and other small animals, especially young lizards. They spend most of their waking hours basking in the sun, hiding in underground chambers at night time or when danger appears. They tend to establish themselves in hilly, rocky areas with good shelter and accessible vegetation. Taxonomy The genus, generic name ''Uromastyx'' is derived from the Ancient Greek words ''ourá'' (οὐρά) meaning "tail" and ''-mastix'' (μάστιξ) meaning "whip" or "scourge", after the thick-spiked tail characteristic of all ''Uromastyx'' species. Species The following species are in the genus ''Uromastyx''.. www.reptile-database.org. Three addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor Lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and West African Nile monitor, one species is also found in south America as an invasive species. About 80 species are recognized. Monitor lizards have long necks, powerful tails and claws, and well-developed limbs. The adult length of extant species ranges from in some species such as ''Dampier Peninsula monitor, Varanus sparnus'', to over in the case of the Komodo dragon, though the extinct megalania (''Varanus priscus'') may have reached lengths of more than . Most monitor species are terrestrial locomotion, terrestrial, but many are also arboreal or semiaquatic. While most monitor lizards are carnivorous, eating smaller reptiles, fish, birds, insects, small mammals, and eggs, a few species also eat fruit and vegetation. Etymology The genus, generic name ''Varanus'' is derived from the Arabic (language), Arabic word ''waral'' [St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gharial
The gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus''), also known as gavial or fish-eating crocodile, is a crocodilian in the family (biology), family Gavialidae and among the longest of all living crocodilians. Mature females are long, and males . Adult males have a distinct boss at the end of the snout, which resembles an earthenware pot known as a ''ghara'', hence the name "gharial". The gharial is well adapted to catching fish because of its long, narrow snout and 110 sharp, interlocking teeth. The gharial probably evolved in the northern Indian subcontinent. Fossil gharial remains were excavated in Pliocene deposits in the Sivalik Hills and the Narmada River valley. It currently inhabits rivers in the plains of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. It is the most thoroughly aquatic crocodilian, and leaves the water only for basking and building nests on moist sandbanks. Adults mate at the end of the cold season. Females congregate in spring to dig nests, in which they lay 20–95 e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mugger Crocodile
The mugger crocodile (''Crocodylus palustris'') is a medium-sized broad-snouted crocodile, also known as mugger and marsh crocodile. It is native to freshwater habitats from south-eastern Iran to the Indian subcontinent, where it inhabits marshes, lakes, rivers and artificial ponds. It rarely reaches a body length of and is a powerful swimmer, but also walks on land in search of suitable waterbodies during the hot season. Both young and adult mugger crocodiles dig burrows to which they retreat when the ambient temperature drops below or exceeds . Females dig holes in the sand as nesting sites and lay up to 46 eggs during the dry season. The sex of hatchlings depends on temperature during incubation. Both parents protect the young for up to one year. They feed on insects, and adults prey on fish, reptiles, birds and mammals. The mugger crocodile evolved at least and has been a symbol for the fructifying and destructive powers of the rivers since the Vedic period. It was fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is a medium-sized antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources. It stands up to high at the shoulder. Males weigh , with an average of . Females are lighter, weighing or on average. Males have long corkscrew Horn (anatomy), horns, and females occasionally develop horns, as well. The white fur on the chin and around the eyes is in sharp contrast with the black stripes on the face. Both sexes' coats feature a two-tone colouration; in males, the majority of the body is dark brown to black, with white circles around the eyes, white ears and tail, and the belly, lower jaw, and inner legs also white. Females and juveniles are yellowish-fawn to tan and display the same white areas, only with more of a beige tone than the males. Females also feature a more pronounced horizontal white side-stripe, starting around the shoulder and ending a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |