|
Macedonian Kings
Macedonia, also called Macedon, was ruled continuously by kings from its inception around the middle of the seventh century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 168 BC. Kingship in Macedonia, its earliest attested political institution, was hereditary, exclusively male, and characterized by dynastic politics. Information regarding the origins of the Argeads, Macedonia's founding dynasty, is very scarce and often contradictory. The Argeads themselves claimed descent from the royal house of Argos, the Temenids, but this story is viewed with skepticism by some scholars as a fifth century BC fiction invented by the Argead court "to 'prove' Greek lineage". It is more likely that the Argeads first surfaced either as part of a tribe living near Mount Bermion who, possibly under the authority of Perdiccas, subjugated neighboring or, according to Herodotus, were of a Doric race that originally resided in Pindus.Herodotus. ''Histories'', 1.56.2–3. During their reign, Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vergina Sun
The Vergina Sun (), also known as the Star of Vergina, Vergina Star or Argead Star, is a rayed solar symbol first appearing in ancient Greek art of the period between the 6th and 2nd centuries BC. The Vergina Sun proper has sixteen triangular rays, while comparable symbols of the same period variously have sixteen, twelve, eight or (rarely) six rays. The name "Vergina Sun" became widely used after the archaeological excavations in and around the small town of Vergina, in northern Greece, during the late 1970s. In older references, the name "Argead Star" or "Star of the Argeadai" is used for the Sun as the possible royal symbol of the Argead dynasty of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia. There it was depicted on a golden larnax found in a 4th-century BC royal tomb belonging to either Philip II or Philip III of Macedon, the father and half-brother of Alexander the Great, respectively. Tentatively interpreted as the historical royal symbol of ancient Macedonia, rather than just a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perdiccas I Of Macedon
Perdiccas I (; ) was king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. By allowing thirty years for the span of an average generation from the beginning of Archelaus' reign in 413 BC, British historian Nicholas Hammond estimated that Perdiccas ruled around 653 BC. There are two separate historical traditions describing the foundation of the Argead dynasty. The earlier, documented by Herodotus and Thucydides in the fifth century BC, records Perdiccas as the first king of Macedonia. The later tradition first emerged sometime at the beginning of the fourth century BC and claimed that Caranus, rather than Perdiccas, was the founder.Greenwalt, William (1985).The Introduction of Caranus into the Argead King List. ''Greek, Roman, and Byzantine Studies''. 26 (1): 43–49. Aside from Satyrus, who adds Coenus and Tyrimmas to the list, Marsyas of Pella, Theopompos, and Justin all agree that Caranus was Perdiccas' father.Sprawski, Sławomir (2010). "The Early Temenid Kings to Alexander I" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhus Of Epirus
Pyrrhus ( ; ; 319/318–272 BC) was a Greeks, Greek king and wikt:statesman, statesman of the Hellenistic period.Plutarch. ''Parallel Lives'',Pyrrhus... He was king of the Molossians, of the royal Aeacidae, Aeacid house, and later he became king (John Malalas, Malalas also called him toparch) of Epirus (ancient state), Epirus. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Roman Republic, Rome, and had been regarded as one of the greatest generals of antiquity. Several of his victorious battles caused him unacceptably heavy losses, from which the phrase "Pyrrhic victory" was coined. Pyrrhus became king of Epirus in 306 BC at the age of 13, but was dethroned by Cassander four years later. He saw action during the Wars of the Diadochi and regained his throne in 297 BC with the support of Ptolemy I Soter. During the eponymous Pyrrhic War of 280–275 BC, Pyrrhus fought Rome at the behest of Taranto, Tarentum, scoring costly victories at Battle of Heraclea, Heraclea and Battle of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
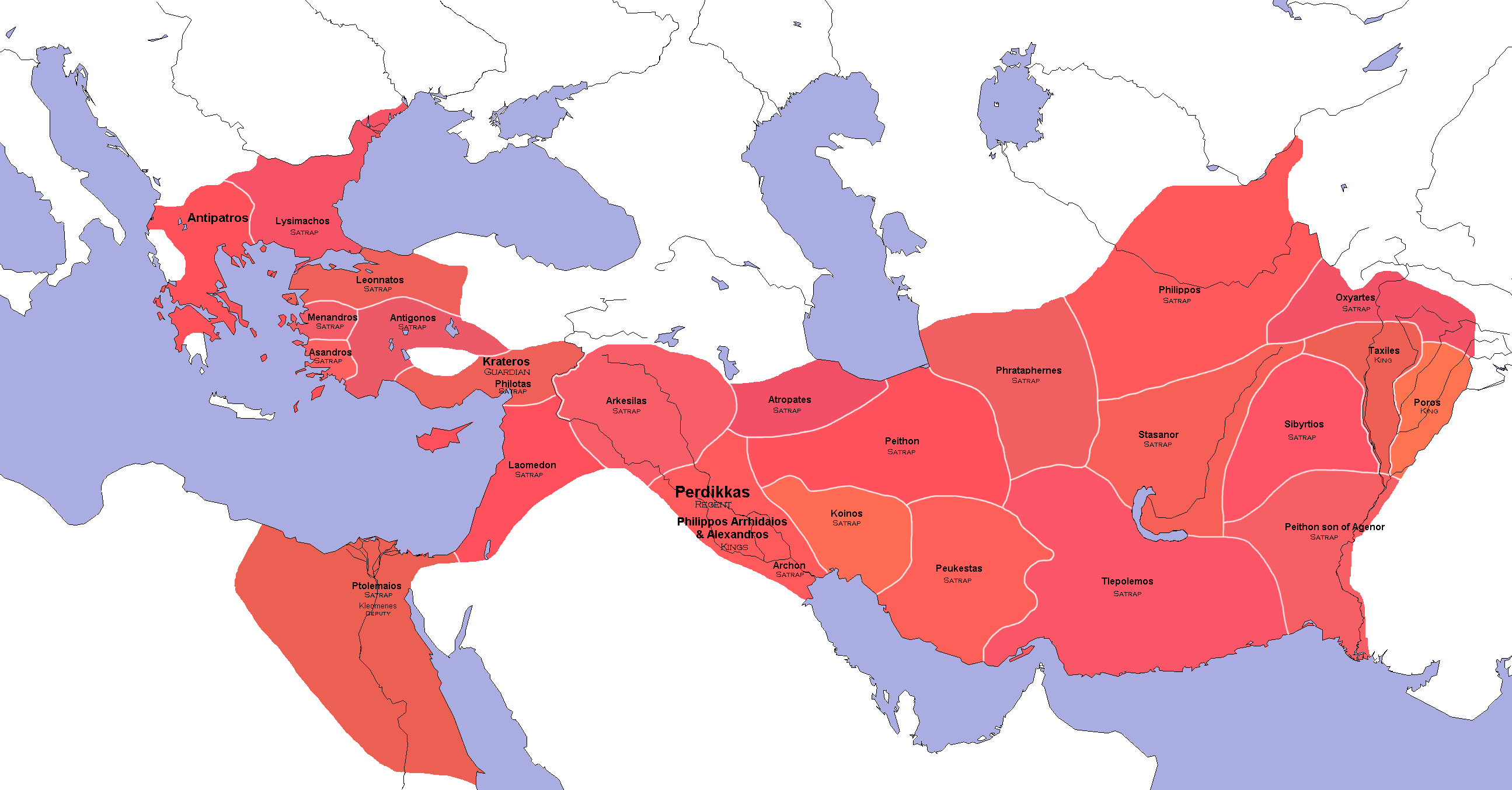
Diadochi
The Diadochi were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indus River Valley. The most notable Diadochi include Ptolemy I Soter, Ptolemy, Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Antigonus, Cassander, and Seleucus I Nicator, Seleucus as the last remaining at the end of the Wars of the Diadochi, Wars of the Successors, ruling in Egypt, Anatolia, Asia-Minor, Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon and Achaemenid Empire, Persia respectively, all forging dynasties lasting several centuries. Background Ancient role In ancient Greek, is a noun (substantive or adjective) formed from the verb, ''diadechesthai'', "succeed to," a compound of ''dia-'' and ''dechesthai'', "receive." The word-set descends straightforwardly from Proto-Indo-European language, Indo-European *dek-, "receive", the substantive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipatrid Dynasty
The Antipatrid dynasty (; ) was a Dorian Greek dynasty of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon founded by Cassander, the son of Antipater, who declared himself King of Macedon in 305 BC. This dynasty did not last long; in 294 BC it was swiftly overthrown by the Antigonid dynasty. Members of the Antipatrid dynasty: *Antipater, regent, not king *Cassander Cassander (; ; 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and '' de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death. A son of Antipater and a contemporary of Alexander the ... (305–297 BC) * Philip IV of Macedon (297 BC) * Alexander V of Macedon (297–294 BC) * Antipater I (296–294 BC) * Antipater II Etesias (279 BC) Family tree of Antipatrids See also * History of Macedonia (ancient kingdom) * Government of Macedonia (ancient kingdom) References External links List of the Kings of Macedonia {{Royal houses of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassander
Cassander (; ; 355 BC – 297 BC) was king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 305 BC until 297 BC, and '' de facto'' ruler of southern Greece from 317 BC until his death. A son of Antipater and a contemporary of Alexander the Great, Cassander was one of the Diadochi who warred over Alexander's empire following the latter's death in 323 BC. Cassander later seized power by having Alexander's son and heir Alexander IV murdered. While governing Macedonia from 317 BC until 297 BC, Cassander focused on strengthening the northern borders and economic development, while founding or restoring several cities (including Thessalonica, Cassandreia, and Thebes); however, his ruthlessness in dealing with political enemies complicates assessments of his rule.Beckett, ''Universal Biography'', Vol. 1, p. 688 Early history In his youth, Cassander was taught by the philosopher Aristotle at the Lyceum in Macedonia. He was educated alongside Alexander the Great in a group that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander IV Of Macedon
Alexander IV (Greek: ; August 323 BC – Late summer 309 BC), sometimes erroneously called Aegus in modern times, was the posthumous son of Alexander the Great (Alexander III of Macedon) by his wife Roxana of Bactria. As his father's only surviving legitimate child, Alexander IV inherited the throne of the Macedonian Empire after him, however he was murdered in his early teens, never wielding actual power. Birth Alexander IV was the son of Alexander the Great (a Macedonian Greek) and Alexander's wife Roxana (a Sogdian). He was their second child together and the only one to survive infancy. Because Roxana was pregnant when Alexander the Great died on 11 June 323 BC and the sex of the baby was unknown, there was dissension in the Macedonian army regarding the order of succession. While the infantry supported Alexander the Great's half-brother Philip III (who had some unknown cognitive disability present throughout his life), the chiliarch Perdiccas, commander of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wars Of The Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi (, Romanization of Greek, romanized: ', ''War of the Crown Princes'') or Wars of Alexander's Successors were a series of conflicts fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule his Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Empire, empire following his death. The fighting occurred between 322 and 281 BC. Background Alexander the Great died on June 10, 323 BC, leaving behind an empire that stretched from Macedon and the rest of Hellenistic Greece, Greece in Europe to the Indus valley in South Asia. The empire had no clear successor, with the Argead dynasty, Argead family, at this point, consisting of Alexander's mentally disabled half-brother, Philip III of Macedon, Arrhidaeus; his unborn son Alexander IV of Macedon, Alexander IV; his reputed illegitimate son Heracles, son of Alexander, Heracles; his mother Olympias; his sister Cleopatra of Macedon, Cleopatra; and his half-sisters Thessalonike of Macedon, Thessalonike and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Of Alexander The Great
The death of Alexander the Great and subsequent related events have been the subjects of debates. According to a Babylonian astronomical diaries, Babylonian astronomical diary, Alexander died in the palace of Nebuchadnezzar II in Babylon between the evening of 10 June and the evening of 11 June 323 BC, at the age of 32. Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians and local residents wept at the news of the death, while Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid subjects were forced to shave their heads. The mother of Darius III, Sisygambis, having learned of Alexander's death, became depressed and killed herself later. Historians vary in their assessments of primary sources about Alexander's death, which has resulted in different views about its cause and circumstances. Background In February 323 BC, Alexander ordered his armies to prepare for the march to Babylon. According to Arrian, after crossing the Tigris Alexander was met by Chaldeans, who advised him not to enter the city because their deit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histories (Herodotus)
The ''Histories'' (, ''Historíai''; also known as ''The History'') of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre and study of history in the Western world (despite the existence of historical records and chronicles beforehand). ''The'' ''Histories'' also stands as one of the earliest accounts of the rise of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Empire, as well as the events and causes of the Greco-Persian Wars between the Persian Empire and the Polis, Greek city-states in the 5th century BC. Herodotus portrays the conflict as one between the forces of slavery (the Persians) on the one hand, and freedom (the Athenians and the confederacy of Greek city-states which united against the invaders) on the other. ''The Histories'' was at some point divided into the nine scroll, books that appear in modern editions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |