|
Mablethorpe 1888
Mablethorpe is a seaside town in the civil parish of Mablethorpe and Sutton, in the East Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England.OS Explorer map 283:Louth and Mablethorpe: (1:25 000): In 1961 the civil parish had a population of 3,611. On 1 April 1974 the parish was changed to form "Mablethorpe and Sutton". The population including nearby Sutton-on-Sea was 12,531 at the 2011 census and estimated at 12,633 in 2019. The town was visited regularly by Alfred, Lord Tennyson, a 19th-century Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom. Some town features have been named after him, such as Tennyson Road and the now closed Tennyson High School. History Roman Empire A hoard of Roman treasure was found in Mablethorpe in the 1980s, as were a Roman brooch and pottery. Mablethorpe Hall Mablethorpe has existed as a town for many centuries, gaining its market town charter in 1253. Coastal erosion means some of it was lost to the sea in the 1540s. Records of the Fitzwilliam family of Mablethorpe Hall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary's Church, Mablethorpe
St Mary's Church is an active Anglican parish church in Mablethorpe, Lincolnshire, England. Built in the early 14th century, it was renovated with additions in 1714, and in 1976 it was extensively rebuilt. In 1966 the church was designated a grade II listed building. History In 1300 Sir Roger de Montalt donated the land for the church and paid for the original arcade of the nave, octagonal piers and double-chamfered arches. The nave was rebuilt in 1714 and in 1976. In 1978 the arches of the nave were timber struts fortified with the old piers left in place. In the church a communion rail dates to 1714. It features a set of turned baluster altar rails. Located at the junction of Church Road and Church Lane it is the town's parish church. On 31 May 1966 it was designated a grade II listed building. In 1976 G.R.A. Mack of Louth rebuilt the majority of the church. The 1976 British Isles heat wave caused the clay bed to shrink and cracks developed on the structure. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, which for centuries were the principal unit of secular and religious administration in most of England and Wales. Civil and religious parishes were formally split into two types in the 19th century and are now entirely separate. Civil parishes in their modern form came into being through the Local Government Act 1894 ( 56 & 57 Vict. c. 73), which established elected parish councils to take on the secular functions of the parish vestry. A civil parish can range in size from a sparsely populated rural area with fewer than a hundred inhabitants, to a large town with a population in excess of 100,000. This scope is similar to that of municipalities in continental Europe, such as the communes of France. However, unlike their continental Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ted Lewis (writer)
Alfred Edward Lewis (15 January 1940 – 27 March 1982) was a British writer known for his crime fiction. Early life Alfred Edward Lewis was born in Stretford, Manchester and was an only child. In 1946, the family moved to Barton-upon-Humber in Lincolnshire. As a child, Lewis contracted rheumatic fever and spent almost a year away from school in bed rest. During that time he read books and comics and drew constantly. From a young age he was a fan of film, particularly Western epics, B-movies and gangster pictures. He had a strict upbringing and his parents did not want their son to go to art school, but his English teacher Henry Treece, recognising his creative talents in writing and art, persuaded them not to stand in his way. Lewis attended Hull Art School for four years. Career Lewis moved to London in 1961 with £70 he earned from his first illustration commission, the Alan Delgado children's book, ''The Hot Water Bottle Mystery''. His first work in London was in adver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sons And Lovers
''Sons and Lovers'' is a 1913 novel by the English writer D. H. Lawrence. It traces emotional conflicts through the protagonist, Paul Morel, and his suffocating relationships with a demanding mother and two very different lovers, which exert complex influences on the development of his manhood. The novel was originally published by Gerald Duckworth and Company Ltd., London, and Mitchell Kennerley Publishers, New York. While the novel initially received a lukewarm critical reception, along with allegations of obscenity, it is today regarded as a masterpiece by many critics and is often regarded as Lawrence's finest achievement. It tells us more about Lawrence's life and his phases, as his first was when he lost his mother in 1910 to whom he was particularly attached. And it was from then that he met Frieda Richthofen, and around this time that he began conceiving his two other great novels, ''The Rainbow'' and ''Women in Love'', which had more sexual emphasis and maturity. Deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
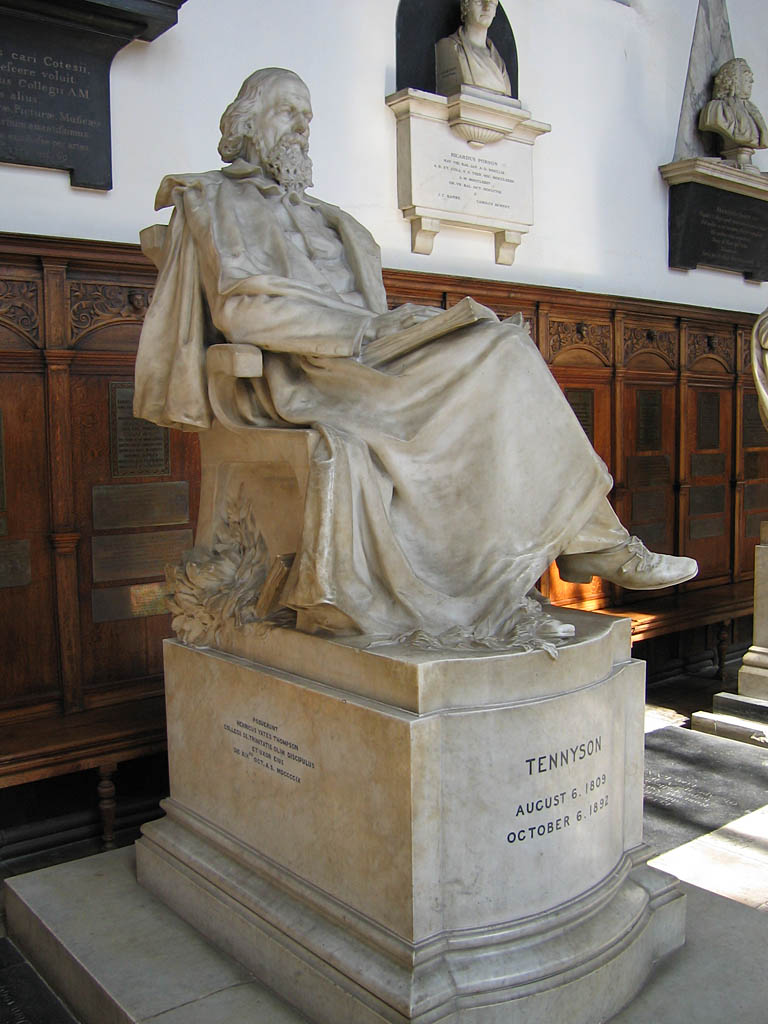
Alfred Tennyson
Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson (; 6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was an English poet. He was the Poet Laureate during much of Queen Victoria's reign. In 1829, Tennyson was awarded the Chancellor's Gold Medal at Cambridge for one of his first pieces, "Timbuktu". He published his first solo collection of poems, '' Poems, Chiefly Lyrical'', in 1830. " Claribel" and " Mariana", which remain some of Tennyson's most celebrated poems, were included in this volume. Although described by some critics as overly sentimental, his poems ultimately proved popular and brought Tennyson to the attention of well-known writers of the day, including Samuel Taylor Coleridge. Tennyson's early poetry, with its medievalism and powerful visual imagery, was a major influence on the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. Tennyson also focused on short lyrics, such as " Break, Break, Break", " The Charge of the Light Brigade", " Tears, Idle Tears", and " Crossing the Bar". Much of his verse was based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea Flood Of 1953
The 1953 North Sea flood () was a major flood caused by a heavy storm surge that struck the Netherlands, north-west Belgium, England and Scotland. Most sea defences facing the surge were overwhelmed, resulting in extensive flooding. The storm and flooding occurred during the night of Saturday, 31 January to the morning of 1 February 1953. A combination of a high spring tide and a severe European windstorm caused a storm tide of the North Sea. The combination of wind, high tide, and low pressure caused the sea to flood land up to above mean sea level. Realising that such infrequent events could reoccur, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom carried out large studies on strengthening of coastal defences. The Netherlands developed the Delta Works, an extensive system of dams and storm surge barriers. The UK constructed storm surge barriers on the Thames Estuary and on the Hull where it meets the Humber Estuary. Flooding summary At the time of the flood, 20% of the lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-class Lifeboat (IB1)
The D-class (IB1) lifeboats are inflatable boats serving in the RNLI inshore lifeboat (ILB) fleet as well as a number of Independent Lifeboats around the UK and Ireland. Although they are known as the "IB1" at times, they are the latest development of the D-class lifeboat and as such are mainly referred to as a "D-class". This class of lifeboat is one of the smallest operated by the RNLI, and they are a common sight at lifeboat stations round the coast. Unlike other members of the ILB fleet, the D-class (IB1) does not have a rigid hull. All others with the exception of the Arancia, hovercraft A hovercraft (: hovercraft), also known as an air-cushion vehicle or ACV, is an amphibious craft capable of travelling over land, water, mud, ice, and various other surfaces. Hovercraft use blowers to produce a large volume of air below the ... and all-weather lifeboat tenders are rigid inflatable boats. The IB1 normally has a crew of three or four and is primarily used for sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifeboat (rescue)
A rescue lifeboat is a boat rescue craft which is used to attend a vessel in distress, or its survivors, to rescue crew and passengers. It can be hand pulled, sail powered or powered by an engine. Lifeboats may be rigid, Inflatable boat, inflatable or rigid-inflatable combination-hulled vessels. Overview There are generally three types of boat, in-land (used on lakes and rivers), in-shore (used closer to shore) and off-shore (into deeper waters and further out to sea). A rescue lifeboat is a boat designed with specialised features for searching for, rescuing and saving the lives of people in peril at sea or other large bodies of water. In the United Kingdom and Ireland rescue lifeboats are typically vessels crewed by volunteers, intended for quick dispatch, launch and transit to reach a ship or individuals in trouble at sea. Off-shore boats are referred to as 'All-weather' and generally have a range of 150–250 nautical miles. Characteristics such as capability to withstand he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
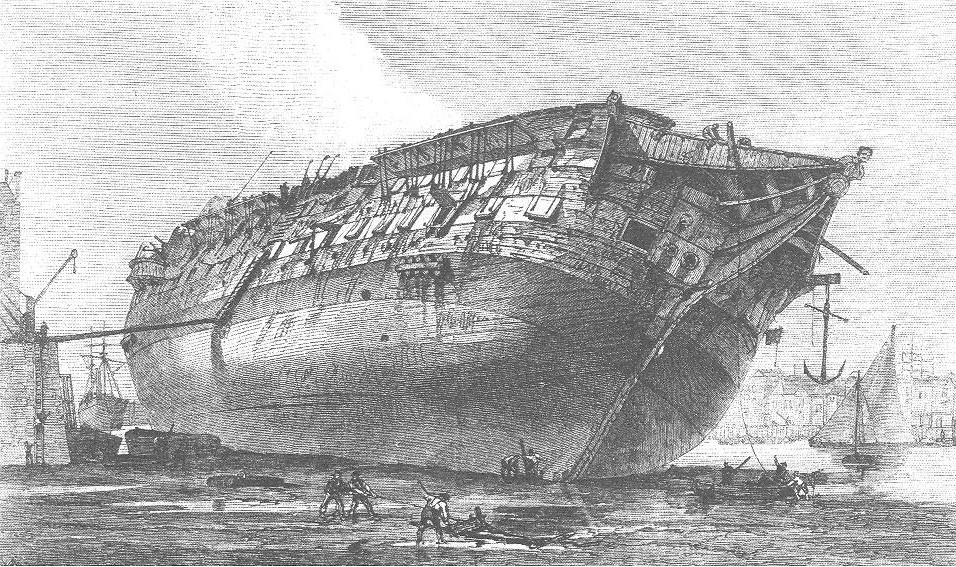
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, Fatigue (material), metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about its use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of Wind wave, waves, Ocean current, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landward retreat of the shoreline can be measured and described over a temporal scale of tides, seasons, and other short-term cyclic processes. Coastal erosion may be caused by hydraulic action, abrasion (geology), abrasion, impact and corrosion by wind and water, and other forces, natural or unnatural. On non-rocky coasts, coastal erosion results in rock formations in areas where the coastline contains rock layers or fracture zones with varying resistance to erosion. Softer areas become eroded much faster than harder ones, which typically result in landforms such as tunnels, bridges, columns, and Column, pillars. Over time the coast generally evens out. The softer areas fill up with sediment eroded from hard areas, and roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |