|
MW 50
MW 50 (Methanol-''Wasser'' 50) was a 50-50 mixture of methanol and water (German: ''Wasser'') that was often sprayed into the supercharger of World War II aircraft engines primarily for its anti-detonation effect, allowing the use of increased boost pressures. Secondary effects were cooling of the engine and charge cooling. Higher boost was only effective at altitudes below the full-throttle height, where the supercharger could still provide additional boost pressure that was otherwise wasted, while the smaller secondary effects were useful even above that altitude. Composition MW 50 is something of a misnomer, as it is actually a mixture of three fluids: 50% methanol acting primarily to achieve optimum anti-detonant effect, secondarily as an anti-freeze; 49.5% water; and 0.5% ''Schutzöl'' 39, an oil-based anti-corrosion additive. The similar MW 30 increased the water to 69.5% and decreased methanol to 30%.Bridgeman 1989, p. 296. This increased the cooling performance but made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, Volatility (chemistry), volatile, colorless and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol), but is more acutely toxic than the latter. Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced through destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl ''tert''-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and Navigation, marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to Calibration, calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead a long-term average of tide gauge readings at a particular reference location. The term ''above sea level'' generally refers to the height above mean sea level (AMSL). The term APSL means above present sea level, comparing sea levels in the past with the level today. Earth's radius at sea level is 6,378.137 km (3,963.191 mi) at the equator. It is 6,356.752 km (3,94 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Emergency Power
War emergency power (WEP) is a throttle setting that was first present on some American World War II military aircraft engines. For use in emergency situations, it produced more than 100% of the engine's normal rated power for a limited amount of time, often about five minutes. Similar systems used by non-US forces are now often referred to as WEP as well, although they may not have been at the time, as with the German Luftwaffe's ''Notleistung'' and Soviet VVS' ''forsazh'' systems. WEP in World War II aircraft Maximum normal power would be limited by a mechanical stop, for instance a wire across the throttle lever slot. A more forceful push would break the wire, allowing extra power. In normal service, the P-51H Mustang was rated at , but WEP would deliver up to , an increase of 61%. In the P-51D Mustang, the model most produced and used during World War II, the WEP increased engine power from , over 15%. The Vought F4U Corsair, not originally equipped for WEP, later boas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Injection (engines)
In internal combustion engines, water injection, also known as anti-detonant injection (ADI), can spray water into the incoming air or fuel- air mixture, or directly into the combustion chamber to cool certain parts of the induction system where "hot points" could produce premature ignition. In jet engines — particularly early turbojets or engines in which it is not practical or desirable to have an afterburner — water injection may be used to increase engine thrust, particularly at low-altitudes and at takeoff. Water injection was used historically to increase the power output of military aviation engines for short durations, such as during aerial combat or takeoff. However it has also been used in motor sports and notably in drag racing. In Otto cycle engines, the cooling effect of water injection also enables greater compression ratios by reducing engine knocking (detonation). Alternatively, this reduction in engine knocking in Otto cycle engines means that some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless Flammability#Definitions, non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful Oxidising agent, oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen. Nitrous oxide has significant Nitrous oxide (medication), medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its Anesthesia, anaesthetic and Analgesic, pain-reducing effects, and it is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Its colloquial name, "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, describes the Euphoria, euphoric effects upon inhaling it, which cause it to be used as a recreational drug inducing a brief "Dissociative, high". When abused chronically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GM-1
GM-1 (''Göring Mischung'' 1) was a system for injecting nitrous oxide into aircraft engines that was used by the ''Luftwaffe'' in World War II. This increased the amount of oxygen in the fuel mixture, and thereby improved high-altitude performance. GM-1 was used on several modifications of existing fighter designs to counter the increasing performance of Allied fighters at higher altitudes. A different system for low-altitude boost known as MW 50 was also used, although GM-1 and MW 50 were rarely used on the same engine. MW-50 injected a methanol-water mixture into the cylinders to cool the mix. Cooling causes the air to become denser, therefore allowing more air into each cylinder for a given volume. This is the same principle that intercoolers use. GM-1 was developed in 1940 by Otto Lutz to improve high-altitude performance.Douglas, pp. 157, 160–161 It could be used by fighters, destroyers, bombers and reconnaissance aircraft, though its first use was in the Bf 109E/Z fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers Jumo 213
The Junkers Jumo 213 was a World War II-era V12 engine, V-12 liquid-cooled aircraft engine, a development of Junkers Motoren's earlier design, the Junkers Jumo 211, Jumo 211. The design added two features, a pressurized cooling system that required considerably less cooling fluid which allowed the engine to be built smaller and lighter, and a number of improvements that allowed it to run at higher RPM. These changes boosted power by over 500 hp and made the 213 one of the most sought-after Axis powers, Axis engine designs in the late-war era. Design and development When the Jumo 211 entered production in the late 1930s it used an unpressurized liquid cooling system based on an "open cycle". Water was pumped through the engine to keep it cool, but the system operated at atmospheric pressure, or only slightly higher. Since the boiling point of water decreases with altitude (pressure) this meant that the temperature of the cooling water had to be kept quite low to avoid boiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Bf 109
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 is a monoplane fighter aircraft that was designed and initially produced by the Nazi Germany, German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt#History, Bayerische Flugzeugwerke (BFW). Together with the Focke-Wulf Fw 190, the Bf 109 formed the backbone of the ''Luftwaffe's'' fighter force during the World War II. It was commonly called the Me 109 by Allied aircrew and some German aces/pilots, even though this was not the official model designation. The Bf 109 was designed by Willy Messerschmitt and Robert Lusser, who worked at BFW during the early to mid-1930s. It was conceived as an interceptor aircraft, interceptor. However, later models were developed to fulfill multiple tasks, serving as Escort fighter, bomber escort, fighter-bomber, day fighter, day-, night fighter, night-, all-weather fighter, ground-attack aircraft, and aerial reconnaissance aircraft. It was one of the most advanced fighters when the fighter first appeared, being furnished with an all-me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interceptor Aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are capable of being or are employed as both "standard" air superiority fighters and as interceptors are sometimes known as fighter-interceptors. In the post-World War 2 jet age, there are two general classes of interceptor: light fighters, designed for high performance over short range; and heavy fighters, which are intended to operate over longer ranges, in contested airspace and adverse meteorological conditions. While the second type was exemplified historically by specialized night fighter and all-weather interceptor designs, the integration of mid-air refueling, satellite navigation, on-board radar, and beyond visual range (BVR) missile systems since the 1960s has allowed most frontline fighter designs to fill the roles once reserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Emergency Power
War emergency power (WEP) is a throttle setting that was first present on some American World War II military aircraft engines. For use in emergency situations, it produced more than 100% of the engine's normal rated power for a limited amount of time, often about five minutes. Similar systems used by non-US forces are now often referred to as WEP as well, although they may not have been at the time, as with the German Luftwaffe's ''Notleistung'' and Soviet VVS' ''forsazh'' systems. WEP in World War II aircraft Maximum normal power would be limited by a mechanical stop, for instance a wire across the throttle lever slot. A more forceful push would break the wire, allowing extra power. In normal service, the P-51H Mustang was rated at , but WEP would deliver up to , an increase of 61%. In the P-51D Mustang, the model most produced and used during World War II, the WEP increased engine power from , over 15%. The Vought F4U Corsair, not originally equipped for WEP, later boas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
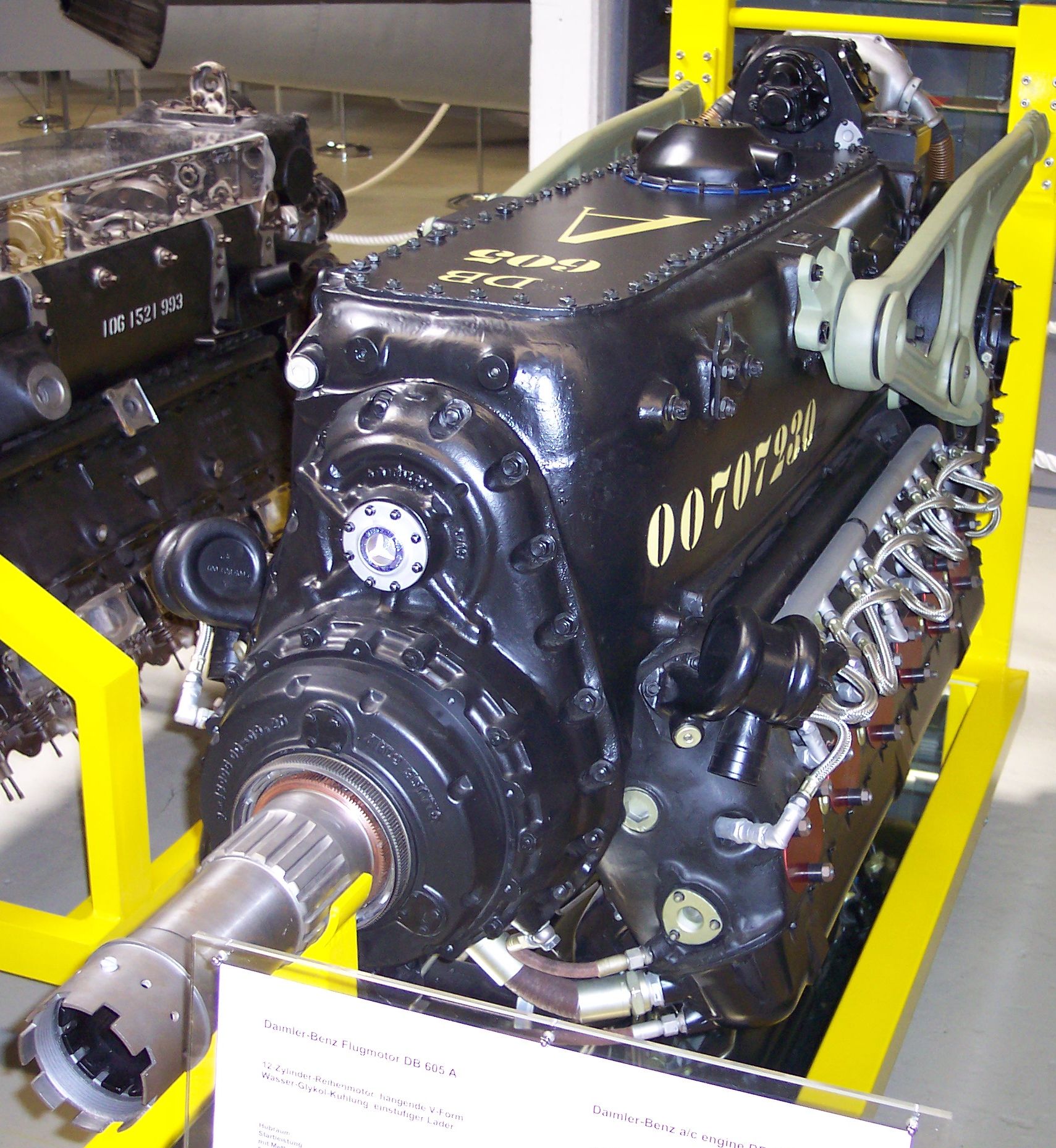
DB 605
The Daimler-Benz DB 605 is a German aircraft engine built during World War II. Developed from the DB 601, the DB 605 was used from 1942 to 1945 in the Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighter, and the Bf 110 and Me 210C heavy fighters. The DB 610, a pair of DB 605s geared to turn a single output shaft that replaced the similar DB 606, was used in the A-3 and all A-5 variants of Germany's only operational heavy bomber, the Heinkel He 177A. License-built versions of the DB 605 were used in the Macchi C.205, Fiat G.55, Reggiane 2005 and some other Italian aircraft. It was also used in the Swedish SAAB B 18B and initially in the pusher-design SAAB J 21. Approximately 42,400 DB 605s of all kinds were built. Design and development The primary differences between the 605 and 601 were greater displacement, higher revolutions, higher compression ratio and a more powerful supercharger. Engineers determined that the cylinders could be bored out to a larger diameter without seriously affectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |