|
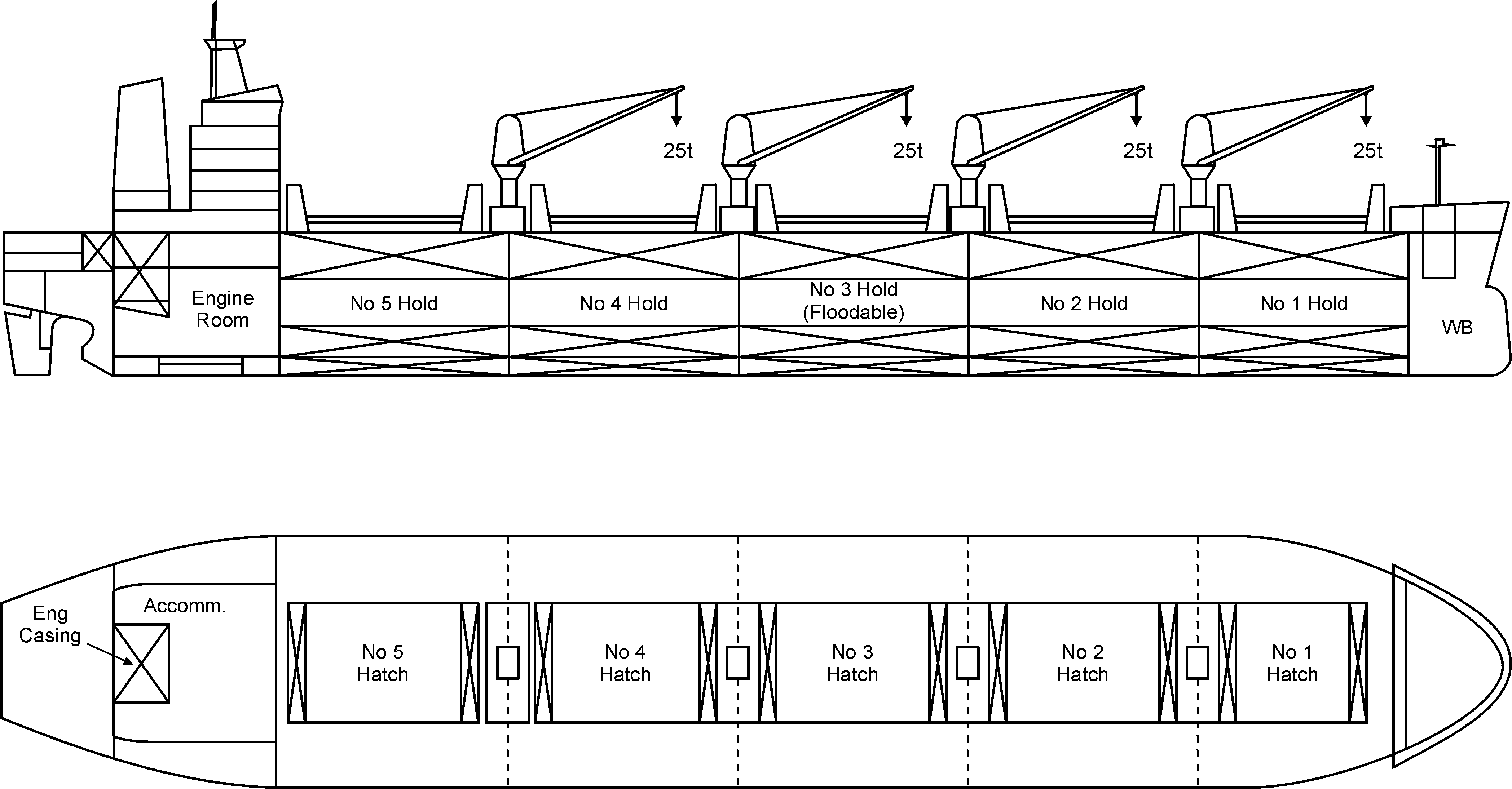
MV Protektor
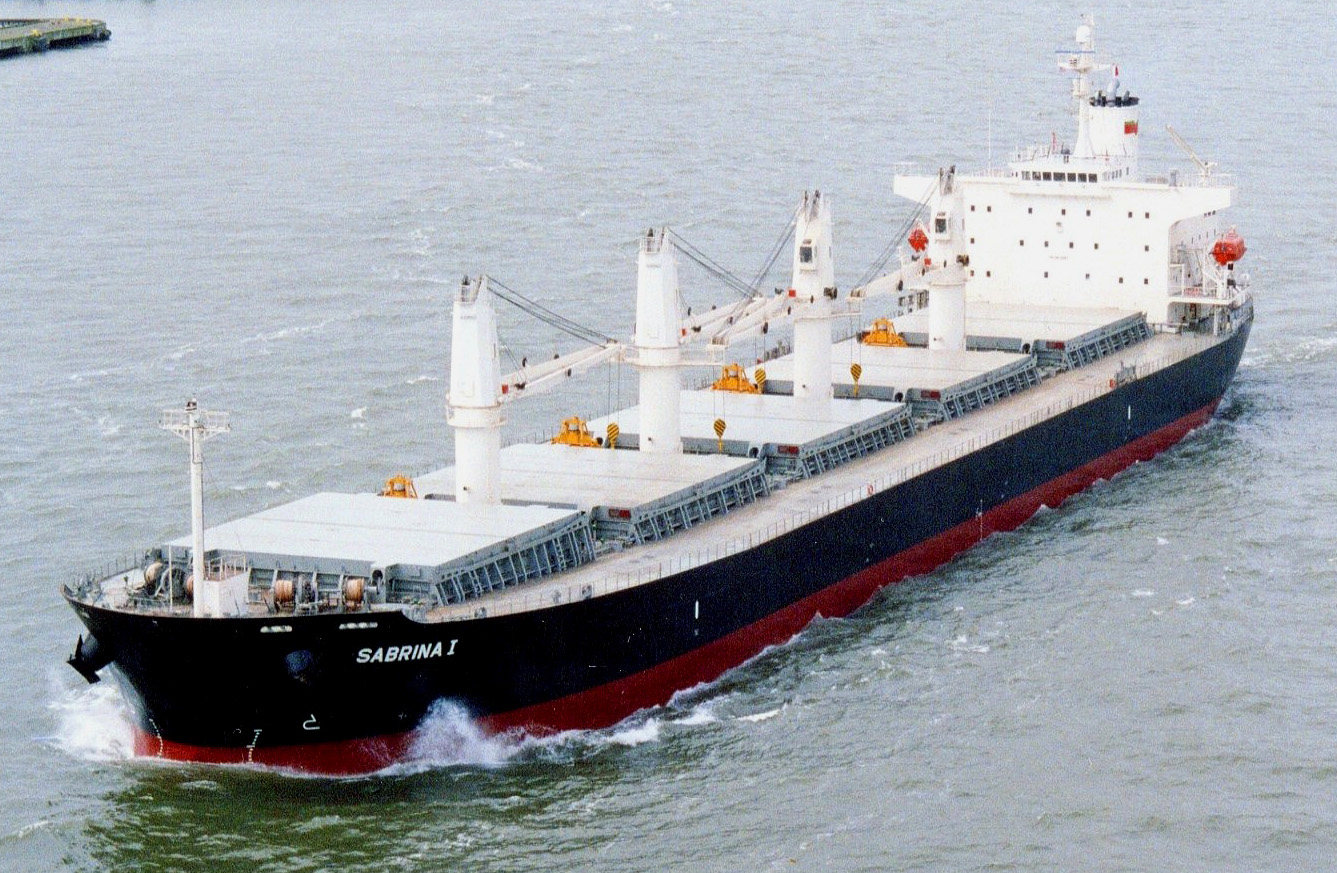
MV ''Protektor'' was a bulk cargo ship that sank in the North Atlantic Ocean in January 1991 with the loss of her entire crew. ''Protektor'' was built by Flender Werke in Lübeck, Germany. She was launched on 17 December 1966 and delivered on 22 March 1967, bearing the name ''Ursula Schulte'' and sailing under the German flag. In 1978, she was renamed ''Protektor'', and was registered in Singapore at the time of her loss. She had a gross tonnage of 43,218 GT and a deadweight tonnage of 78,918 DWT, and measured in length, with a beam of . She was powered by a single diesel engine that gave her a speed of . In January 1991, ''Protektor'' was sailing eastbound from Port-Cartier, Quebec to Oxelösund, Sweden with a cargo of iron ore when she ran into a severe winter storm about southeast of Newfoundland. Early on the morning of 13 January, the crew made a distress call indicating that the ship's cargo hold had been breached and she was taking on water, leading the crew to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Carrier
A bulk carrier or bulker is a merchant ship specially designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo — such as grains, coal, ore, steel coils, and cement — in its cargo holds. Since the first specialized bulk carrier was built in 1852, economic forces have led to continued development of these ships, resulting in increased size and sophistication. Today's bulk carriers are specially designed to maximize capacity, safety, efficiency, and durability. Today, bulk carriers make up 21 percent of the world's merchant fleets, and they range in size from single-hold mini-bulk carriers to mammoth ore ships able to carry 400,000 metric tons of deadweight (DWT). A number of specialized designs exist: some can unload their own cargo, some depend on port facilities for unloading, and some even package the cargo as it is loaded. Over half of all bulk carriers have Greek, Japanese, or Chinese owners, and more than a quarter are registered in Panama. South Korea is the largest sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flender Werke
Flender Werke was a German shipbuilding company, located in Lübeck. It was founded in 1917 as a branch of Brückenbau Flender AG of Benrath on the Rhine. In 1926 it was made a fully independent business and renamed Lübecker Flenderwerke AG. It went on to become one of the largest shipyards in Germany, building nearly 700 ships in all. During World War II, Flender Werke built 2 Type II and 40 Type VII U-boats for the Kriegsmarine. After the war, Flender Werke continued to build merchant ships, and in 1973 were renamed Flender Werft AG. In 2002 they were forced to close because of insolvency In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company (debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be ''insolvent''. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet in .... References External links * Shipbuilding companies of Germany Manufacturing companies established in 1917 Defunct companies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, after its capital of Kiel, and is the 35th-largest city in Germany. The city lies in Holstein, northeast of Hamburg, on the mouth of the River Trave, which flows into the Bay of Lübeck in the borough of Travemünde, and on the Trave's tributary Wakenitz. The city is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, and is the southwesternmost city on the Baltic, as well as the closest point of access to the Baltic from Hamburg. The port of Lübeck is the second-largest German Baltic port after the port of Rostock. The city lies in the Northern Low Saxon dialect area of Low German. Lübeck is famous for having been the cradle and the ''de facto'' capital of the Hanseatic League. Its city centre is Germany's most e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Tonnage
Gross tonnage (GT, G.T. or gt) is a nonlinear measure of a ship's overall internal volume. Gross tonnage is different from gross register tonnage. Neither gross tonnage nor gross register tonnage should be confused with measures of mass or weight such as deadweight tonnage or displacement. Gross tonnage, along with net tonnage, was defined by the ''International Convention on Tonnage Measurement of Ships, 1969'', adopted by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) in 1969, and came into force on 18 July 1982. These two measurements replaced gross register tonnage (GRT) and net register tonnage (NRT). Gross tonnage is calculated based on "the moulded volume of all enclosed spaces of the ship" and is used to determine things such as a ship's manning regulations, safety rules, registration fees, and port dues, whereas the older gross register tonnage is a measure of the volume of only certain enclosed spaces. History The International Convention on Tonnage Measurement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadweight Tonnage
Deadweight tonnage (also known as deadweight; abbreviated to DWT, D.W.T., d.w.t., or dwt) or tons deadweight (DWT) is a measure of how much weight a ship can carry. It is the sum of the weights of cargo, fuel, fresh water, ballast water, provisions, passengers, and crew. DWT is often used to specify a ship's maximum permissible deadweight (i.e. when it is fully loaded so that its Plimsoll line is at water level), although it may also denote the actual DWT of a ship not loaded to capacity. Definition Deadweight tonnage is a measure of a vessel's weight carrying capacity, not including the empty weight of the ship. It is distinct from the displacement (weight of water displaced), which includes the ship's own weight, or the volumetric measures of gross tonnage or net tonnage (and the legacy measures gross register tonnage and net register tonnage). Deadweight tonnage was historically expressed in long tonsOne long ton (LT) is but is now usually given internationally i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port-Cartier
Port-Cartier is a city in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It is located on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River at the mouth of the Aux-Rochers River, exactly southwest of Sept-Îles, Quebec. Port-Cartier had a population of 6,651 at the 2011 Canadian census. It has a land area of , ranking 27th in area among all Canadian cities and towns. Besides Port-Cartier itself, the communities of Rivière-Pentecôte () and Pointe-aux-Anglais are also within its municipal boundaries, all located along Quebec Route 138. History In 1915, Colonel Robert R. McCormick, owner of the Chicago Tribune, visited the Rochers River area to evaluate its forest potential. Soon after, a settlement was established on the west side of the mouth of this river, originally called Shelter Bay. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxelösund
Oxelösund is a locality and the seat of Oxelösund Municipality in Södermanland County, Sweden with 11,488 inhabitants in 2018. It is located less than south from the city centre of its larger neighbour Nyköping, with the two urban areas forming a wider agglomeration of nearly 50,000 people. History The harbour at Oxelösund has been used for at least 500 years. In the 19th century, an increased extraction from the mining district of Central Sweden (e.g. ''Bergslagen''), made Oxelösund a harbour of transport. A local railroad company was established in 1873, and bought virtually the entire peninsula which at the time belonged to the estates of the Stjärnholm Castle. An iron works was constructed in 1913, and the community Oxelösund expanded, with the harbour, rail road and iron works being its cornerstones. In 1950, the city was sufficiently developed to get the title of a city and was one of the last towns to receive city status in Sweden. Since 1971 this status is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Air Force
The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF; french: Aviation royale canadienne, ARC) is the air and space force of Canada. Its role is to "provide the Canadian Forces with relevant, responsive and effective airpower". The RCAF is one of three environmental commands within the unified Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2020, the Royal Canadian Air Force consists of 12,074 Regular Force and 1,969 Primary Reserve personnel, supported by 1,518 civilians, and operates 258 manned aircraft and nine unmanned aerial vehicles. Lieutenant-General Eric Kenny is the current commander of the Royal Canadian Air Force and chief of the Air Force Staff. The Royal Canadian Air Force is responsible for all aircraft operations of the Canadian Forces, enforcing the security of Canada's airspace and providing aircraft to support the missions of the Royal Canadian Navy and the Canadian Army. The RCAF is a partner with the United States Air Force in protecting continental airspace under the North American Aerospace D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Incidents In 1991
Maritime may refer to: Geography * Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps * Maritime Region, a region in Togo * Maritime Southeast Asia * The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island * Maritime County, former county of Poland, existing from 1927 to 1939, and from 1945 to 1951 * Neustadt District, Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, known from 1939 to 1942 as ''Maritime District'', a former district of Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Nazi Germany, from 1939 to 1945 * The Maritime Republics, thalassocratic city-states on the Italian peninsula during the Middle Ages Museums * Maritime Museum (Belize) * Maritime Museum (Macau), China * Maritime Museum (Malaysia) * Maritime Museum (Stockholm), Sweden Music * ''Maritime'' (album), a 2005 album by Minotaur Shock * Maritime (band), an American indie pop group * "The Maritimes" (song), a song on the 2005 album ''Boy-Cott-In the Industry'' by Classified * " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1966 Ships
Events January * January 1 – In a coup, Colonel Jean-Bédel Bokassa takes over as military ruler of the Central African Republic, ousting President David Dacko. * January 3 – 1966 Upper Voltan coup d'état: President Maurice Yaméogo is deposed by a military coup in the Republic of Upper Volta (modern-day Burkina Faso). * January 10 ** Pakistani–Indian peace negotiations end successfully with the signing of the Tashkent Declaration, a day before the sudden death of Indian prime minister Lal Bahadur Shastri. ** The House of Representatives of the US state of Georgia refuses to allow African-American representative Julian Bond to take his seat, because of his anti-war stance. ** A Commonwealth Prime Ministers' Conference convenes in Lagos, Nigeria, primarily to discuss Rhodesia. * January 12 – United States President Lyndon Johnson states that the United States should stay in South Vietnam until Communist aggression there is ended. * January 15 – 1966 Nigerian coup d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Carriers
A bulk carrier or bulker is a merchant ship specially designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo — such as grains, coal, ore, steel coils, and cement — in its cargo holds. Since the first specialized bulk carrier was built in 1852, economic forces have led to continued development of these ships, resulting in increased size and sophistication. Today's bulk carriers are specially designed to maximize capacity, safety, efficiency, and durability. Today, bulk carriers make up 21 percent of the world's merchant fleets, and they range in size from single-hold mini-bulk carriers to mammoth ore ships able to carry 400,000 metric tons of deadweight (DWT). A number of specialized designs exist: some can unload their own cargo, some depend on port facilities for unloading, and some even package the cargo as it is loaded. Over half of all bulk carriers have Greek, Japanese, or Chinese owners, and more than a quarter are registered in Panama. South Korea is the largest singl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |