|
MP4
MP4 (formally MPEG-4 Part 14), is a digital multimedia container format most commonly used to store video and audio, but it can also be used to store other data such as subtitles and still images. Like most modern container formats, it allows streaming over the Internet. The only filename extension for MPEG-4 Part 14 files as defined by the specification is .mp4. MPEG-4 Part 14 is a standard specified as a part of the MPEG-4 specifications, formally as ISO/ IEC 14496-14:2003. Unlike the audio-only compression formats MP3 and MP2, MP4 is a container format that can hold various types of media from various codecs. During the 2000s, portable media players were sometimes erroneously advertised as "MP4 players", even if they may play a different format like AMV video and not necessarily the MPEG-4 Part 14 format. Data streams Most kinds of data can be embedded in MPEG-4 Part 14 files through ''private streams''. A separate hint track is used to include streaming information in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 Part 12
The ISO base media file format (ISOBMFF) is a container file format that defines a general structure for files that contain time-based multimedia data such as video and audio. It is standardized in ISO/ IEC 14496-12, a.k.a. MPEG-4 Part 12, and was formerly also published as ISO/IEC 15444-12, a.k.a. JPEG 2000 Part 12. It is designed as a flexible, extensible format that facilitates interchange, management, editing and presentation of the media. The presentation may be local, or via a network or other stream delivery mechanism. The file format is designed to be independent of any particular network protocol while enabling support for them in general. The format has become very widely used for media file storage and as the basis for various other media file formats (e.g. the MP4 and 3GP container formats), and its widespread use was recognized by a Technology & Engineering Emmy Award presented on 4 November 2021 by the National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Media Player
A portable media player (PMP) or digital audio player (DAP) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. Normally they refer to small, Electric battery, battery-powered devices utilising flash memory or a Hard disk drive, hard disk for storing various media Computer file, files. MP3 players has been a popular alternative name used for such devices, even if they also support other file formats and media types other than MP3 (for example Advanced Audio Coding, AAC, FLAC, Windows Media Audio, WMA). Generally speaking, PMPs are equipped with a 3.5 mm headphone jack which can be used for headphones or to connect to a boombox, home audio system, or connect to car audio and home High fidelity, stereos wired or via a wireless connection such as Bluetooth, and some may include radio tuners, voice recording and other features. In contrast, analogue portable audio players play music from non-digital m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickTime File Format
QuickTime File Format (QTFF) is a computer file format used natively by the QuickTime framework. Design The format specifies a multimedia container file that contains one or more tracks, each of which stores a particular type of data: audio, video, or text (e.g. for subtitles). Each track either contains a digitally-encoded media stream (using a specific format) or a data reference to the media stream located in another file. Tracks are maintained in a hierarchical data structure consisting of objects called atoms. An atom can be a parent to other atoms or it can contain media or edit data, but it is not supposed to do both. The ability to contain abstract data references for the media data, and the separation of the media data from the media offsets and the track edit lists means that QuickTime is particularly suited for editing, as it is capable of importing and editing in place (without data copying). Other later-developed media container formats such as Microsoft's Adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. It was developed by Dolby, AT&T, Fraunhofer and Sony, originally as part of the MPEG-2 specification but later improved under MPEG-4.ISO (2006ISO/IEC 13818-7:2006 – Information technology — Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information — Part 7: Advanced Audio Coding (AAC), Retrieved on 2009-08-06ISO (2006, Retrieved on 2009-08-06 AAC was designed to be the successor of the MP3 format (MPEG-2 Audio Layer III) and generally achieves higher sound quality than MP3 at the same bit rate. AAC encoded audio files are typically packaged in an MP4 container most commonly using the filename extension .m4a. The basic profile of AAC (both MPEG-4 and MPEG-2) is called AAC-LC (''Low Complexity''). It is widely supported in the industry and has been adopted as the default or standard audio format on products including Apple's iTunes Store, Nintendo's Wii, DSi and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 Part 2
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual (formally International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC 14496-2) is a video encoding specification designed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC family of encoders. It uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous encoders such as MPEG-1#Part 2: Video, MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2. Examples of popular implementations of the encoder specifications include DivX, Xvid and Nero Digital. MPEG-4 Part 2 is H.263 compatible in the sense that a basic H.263 bitstream is correctly decoded by an MPEG-4 Video decoder. (MPEG-4 Video decoder is natively capable of decoding a basic form of H.263.) In MPEG-4 Visual, there are two types of video object layers: the video object layer that provides full MPEG-4 functionality, and a reduced functionality video object layer, the video object layer with short headers (which prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
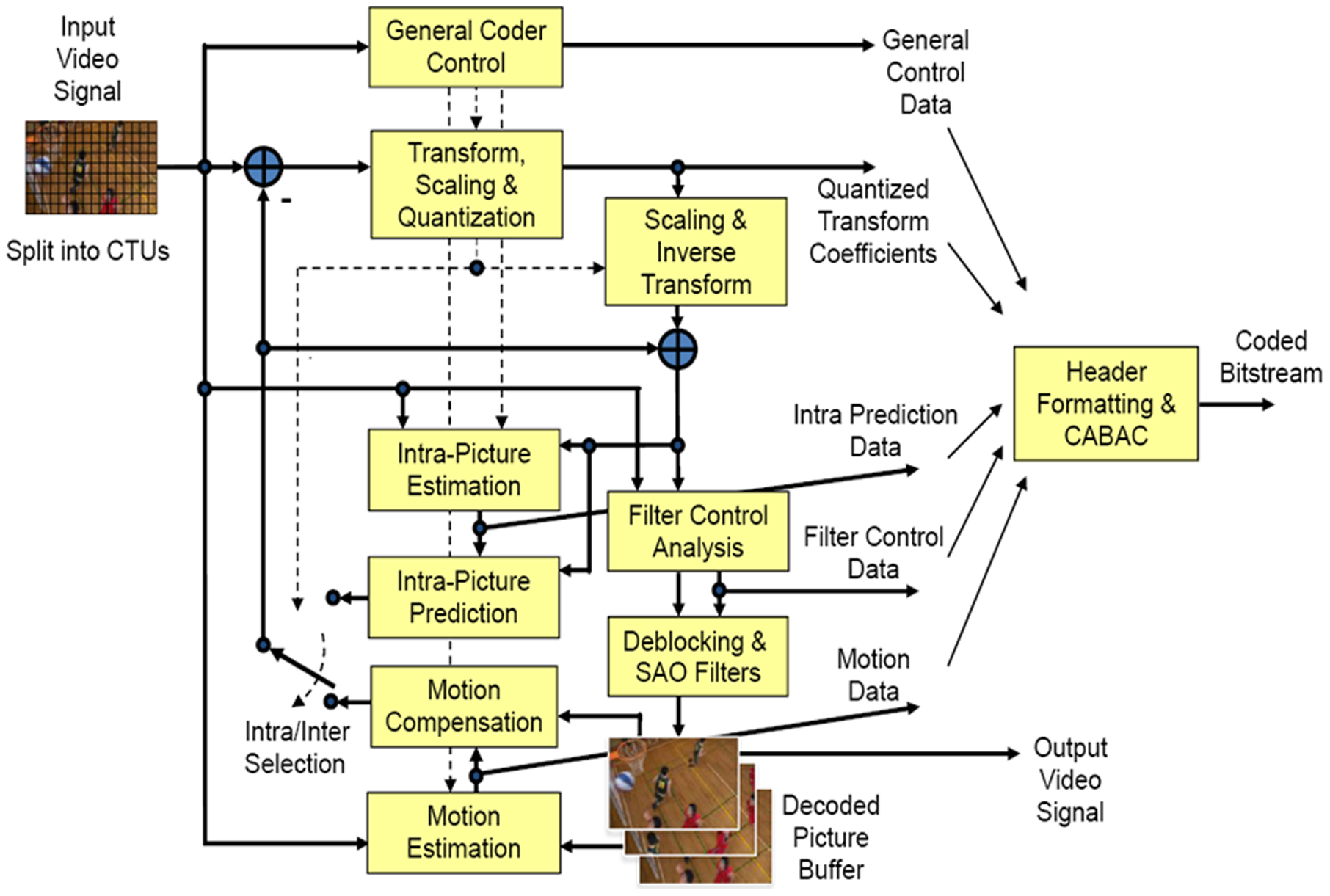
High Efficiency Video Coding
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses both integer DCT and discrete sine transform (DST) with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extension of the concepts in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Both work by comparing different parts of a fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Container Format (digital)
A container format (informally, sometimes called a wrapper) or metafile is a file format that allows multiple data streams to be embedded into a single computer file, file, usually along with metadata for identifying and further detailing those streams. Notable examples of container formats include archive files (such as the ZIP (file format), ZIP format) and formats used for multimedia playback (such as Matroska, MPEG-4 Part 14, MP4, and Audio Video Interleave, AVI). Among the earliest cross-platform container formats were Distinguished Encoding Rules and the 1985 Interchange File Format. Design Although containers may identify how data or metadata is encoded, they do not actually provide instructions about how to decode that data. A Computer program, program that can open a container must also use an appropriate codec to decode its contents. If the program doesn't have the required algorithm, it can't use the contained data. In these cases, programs usually emit an error mess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Lossless Coding
MPEG-4 Audio Lossless Coding, also known as MPEG-4 ALS, is an extension to the MPEG-4 Part 3 audio standard to allow lossless audio compression. The extension was finalized in December 2005 and published as ISO/ IEC 14496-3:2005/Amd 2:2006 in 2006. The latest description of MPEG-4 ALS was published as subpart 11 of the MPEG-4 Audio standard (ISO/IEC 14496-3:2019) (5th edition) in December 2019. MPEG-4 ALS combines a short-term predictor and a long term predictor. The short-term predictor is similar to FLAC in its operation – it is a quantized LPC predictor with a losslessly coded residual using Golomb Rice Coding or Block Gilbert Moore Coding (BGMC). The long term predictor is modeled by 5 long-term weighted residues, each with its own lag (delay). The lag can be hundreds of samples. This predictor improves the compression for sounds with rich harmonics (containing multiples of a single fundamental frequency, locked in phase) present in many musical instruments and human vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4 Part 3
MPEG-4 Part 3 or MPEG-4 Audio (formally ISO/ IEC 14496-3) is the third part of the ISO/ IEC MPEG-4 international standard developed by Moving Picture Experts Group. It specifies audio coding methods. The first version of ISO/IEC 14496-3 was published in 1999. The MPEG-4 Part 3 consists of a variety of audio coding technologies – from lossy speech coding ( HVXC, CELP), general audio coding ( AAC, TwinVQ, BSAC), lossless audio compression (MPEG-4 SLS, Audio Lossless Coding, MPEG-4 DST), a Text-To-Speech Interface (TTSI), Structured Audio (using SAOL, SASL, MIDI) and many additional audio synthesis and coding techniques. MPEG-4 Audio does not target a single application such as real-time telephony or high-quality audio compression. It applies to every application which requires the use of advanced sound compression, synthesis, manipulation, or playback. MPEG-4 Audio is a new type of audio standard that integrates numerous different types of audio coding: natural sound and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Container Format
A container format (informally, sometimes called a wrapper) or metafile is a file format that allows multiple data streams to be embedded into a single file, usually along with metadata for identifying and further detailing those streams. Notable examples of container formats include archive files (such as the ZIP format) and formats used for multimedia playback (such as Matroska, MP4, and AVI). Among the earliest cross-platform container formats were Distinguished Encoding Rules and the 1985 Interchange File Format. Design Although containers may identify how data or metadata is encoded, they do not actually provide instructions about how to decode that data. A program that can open a container must also use an appropriate codec to decode its contents. If the program doesn't have the required algorithm, it can't use the contained data. In these cases, programs usually emit an error message that complains of a missing codec, which users may be able to acquire. Container ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a group of international standards for the compression of digital audio and visual data, multimedia systems, and file storage formats. It was originally introduced in late 1998 as a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) (ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC29/WG11) under the formal standard ISO/IEC 14496 – ''Coding of audio-visual objects''. Uses of MPEG-4 include compression of audiovisual data for Internet video and CD distribution, voice (telephone, videophone) and broadcast television applications. The MPEG-4 standard was developed by a group led by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president) and Fernando Pereira. Background MPEG-4 absorbs many of the features of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 and other related standards, adding new features such as (extended) VRML support for 3D rendering, object-oriented composite files (including audio, video and VRML objects), support for externally specified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
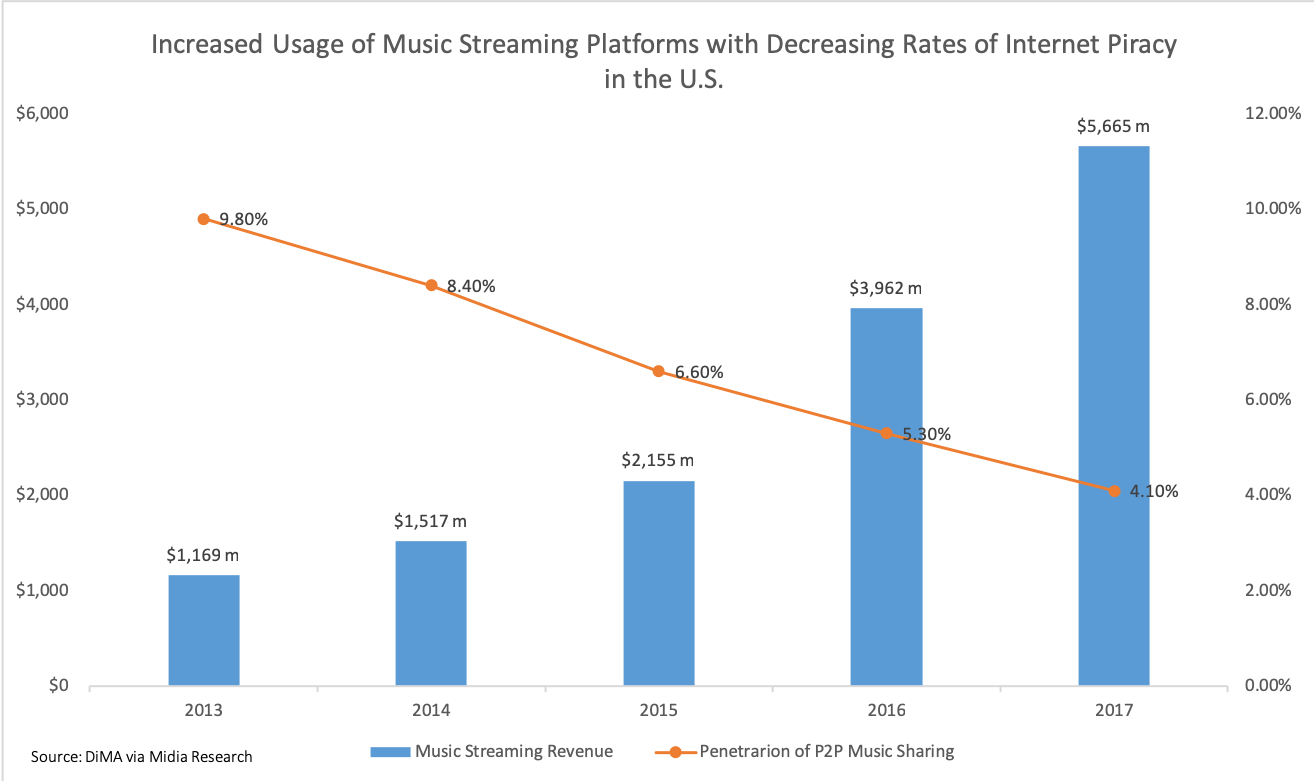
Streaming Media
Streaming media refers to multimedia delivered through a Computer network, network for playback using a Media player (other), media player. Media is transferred in a ''stream'' of Network packet, packets from a Server (computing), server to a client-server model, client and is rendered in real-time; this contrasts with file downloading, a process in which the end-user obtains an entire media file before consuming the content. Streaming is more commonly used for video on demand, streaming television, and music streaming services over the Internet. While streaming is most commonly associated with multimedia from a remote server over the Internet, it also includes offline multimedia between devices on a local area network. For example, using DLNA and a home server, or in a personal area network between two devices using Bluetooth (which uses radio waves rather than Internet Protocol, IP). Online streaming was initially popularized by RealNetworks and Microsoft in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |