|
ML Aviation
ML Aviation was a British aerospace company. Until 1946 it was R Malcolm & Co, taking its new name from the businessman Noel Mobbs and the aircraft designer Marcel Lobelle. R Malcom Co. developed the "Malcolm hood", an improved visibility aircraft canopy for, initially, the Supermarine Spitfire during the war. History The company Wrightson Aircraft Sales was formed in 1934, this became Malcolm and Farquharson in 1936 and a separate company R. Malcom & Co was formed from that. By 1939 Malcolm and Farquharson was a holding company for R. Malcolm which made aircraft components including plywood structures. The company expanded due to increased demand during the Second World War. To accommodate this, a drawing office and experimental works was set up at White Waltham in Berkshire with production activities staying at Slough. In 1943, Mobbs who had bought into R. Malcolm in 1940 took full control of the company with Lobelle, who had left Fairey Aviation Company in 1940 to join R Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slough
Slough () is a town in Berkshire, England, in the Thames Valley, west of central London and north-east of Reading, at the intersection of the M4, M40 and M25 motorways. It is part of the historic county of Buckinghamshire. In 2021, the population of the town was 143,184. The wider Borough of Slough had a population of 158,500. Slough's population is one of the most ethnically diverse in the United Kingdom, attracting people from across the country and the world for labour since the 1920s, which has helped shape it into a major trading centre. In 2017, unemployment stood at 1.4%, one-third the UK average of 4.5%. Slough has the highest concentration of UK HQs of global companies outside London. Slough Trading Estate is the largest industrial estate in single private ownership in Europe, with over 17,000 jobs in 400 businesses. Blackberry, McAfee, Burger King, DHL, Telefonica and Lego have head offices in the town. History The name was first recorded in 1195 as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
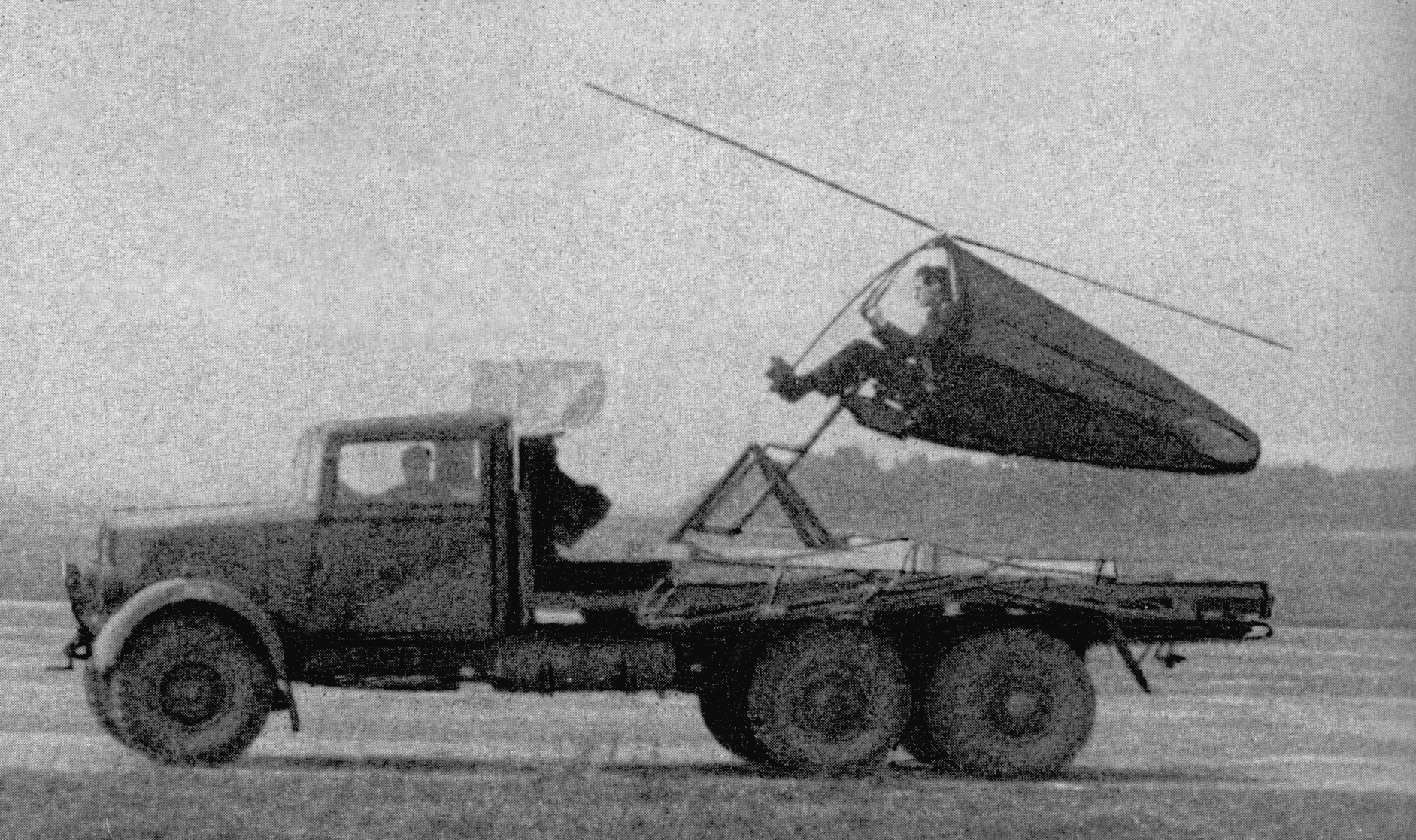
Hafner Rotabuggy
The Hafner Rotabuggy (formally known as the Malcolm Rotaplane and as the "M.L. 10/42 Flying Jeep") was a British experimental aircraft that was essentially a Willys MB combined with a rotor kite, developed with the intention of producing a way of air-dropping off-road vehicles. Design and development It was designed by Raoul Hafner of the Airborne Forces Experimental Establishment (AFEE) after their development of the Rotachute enjoyed some success. The prototype was built by the R. Malcolm & Co. Ltdlater ML Aviation (also producer of the Malcolm hood) at White Waltham in 1942. Air Ministry specification 10/42 for a "Special Rotating Wing Glider" was used to identify the project.Meekcoms/Morgan 1994, p. 306 Initial testing showed that a Willys MB could be dropped from heights up to without damage to the vehicle. A diameter rotor was attached, along with a tail fairing and fins, but no rudders. Two men were required to pilot the aircraft: one to drive it as an aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folland Gnat
The Folland Gnat is a British compact swept-wing subsonic aircraft, subsonic fighter aircraft that was developed and produced by Folland Aircraft. Envisioned as an affordable light fighter in contrast to the rising cost and size of typical combat aircraft, it was procured as a trainer aircraft for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as well as by export customers, who used the Gnat in both combat and training capacities. Designed by W. E. W. Petter, the Gnat has its origins in the preceding private venture Folland Midge. The issuing of Operational Requirement List of Air Ministry specifications#Naval requirement/Aircraft, Naval Staff requirements, OR.303 by the British Air Ministry served to motivate the type's development; the Gnat was later submitted to meet this requirement. Its design allowed for its construction and maintenance tasks to be carried out without specialised tools, making it suitable for use in countries that had not yet become highly industrialisation, industrialised.Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saab AB
Saab AB (originally , , acronym SAAB), with subsidiaries collectively known as the Saab Group (), is a Swedish aerospace and defense company, defence company primarily operating from Sweden. The company is headquartered in Stockholm, but its development and manufacturing operations are undertaken in Linköping. The company was formally founded by AB Bofors in 1937, by reforming the aero engine division of company NOHAB (founded in 1930), located in Trollhättan, into a proper aircraft manufacturer. It would soon merge with aircraft manufacturer AB Svenska Järnvägsverkstädernas Aeroplanavdelning, ASJA (founded in 1931), located in Linköping, in 1940, which had it own design bureau and is considered the spiritual predecessor to today's Saab AB. This formed the SAAB-Concern (business), concern, with the factory in Trollhättan becoming ''SAAB/T'' and the factory in Linköping (previously ASJA) becoming ''SAAB/L'' and design headquarters. From 1947, Saab started producing autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folland
Folland is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Alison Folland Alison Folland (born August 10, 1978) is an American actress and filmmaker. Folland was born in Boston to a travel agent mother and a cardiologist father. She grew up in Wellesley, and attended high school at Buckingham Browne & Nichols, a priv ... (born 1978), American actress and filmmaker * Gerald Folland (born 1947), American mathematician * Henry Folland (1889–1954), British aviation engineer and aircraft designer * Leah Norah Folland (1874–1957), British educationalist, philanthropist and politician * Michael Fleming Folland (1949–1969), United States Army soldier * Neil Folland (born 1960), British cricketer * Nicholas Folland (born 1967), Australian artist and arts educator * Nick Folland (born 1963), British cricketer * Rob Folland (born 1979), British footballer * William H. Folland (c. 1878–1941), associate justice of the Utah Supreme Court See also * * Folland (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevor Sidney Wade
Sqn Ldr Trevor Sidney "Wimpy" Wade, (27 January 1920 – 3 April 1951) was a Royal Air Force (RAF) fighter ace, one of The Few and later a test pilot. He was killed test flying the Hawker P.1081 prototype fighter. Early life Wade was born on 27 January 1920 in Wandsworth, London. He was educated at Yardley Court and Tonbridge School. In April 1938, aged 18, he joined the Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve as an Airman u/t (under training) and learned to fly at No. 19 Elementary and Reserve Flying Training School, Gatwick. He was called to full-time service at the outbreak of war and was commissioned as a Pilot Officer (on probation) on 30 April 1940. Fighter pilot A month later Wade was posted to No. 92 Squadron, part of No. 10 Group RAF and then based at Croydon Airport. On his first day (26 May) he borrowed Tony Bartley's Spitfire to get more flying hours on type, performing a low level roll immediately after takeoff. His nickname "Wimpy" was borrowed from the American ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker P
Hawker or Hawkers may refer to: Places *Hawker, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra *Hawker, South Australia, a town *Division of Hawker, an Electoral Division in South Australia *Hawker Island, Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica *Hawker Creek, Missouri, United States In business * Hawker (trade), a vendor of food or merchandise * Hawker Aircraft, a British aircraft manufacturer * Hawkers (company), a Spanish sunglasses company Other uses * Hawker (surname) * One who practices falconry, hunting with hawks * Hawker College Hawker College is a senior secondary college in Hawker, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Aus ..., a senior secondary college in the Australian Capital Territory * Hawker (dragonfly), a family of dragonflies in North America and Europe {{DEFAULTSORT:Hawker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulton Paul Defiant
The Boulton Paul Defiant is a British interceptor aircraft that served with the Royal Air Force (RAF) during World War II. The Defiant was designed and built by Boulton Paul Aircraft as a "turret fighter" to meet the RAF requirement for day and night fighters that could concentrate their firepower on enemy bombers which were not expected to have fighter escorts due to the distance from Germany to the United Kingdom. The Defiant had all its armament in a dorsal turret offering the ability to fire in most directions. The same principle was used in the Royal Navy's Blackburn Roc which was also built by Boulton Paul. In combat, the Defiant was found to be effective at destroying unescorted bombers, the role it was designed for,Verkaik, 2020 p334 but was vulnerable to the ''Luftwaffe''s more manoeuvrable, single-seat Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighters operating from bases in Northern France, allowing them to escort bombers to London, although with fuel for only ten minutes of flying time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin-Baker
Martin-Baker Aircraft Company Limited is a British manufacturer of ejection seats and safety-related equipment for aviation. The company was originally an aircraft manufacturer before becoming a pioneer in the field of ejection seats. The company's headquarters are in Denham, Buckinghamshire, Higher Denham, Buckinghamshire, England, with other sites in France, Italy and the United States. Martin-Baker supplies ejection seats for 93 air forces worldwide."Martin-Basker: About." ''Martin-Baker.'' Retrieved: 31 October 2012. Martin-Baker seats have been fitted into over 200 fixed-wing and rotary types with the most recent being the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II programme. Martin-Baker claimed in 2022 that since the first live ejection test in 1945, a total of 7,777 lives have been saved by the company's ejection seats. Martin-Baker also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejector Seat
In aircraft, an ejection seat or ejector seat is a system designed to rescue the aircraft pilot, pilot or other aircrew, crew of an aircraft (usually military) in an emergency. In most designs, the seat is propelled out of the aircraft by an explosive charge or rocket motor, carrying the pilot with it. The concept of an ejectable escape crew capsule has also been tried (see B-58 Hustler). Once clear of the aircraft, the ejection seat deploys a parachute. Ejection seats are common on certain types of military aircraft. History A bungee cord, bungee-assisted escape from an aircraft took place in 1910. In 1916, Everard Calthrop, an early inventor of parachutes, patented an ejector seat using compressed air. Compression springs installed under the seat were tested. The modern layout for an ejection seat was first introduced by Romanian inventor Anastase Dragomir in the late 1920s. The design featured a ''parachuted cell'' (a dischargeable chair from an aircraft or other vehicle) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airborne Forces Experimental Establishment
The Airborne Forces Experimental Establishment (AFEE) was a branch of the British Air Ministry, that researched and developed non-traditional airborne applications, such as gliders, rotary wing aircraft, and dropping of personnel and equipment by parachute, in the period 1942–1950. Formation (1942) On 15 February 1942, the Airborne Forces Experimental Establishment was formed as a reorganisation of the Airborne Forces Establishment, that itself was a September 1941 renaming of the Central Landing Establishment. The AFEE was initially based at RAF Ringway as part of No. 70 Group RAF, with two flying units, A Flight and B Flight. At Ringway, one of the existing projects was the Hafner Rotachute, a rotor kite (unpowered autogiro) that was planned to deliver an armed soldier to a battlefield more accurately and reliably than conventional parachute methods. During 1941, unmanned models had already completed ground-based tests plus some releases from aircraft in flight.Sturtivant 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 194. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', p. 10 (27th revised edition) The term derives from the French language verb which means " to feather an arrow". Most aircraft feature an empennage incorporating vertical and horizontal stabilising surfaces which stabilise the flight dynamics of yaw and pitch, as well as housing control surfaces. In spite of effective control surfaces, many early aircraft that lacked a stabilising empennage were virtually unflyable. Even so-called "tailless aircraft" usually have a tail fin (usually a vertical stabiliser). Heavier-than-air aircraft without any kind of empennage (such as the Northrop B-2) are rare, and generally use specially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |