|
MIDI (other)
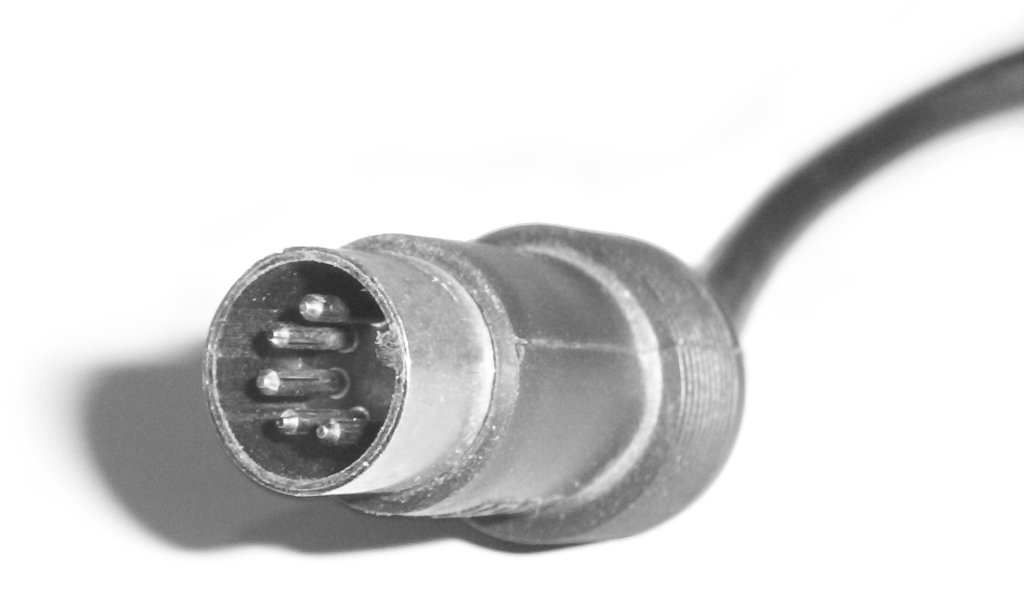
MIDI (; Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music. A single MIDI cable can carry up to sixteen channels of MIDI data, each of which can be routed to a separate device. Each interaction with a key, button, knob or slider is converted into a MIDI event, which specifies musical instructions, such as a note's pitch, timing and loudness. One common MIDI application is to play a MIDI keyboard or other controller and use it to trigger a digital sound module (which contains synthesized musical sounds) to generate sounds, which the audience hears produced by a keyboard amplifier. MIDI data can be transferred via MIDI or USB cable, or recorded to a sequencer or digital audio workstation to be edited or played back. MIDI also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI LOGO
MIDI (; Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music. The specification originates in the paper ''Universal Synthesizer Interface'' published by Dave Smith and Chet Wood of Sequential Circuits at the 1981 Audio Engineering Society conference in New York City. A single MIDI cable can carry up to sixteen channels of MIDI data, each of which can be routed to a separate device. Each interaction with a key, button, knob or slider is converted into a MIDI event, which specifies musical instructions, such as a note's pitch, timing and loudness. One common MIDI application is to play a MIDI keyboard or other controller and use it to trigger a digital sound module (which contains synthesized musical sounds) to generate sounds, which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Size
File size is a measure of how much data a computer file contains or, alternately, how much storage it consumes. Typically, file size is expressed in units of measurement based on the byte. By convention, file size units use either a metric prefix (as in megabyte and gigabyte) or a binary prefix (as in mebibyte and gibibyte). When a file is written to a file system, which is the case in most modern devices, it may consume slightly more disk space than the file requires. This is because the file system rounds the size up to include any unused space left over in the last disk sector used by the file. (A ''sector'' is the smallest amount of space addressable by the file system. The size of a disk sector ranges from several hundred to several thousand bytes.) The unused space is called slack space or internal fragmentation. Although smaller sector sizes allow for denser use of disk space, they decrease the operational efficiency of the file system. Maximum size The maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Oberheim
Thomas Elroy Oberheim (born July 7, 1936, Manhattan, Kansas), known as Tom Oberheim, is an American audio engineer and electronics engineer best known for designing effects processors, analog synthesizers, sequencers, and drum machines. He has been the founder of four audio electronics companies, most notably Oberheim Electronics. He was also a key figure in the development and adoption of the MIDI standard. He is also a trained physicist. Early life and education Oberheim was born and raised in Manhattan, Kansas, also the home of Kansas State University. Beginning in junior high school, he put his interest in electronics into practice by building hi-fi components and amplifiers for friends. A fan of jazz music, Oberheim decided to move to Los Angeles after seeing an ad on the back of '' Downbeat Magazine'' about free jazz performances at a club there. He arrived in Los Angeles in July 1956 at the age of 20 with $10 in his pocket. He worked as a draftsman trainee a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberheim Electronics
Oberheim is an American synthesizer manufacturer founded in 1969 by Tom Oberheim. History and products Tom Oberheim founded the company in 1969, originally as a designer and contract manufacturer of electronic effects devices for Maestro (most notably the Maestro PS-1A Phase Shifter),, and briefly a retail dealer for ARP Instruments, eventually designing the company's first Oberheim-branded product, the Oberheim DS-2, one of the first digital music sequencers. In 1975 Oberheim introduced the Synthesizer Expander Module (SEM) to complement the DS-2 sequencer and enable a user to play one synthesizer while the DS-2 played a sequence on another. The SEM featured a two-pole filter that could operate as a low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-reject filter, giving it a different sound than the Moog and ARP filters popular at the time. The company later combined multiple SEM modules with a digitally-scanned keyboard and a 2-channel voltage-controlled sequencer to create a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Corporation
is a Japanese manufacturer of electronic musical instruments, electronic equipment, and software. It was founded by Ikutaro Kakehashi in Osaka on 18 April 1972. In 2005, its headquarters relocated to Hamamatsu in Shizuoka Prefecture. It has factories in Malaysia, Taiwan, Japan, and the United States. As of 31 March 2010, it employed 2,699 people. In 2014, it was subject to a management buyout by its CEO, Junichi Miki, supported by Taiyo Pacific Partners. Roland has manufactured numerous instruments that have had lasting impacts on music, such as the Juno-106 synthesizer, TB-303 bass synthesizer, and TR-808 and TR-909 drum machines. It was also instrumental in the development of MIDI, a standardized means of synchronizing electronic instruments manufactured by different companies. In 2016, ''Fact'' wrote that Roland had arguably had more influence on electronic music than any other company. History 1970s Having created Ace Electronic Industries Inc in 1960, Ikutaro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
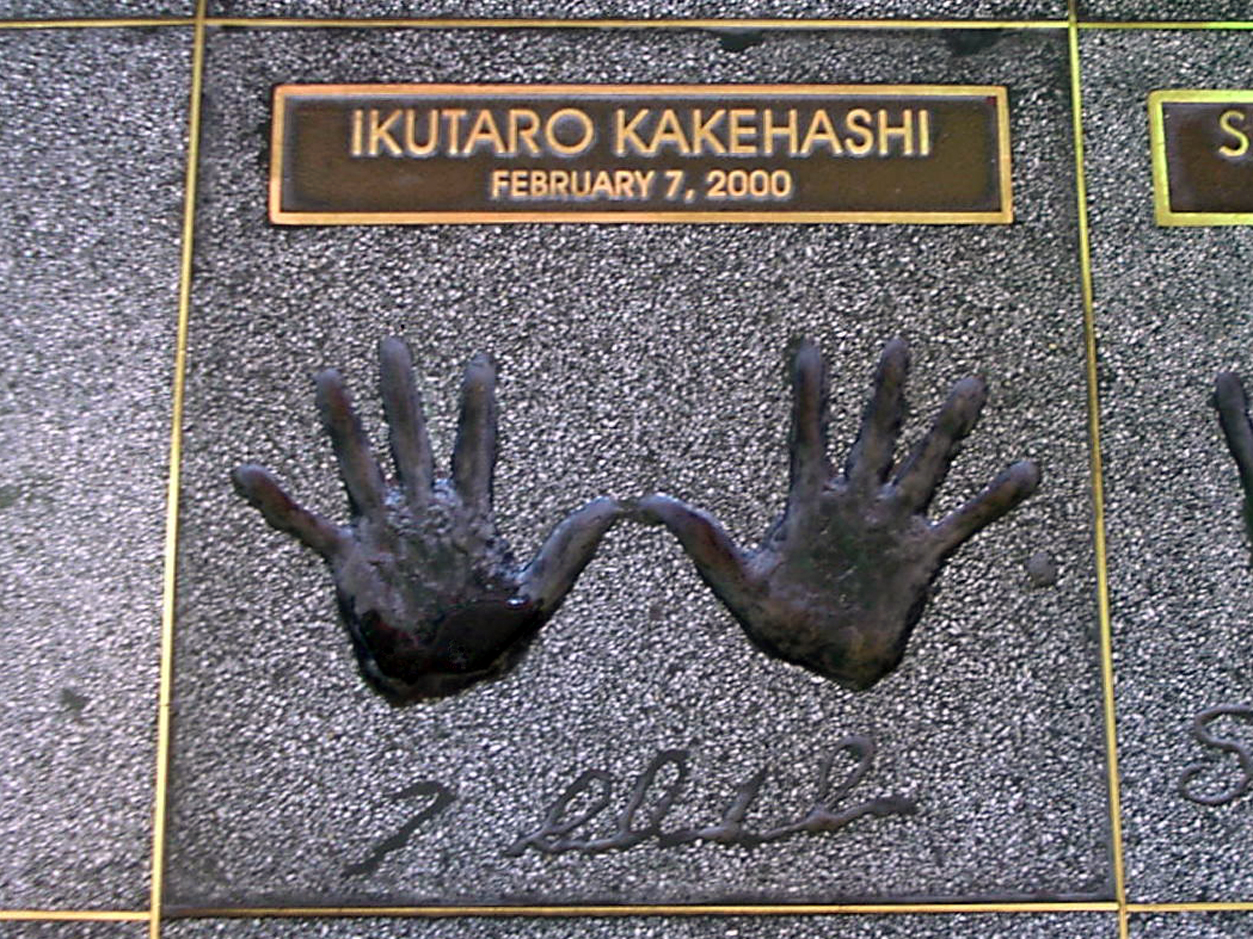
Ikutaro Kakehashi
, also known by the nickname Taro, was a Japanese engineer, inventor, and entrepreneur. He founded the musical instrument manufacturers Ace Tone, Roland Corporation, and Boss Corporation, and the audiovisual electronics company ATV Corporation. Kakehashi founded Ace Tone in 1960 to produce electronic organs and early drum machines. He founded Roland in 1972 and was involved in the development of various influential electronic instruments, such as the TR-808 and TR-909 drum machines and the TB-303 and Juno-60 synthesizers, in addition to Boss guitar amplifiers and effects pedals. He was also key to the development of MIDI, a technical standard that connects a wide variety of electronic instruments, in the 1980s; in 2013, Kakehashi received a Technical Grammy Award, shared with Dave Smith of Sequential, for the invention of MIDI. Kakehashi's inventions are credited with shaping popular music genres such as electronic, dance, hip hop, R&B, rock and pop music. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Control Bus
DCB (Digital Control Bus, Digital Connection Bus or Digital Communication Bus in some sources) was a proprietary data interchange interface by Roland Corporation, developed in 1981 and introduced in 1982 in their Roland Juno-60 and Roland Jupiter-8 products. DCB functions were basically the same as MIDI, but unlike MIDI (which is capable of transmitting a wide array of information), DCB could provide note on/off, program change and VCF/VCA control only. DCB-to-MIDI adapters were produced for a number of early Roland products. The DCB interface was made in 2 variants, the earlier one used 20-pin sockets and cables, later switching to the 14-pin Amphenol DDK connector vaguely resembling a parallel port. Supporting equipment DCB was quickly replaced by MIDI in the early 1980s which Roland helped co-develop with Sequential Circuits. The only DCB-equipped instruments produced were the Roland Jupiter-8 The Jupiter-8, or JP-8, is an eight-voice polyphonic analog subtractive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIN Sync
DIN sync, also called Sync24, is a synchronization interface for electronic musical instruments. It was introduced in the early 1980s by Roland Corporation and has been superseded by MIDI. Definition and history DIN sync was introduced in the early 1980s by Roland Corporation for the synchronization of music sequencers, drum machines, arpeggiators and similar devices. It was superseded by MIDI, in the mid to late 1980s. DIN sync consists of two signals, clock (tempo) and run/stop. Both signals are transistor-transistor logic, TTL compatible, meaning the low state is 0 V and the high state is about +5 V. The clock signal is a low-frequency pulse wave suggesting the tempo. Instead of measuring the waveform's frequency, the machine receiving the signal merely has to count the number of pulses to work out when to increment its position in the music. Roland equipment uses 24 pulses per quarter note, known as Sync24. Therefore, a Roland-compatible device playing sixte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CV/gate
CV/gate (an abbreviation of ''control voltage/gate'') is an analog method of controlling synthesizers, drum machines, and similar equipment with external sequencers. The control voltage typically controls pitch and the gate signal controls note on-off. This method was widely used in the epoch of analog modular synthesizers and CV/Gate music sequencers, since the introduction of the Roland MC-8 Microcomposer in 1977 through to the 1980s, when it was eventually superseded by the MIDI protocol (introduced in 1983), which is more feature-rich, easier to configure reliably, and more readily supports polyphony. The advent of digital synthesizers also made it possible to store and retrieve voice "patches" – eliminating patch cables and (for the most part) control voltages. However, numerous companies – including Doepfer, who designed a modular system for Kraftwerk in 1992, Buchla, MOTM, Analogue Systems, and others continue to manufacture modular synthesizers that are increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standardization
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization can help maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality. It can also facilitate a normalization of formerly custom processes. In social sciences, including economics, the idea of ''standardization'' is close to the solution for a coordination problem, a situation in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by making mutually consistent decisions. History Early examples Standard weights and measures were developed by the Indus Valley civilization.Iwata, Shigeo (2008), "Weights and Measures in the Indus Valley", ''Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures (2nd edition)'' edited by Helaine Selin, pp. 2254–2255, Springer, . The centralized wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Of Musical Electronics Industry
The Association of Musical Electronics Industry (AMEI) is an organization where companies work together to create the standards that assure compatibility among electronic musical instruments, particularly MIDI MIDI (; Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, an ... products. The AMEI is a Japanese organization established in 1996. See also * MIDI Manufacturers Association * Japan MIDI Standards Committee References External links Association of Musical Electronics Industry (AMEI) MIDI {{business-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI Manufacturers Association
The MIDI Manufacturers Association (MMA) is a non-profit trade organization where companies work together to create MIDI standards that assure compatibility among MIDI products. The MMA is a U.S. organization established in 1985 by the original developers of the MIDI 1.0 Specification in 1983. Since 1985 the MMA has produced 11 new specifications and adopted 38 sets of enhancements to MIDI. See also *Association of Musical Electronics Industry The Association of Musical Electronics Industry (AMEI) is an organization where companies work together to create the standards that assure compatibility among electronic musical instruments, particularly MIDI MIDI (; Musical Instrument D ... * Show control ** Comparison of MIDI standards ** Standard MIDI File ** DLS format ** XMF References External links MIDI Manufacturers Association [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |