|
MB 3
MB3 is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy discovered in 1997 and located about 10 million light-years away from the Earth. It was discovered during an optical survey of the IC 342/Maffei group to which the galaxy is a member. MB3 is a companion galaxy of Dwingeloo 1 and situated in the Zone of Avoidance. MB 3 is thought to be a member of the IC 342/Maffei Group The IC 342/Maffei Group (also known as the IC 342 Group or the Maffei 1 Group) corresponds to one or two galaxy groups close to the Local Group. The member galaxies are mostly concentrated around either IC 342 or Maffei 1, which would be the brig ..., a galaxy group adjacent to the Local Group. The visible diameter of MB 3 is approximately 1.9′, which at the distance of 3 Mpc corresponds to about 2 kpc. In optical images it appears as a highly flattened diffuse oval located approximately 9.2′ to the southwest of Dwingeloo 1. No neutral or molecular hydrogen has been detected in it, which is consistent with its cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the positions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 E23 M
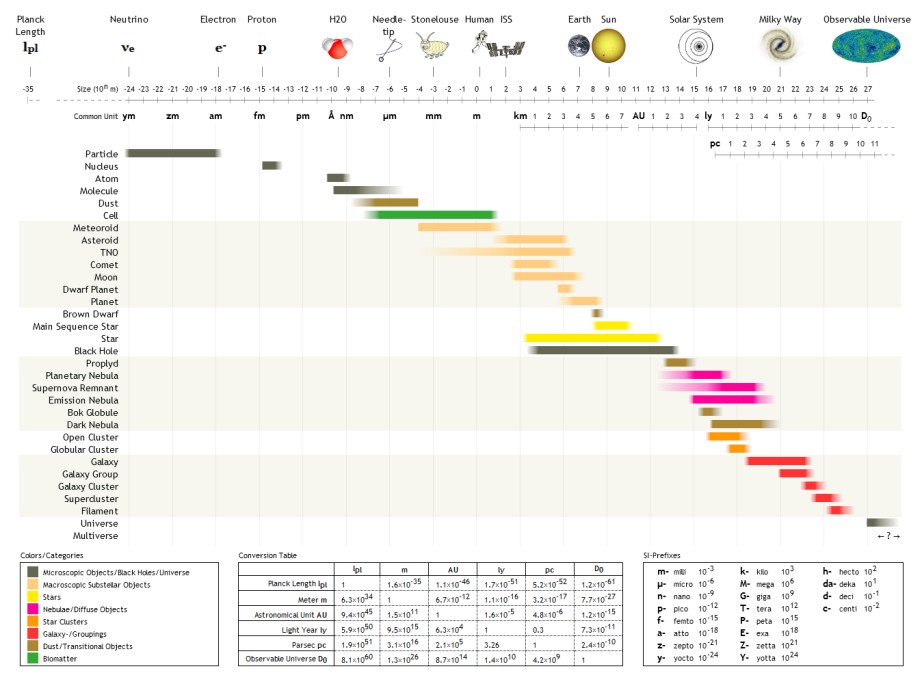
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' ( SI symbol: ') is a unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one octilliont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 au subtends an angle of one arcsecond ( of a degree). This corresponds to astronomical units, i.e. 1\, \mathrm = 1/\tan \left( \ \mathrm \right)\, \mathrm. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. The word ''parsec'' is a portmanteau of "parallax of one second" and was coined by the British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913 to make calculations of astronomical distances from only raw observational data easy for astronomers. Partly for this reason, it is the unit preferred in astronomy and astrophysics, though the light-year remains prominent in popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC 342/Maffei Group
The IC 342/Maffei Group (also known as the IC 342 Group or the Maffei 1 Group) corresponds to one or two galaxy groups close to the Local Group. The member galaxies are mostly concentrated around either IC 342 or Maffei 1, which would be the brightest two galaxies in the group. The group is part of the Virgo Supercluster. However, recent studies have found that the two subgroups are unrelated; while the IC 342 group is the nearest galaxy group to the Milky Way, the Maffei 1 group is several times farther away, and is not gravitationally bound to the IC 342 group. Members The table below lists galaxies that have been identified as associated with the IC342/Maffei 1 Group by I. D. Karachentsev. Note that Karachentsev divides this group into two subgroups centered around IC 342 and Maffei 1. Additionally, KKH 37 is listed as possibly being a member of the IC 342 Subgroup, and KKH 6 is listed as possibly being a member of the Maffei 1 Subgroup. Foreground dust obsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiopeia (constellation)
Cassiopeia () is a constellation in the northern sky named after the vain queen Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda, in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivaled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive ' W' shape, formed by five bright stars. Cassiopeia is located in the northern sky and from latitudes above 34°N it is visible year-round. In the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November, and at low southern, tropical, latitudes of less than 25°S it can be seen, seasonally, low in the North. At magnitude 2.2, Alpha Cassiopeiae, or Schedar, is generally the brightest star in Cassiopeia, though it is occasionally outshone by the variable Gamma Cassiopeiae, which has reached magnitude 1.6. The constellation hosts some of the most luminous stars known, including the yel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwingeloo 1
Dwingeloo 1 is a barred spiral galaxy about 10 million light-years away from the Earth, in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies in the Zone of Avoidance and is heavily obscured by the Milky Way. The size and mass of Dwingeloo 1 are comparable to those of Triangulum Galaxy. Dwingeloo 1 has two smaller satellite galaxies — Dwingeloo 2 and MB 3 — and is a member of the IC 342/Maffei Group of galaxies. Discovery The Dwingeloo 1 galaxy was discovered in 1994 by the Dwingeloo Obscured Galaxy Survey (DOGS) using the Dwingeloo Radio Observatory, which searched for neutral hydrogen (HI) radio emissions at the wavelength of 21 cm from objects in the Zone of Avoidance. In this zone gas and dust in the disk of the Milky Way galaxy block the light from the galaxies lying behind it. The galaxy was, however, first noted as an unremarkable feature on Palomar Sky Survey plates earlier in the same year, but was not recognized as such. It was also independently discovered a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy
A dwarf spheroidal galaxy (dSph) is a term in astronomy applied to small, low-luminosity galaxies with very little dust and an older stellar population. They are found in the Local Group as companions to the Milky Way and to systems that are companions to the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). While similar to dwarf elliptical galaxies in appearance and properties such as little to no gas or dust or recent star formation, they are approximately spheroidal in shape and generally have lower luminosity. Discovery Despite the radii of dSphs being much larger than those of globular clusters, they are much more difficult to find due to their low luminosities and surface brightnesses. Dwarf spheroidal galaxies have a large range of luminosities, and known dwarf spheroidal galaxies span several orders of magnitude of luminosity. Their luminosities are so low that Ursa Minor, Carina, and Draco, the known dwarf spheroidal galaxies with the lowest luminosities, have mass-to-light ratios (M/L) gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zone Of Avoidance
The Zone of Avoidance (ZOA, ZoA), or Zone of Galactic Obscuration (ZGO), is the area of the sky that is obscured by the Milky Way. The Zone of Avoidance was originally called the Zone of Few Nebulae in an 1878 paper by English astronomer Richard Proctor that referred to the distribution of "nebulae" in John Herschel's '' General Catalogue of Nebulae''.Kraan-Korteweg & Lahav 2000, p. 2 Background When viewing space from Earth, the attenuation, interstellar dust and stars in the plane of the Milky Way (the galactic plane) obstruct the view of around 20% of the extragalactic sky at visible wavelengths. As a result, optical galaxy catalogues are usually incomplete close to the galactic plane. Modern developments Many projects have attempted to bridge the gap in knowledge caused by the Zone of Avoidance. The dust and gas in the Milky Way cause extinction at optical wavelengths, and foreground stars can be confused with background galaxies. However, the effect of extinction drops at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Group
A galaxy group or group of galaxies (GrG) is an aggregation of galaxies comprising about 50 or fewer gravitationally bound members, each at least as luminous as the Milky Way (about 1010 times the luminosity of the Sun); collections of galaxies larger than groups that are first-order clustering are called galaxy clusters. The groups and clusters of galaxies can themselves be clustered, into superclusters of galaxies. The Milky Way galaxy is part of a group of galaxies called the Local Group. Characteristics Groups of galaxies are the smallest aggregates of galaxies. They typically contain no more than 50 galaxies in a diameter of 1 to 2 megaparsecs (Mpc).see 1022 m for distance comparisons Their mass is approximately 1013 solar masses. The spread of velocities for the individual galaxies is about 150 km/s. However, this definition should be used as a guide only, as larger and more massive galaxy systems are sometimes classified as galaxy groups. Groups are the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Group
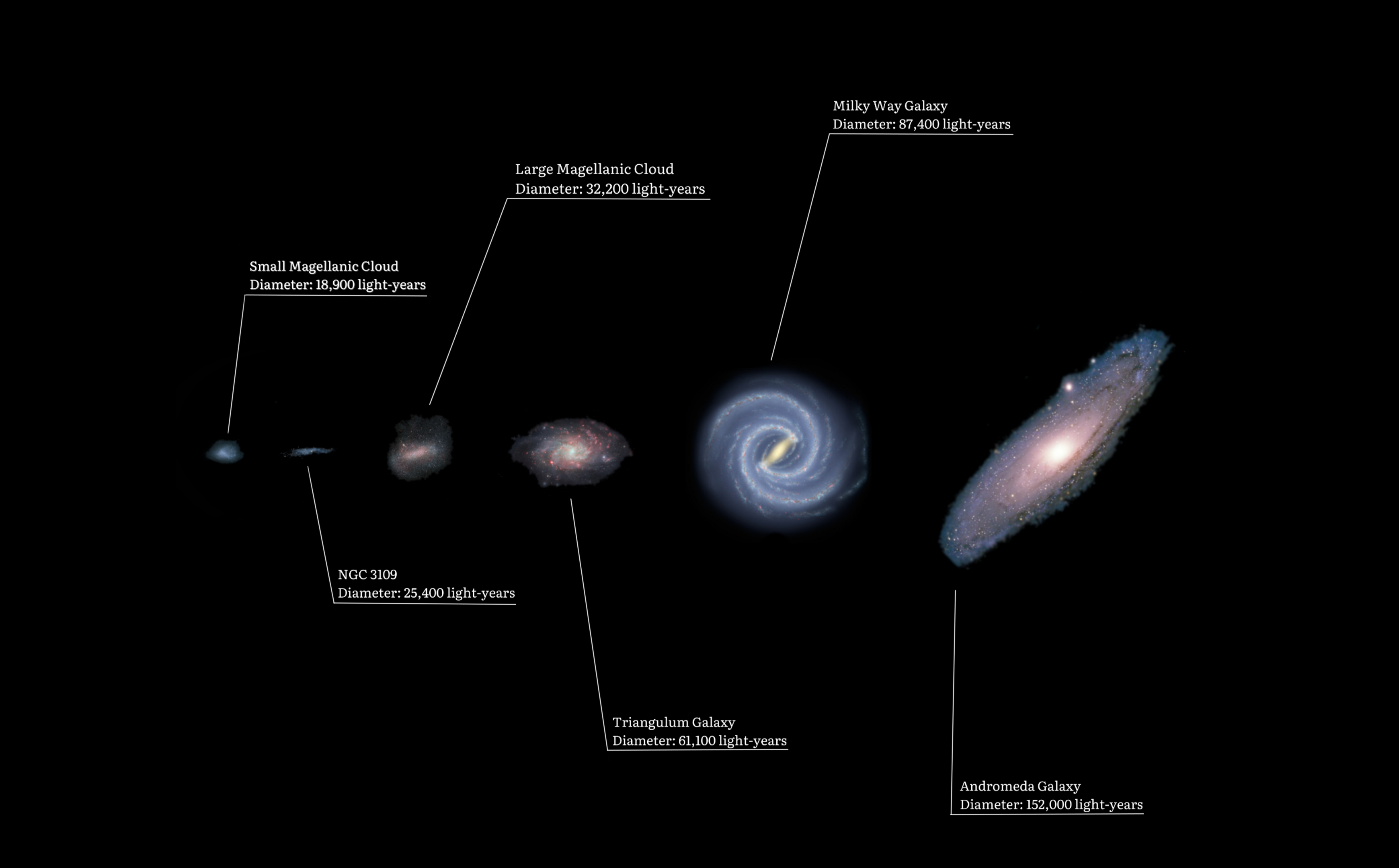
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Galaxies
A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition. Formation One theory states that most galaxies, including dwarf galaxies, form in association with dark matter, or from gas that contains metals. However, NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer space probe identified new dwarf galaxies forming out of gases with low metallicity. These galaxies were located in the Leo Ring, a cloud of hydrogen and helium around two massive galaxies in the constellation Leo. Because of their small size, dwarf galaxies have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |