|
MAP2K
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (also known as MAP2K, MEK, MAPKK) is a dual-specificity kinase enzyme which phosphorylates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). MAP2K is classified as . There are seven genes: * (a.k.a. MEK1) * (a.k.a. MEK2) * (a.k.a. MKK3) * (a.k.a. MKK4) * (a.k.a. MKK5) * (a.k.a. MKK6) * (a.k.a. MKK7) The activators of p38 (MKK3 and MKK6), JNK (MKK4 and MKK7), and ERK (MEK1 and MEK2) define independent MAP kinase signal transduction pathways. The acronym MEK derives from MAPK/ERK Kinase. Role in melanoma MEK is a member of the MAPK signaling cascade that is activated in melanoma. When MEK is inhibited, cell proliferation is blocked and apoptosis (controlled cell death) is induced. See also * Signal transduction * MAP kinase * MAP kinase kinase kinase * MAP kinase kinase kinase kinase Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase (MAP4K) is a family of proteins involved in cellular signal transduction. * MAP4K1 (aka HPK1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
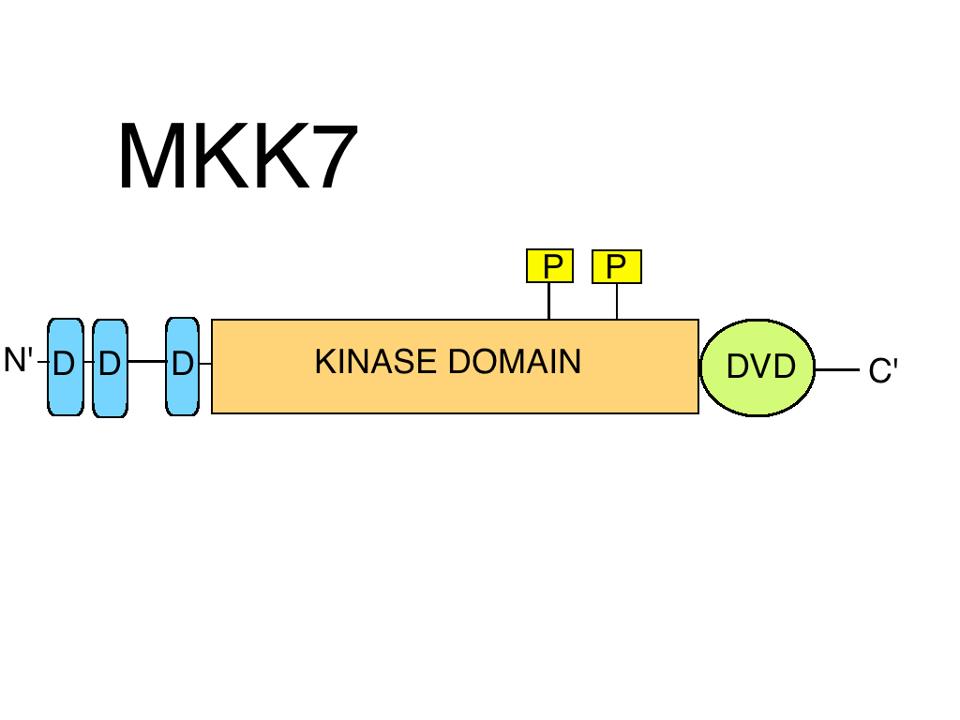
MKK7
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7, also known as MAP kinase kinase 7 or MKK7, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K7'' gene. This protein is a member of the MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase family. The MKK7 protein exists as six different isoforms with three possible N-termini (α, β, and γ isoforms) and two possible C-termini (1 and 2 isoforms). MKK7 is involved in signal transduction mediating the cell responses to proinflammatory cytokines, and environmental Stress (biology), stresses. This kinase specifically activates MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK9/JNK2, and this kinase itself is phosphorylated and activated by MAPKKK, MAP kinase kinase kinases including MAP3K1/MEKK1, MAP3K2/MEKK2, MAP3K3/MEKK5, and MAP4K2/GCK. MKK7 is ubiquitously expressed in all tissue. However, it displays a higher level of expression in skeletal muscle. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found. Nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAP Kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. MAP kinases are found in eukaryotes only, but they are fairly diverse and encountered in all animals, fungi and plants, and even in an array of unicellular eukaryotes. MAPKs belong to the CMGC (CDK/MAPK/GSK3/CLK) kinase group. The closest relatives of MAPKs are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Discovery The first mitogen-activated protein kinase to be discovered was ERK1 (MAPK3) in mammals. Since ERK1 and its close relative ERK2 (MAPK1) are both involved in growth factor signaling, the family was termed "mitogen-activated". With the discovery of other members, even from distant organisms (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MKK4
Dual-specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K4'' gene. ''MAP2K4'' encodes a dual-specificity kinase that belongs to the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. MAP2K4 phosphorylates MAP kinases in response to various environmental stresses or mitogenic stimuli. MAPK8/JNK1, MAPK9/JNK2, and MAPK14/p38 are substrates for MAP2K4, but MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are not phosphorylated by MAP2K4. Structurally, MAP2K4 contains a kinase domain that is phosphorylated and activated by MAP3K1(aka MEKK1). MAP2K4 contains multiple amino acid sites that are phosphorylated and ubiquitinated. Genetic studies using ''Map2k4'' knockout mice revealed embryonic lethality, impaired hepatogenesis and defective liver formation. Analysis of chimeric mice identified a role for ''Map2k4'' in T cell cytokine production and proliferation. ''Map2k4''-deficient chimeric mice frequently develop lymphadenopathy. MAP2K4 is altered in 1.97% of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. MAP kinases are found in eukaryotes only, but they are fairly diverse and encountered in all animals, fungi and plants, and even in an array of unicellular eukaryotes. MAPKs belong to the CMGC (CDK/MAPK/GSK3/CLK) kinase group. The closest relatives of MAPKs are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Discovery The first mitogen-activated protein kinase to be discovered was ERK1 (MAPK3) in mammals. Since ERK1 and its close relative ERK2 (MAPK1) are both involved in growth factor signaling, the family was termed "mitogen-activated". With the discovery of other members, even from distant organisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEK1
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual-specificity protein kinase family that acts as a mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals. This protein kinase lies upstream of MAP kinases and stimulates the enzymatic activity of MAP kinases upon activation by a wide variety of extra- and intracellular signals. As an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway, this kinase is involved in many cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. MAP2K1 is altered in 1.05% of all human cancers. Meiosis The genomes of diploid organisms in natural populations are highly polymorphic for insertions and deletions. During meiosis d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEK2
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K2'' gene. It is more commonly known as MEK2, but has many alternative names including CFC4, MKK2, MAPKK2 and PRKMK2. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the MAP kinase kinase family. This kinase is known to play a critical role in mitogen growth factor signal transduction. It phosphorylates and thus activates MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1. The activation of this kinase itself is dependent on the Ser/Thr phosphorylation by MAP kinase kinase kinases. The inhibition or degradation of this kinase is found to be involved in the pathogenesis of Yersinia and anthrax. Interactions MAP2K2 has been shown to interact with MAPK3 and ARAF Serine/threonine-protein kinase A-Raf, or simply A-Raf, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ARAF'' gene. It belongs to the Raf kinase family of serine/threonine-specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MKK3
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K3'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the MAP kinase kinase family. This kinase is activated by mitogenic and environmental stress, and participates in the MAP kinase-mediated signaling cascade. It phosphorylates and thus activates MAPK14/p38-MAPK. This kinase can be activated by insulin, and is necessary for the expression of glucose transporter. Expression of RAS oncogene is found to result in the accumulation of the active form of this kinase, which thus leads to the constitutive activation of MAPK14, and confers oncogenic transformation of primary cells. The inhibition of this kinase is involved in the pathogenesis of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode distinct isoforms have been reported for this gene. Interactions MAP2K3 has been shown to interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MKK5
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K5'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the MAP kinase kinase family. This kinase specifically interacts with and activates MAPK7/ERK5. This kinase itself can be phosphorylated and activated by MAP3K3/MEKK3, as well as by atypical protein kinase C isoforms (aPKCs). The signal cascade mediated by this kinase is involved in growth factor stimulated cell proliferation and muscle cell differentiation. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been described. Upstream This kinase itself can be phosphorylated and activated by MAP3K3/MEKK3, as well as by atypical protein kinase C isoforms (aPKCs). Downstream This kinase specifically interacts with and activates MAPK7/ERK5. Interactions MAP2K5 has been shown to interact with MAPK7, MAP3K2, Protein kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MKK6
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 also known as MAP kinase kinase 6 (MAPKK 6) or MAPK/ERK kinase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K6'' gene, on chromosome 17. Function MAPKK 6 is a member of the dual specificity protein kinase family, which functions as a mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals. This protein phosphorylates and activates p38 MAP kinase in response to inflammatory cytokines or environmental stress. As an essential component of p38 MAP kinase mediated signal transduction pathway, this gene is involved in many cellular processes such as stress-induced cell cycle arrest, transcription activation and apoptosis. Interactions MAP2K6 has been shown to interact with TAOK2, ASK1, MAPK14 and MAP3K7 Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 (MAP3K7), also known as TAK1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase
Mitogen Activated Protein (MAP) kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK, MKKK, M3K, or, MAP3K) is a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase which acts upon MAP kinase kinase. Subsequently, MAP kinase kinase activates MAP kinase. Several types of MAPKKK can exist but are mainly characterized by the MAP kinases they activate. MAPKKKs are stimulated by a large range of stimuli, primarily environmental and intracellular stressors. MAPKKK is responsible for various cell functions such as cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. The duration and intensity of signals determine which pathway ensues. Additionally, the use of protein scaffolds helps to place the MAPKKK in close proximity with its substrate to allow for a reaction. Lastly, because MAPKKK is involved in a series of several pathways, it has been used as a therapeutic target for cancer, amyloidosis, and neurodegenerative diseases. In humans, there are at least 19 genes which encode MAP kinase kinase kinases: * MAP3K1 (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Jun N-terminal Kinases
c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), were originally identified as kinases that bind and phosphorylate c-Jun on Ser-63 and Ser-73 within its transcriptional activation domain. They belong to the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, and are responsive to stress stimuli, such as cytokines, ultraviolet irradiation, heat shock, and osmotic shock. They also play a role in T cell differentiation and the cellular apoptosis pathway. Activation occurs through a dual phosphorylation of threonine (Thr) and tyrosine (Tyr) residues within a Thr- Pro-Tyr motif located in kinase subdomain VIII. Activation is carried out by two MAP kinase kinases, MKK4 and MKK7, and JNK can be inactivated by Ser/Thr and Tyr protein phosphatases. It has been suggested that this signaling pathway contributes to inflammatory responses in mammals and insects. Isoforms The c-Jun N-terminal kinases consist of ten isoforms derived from three genes: JNK1 (four isoforms), JNK2 (four isoforms) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |