|
Lāčplēsis Day
Lāčplēsis Day () is a memorial day for soldiers who fought for the independence of Latvia. It is celebrated on 11 November, November 11th, marking the decisive victory by the Latvian National Armed Forces, Latvian Army over the joint Russian-German West Russian Volunteer Army led by the warlord Pavel Bermondt-Avalov at the 1919 Battle of Riga during the Latvian War of Independence, thus safeguarding the independence of the nascent nation. It initially was a day of honoring the 743 soldiers that fell in the battles around the Riga area. A popular commemorative symbol, introduced by the Latvijas Neatkarīgā Televīzija, LNT television channel in 2007 and supported by the Ministry of Defence (Latvia), Latvian Ministry of Defence, is a V sign, victory sign-shaped Flag of Latvia, Latvian flag ribbon worn on the left chest. Often it is worn throughout November. Background The Republic of Latvia Independence Day (Latvia), was proclaimed on November 18, 1918, by the People's Counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Council Of Latvia
The People's Council of Latvia (, LTP) was a temporary council which declared Latvia's independence on November 18, 1918 and then acted as the temporary parliament of the country until a Constitutional Assembly was elected. The People's Council was formed on November 17, 1918 as a result of merging two councils of Latvian organizations: Latvian Provisional National Council ('','' LPNP) and the Democratic Bloc. Originally, the People's Council had 40 members representing all the major Latvian political organizations, except the far right and the far left (communists). It was later expanded to 245 representatives. On November 18, 1918, the People's Council declared Latvia an independent country at the now National Theatre of Latvia. It chose Jānis Čakste as the President of the Council and Kārlis Ulmanis as the Prime Minister of the Latvian Provisional Government The Latvian Provisional Government () was formed on November 18, 1918 by the People's Council of Latvia as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jānis Čakste
Jānis Kristaps Čakste (; 14 September 1859 – 14 March 1927) was a Latvian politician and lawyer who served as the first head of an independent Latvian state as the Chairman of the Tautas Padome, People's Council (1918–1920), the Speaker of the Constitutional Assembly (1920–1922), and as the first President of Latvia (1922–1927). Youth Čakste was born in the Sesava Parish, Lielsesava parish of Dobele county in Courland Governorate, the son of a farmer.Švābe, Arveds. Latvijas Encyclopēdija. Trīs Zvaigznes, Stockholm. 1950–1951 He received his primary education at St Anne's Primary School, and entered the Jelgava Gymnasium, Academia Petrina in Jelgava, where he participated in student "evenings" advocating Neo-Latvian ideals. After graduating in 1882, he entered the law faculty of Moscow University. While studying in Moscow, Čakste founded a local Latvian Student Society in 1883, which later became the academic fraternity :lv:Akadēmiskā vienība "Austrums", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Lāčplēsis
The Order of Lāčplēsis (also Lāčplēsis Military Order, ), the first and the highest Latvian military award, was established in 1919 on the initiative of Jānis Balodis, the Commander of the Latvian Army during the Latvian War of Independence. The Lāčplēsis Order is awarded in the first, second and third class. Initially, a holder of the order had to be a recipient of the third class before being promoted to a higher class. It was named after the Latvian epic hero, Lāčplēsis. As a young man, Lāčplēsis kills a bear with his bare hands and thus the order is also known as the Order of the Bearslayer. Description The medal of the Lāčplēsis Military Order is a white enameled Thunder and Fire Cross (Latvian left facing swastika) with red and golden edging. In the centre of the obverse there is a medallion with picture of the folk hero Lāčplēsis wrestling with a bear. On the reverse side there is the date 11 November 1919, the date when the Latvian Army expelled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Assembly Of Latvia
The Constitutional Assembly of Latvia () was independent Latvia's first elected legislative body. Its main task was creating the constitution of Latvia, the Satversme, which is still in effect to this day. The Speaker of Assembly was Jānis Čakste, who later became the first President of Latvia. The assembly functioned from May 1, 1920, until November 7, 1922, when the 1st Saeima convened. Electing the Constitutional Assembly On August 19, 1919, People's Council of Latvia issued the law about elections of Constitutional Assembly. Elections were open to male and female citizens who were older than 21, no minimal vote percentage was set, so many small parties were elected. After the end of Latvian War of Independence in January, 1920 1920 Latvian Constituent Assembly election, Constitutional Assembly elections were quickly organized and held on April 17–18, 1920 when the people of Latvia voted in universal, equal, direct and proportional elections. 25 parties competed for 150 se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kārlis Skalbe
Kārlis Skalbe ( – April 14, 1945) was a Latvian writer, poet, and activist. He is best known for his 72 fairy tales which are really written for adults. He has been called the 'King of Fairytales', and his words, ''Tēvzemei un Brīvībai'' (''For Fatherland and Freedom''), are inscribed on the Monument of Freedom in Riga. Childhood and schooling Skalbe was born in Vecpiebalga Parish, in the heart of Vidzeme, symbolically the same year that one of the other greats of Latvian literature, the poet Auseklis (Miķelis Krogzemis), died in exile. His father Jānis was a blacksmith; his mother, Ede, was, like his father, a Piebalga native. The Skalbes had ten children of which Kārlis was the youngest; five of his siblings died in early childhood.Ērnmanis, P. biographer, ''Kārlis Skalbe—Kopoti Raksti'' (Collected Works). Auseklis (UNRRA authorized), Stuttgart, 1947. Skalbe's parents were devout Moravian Christians. His father was an avid reader both of contemporary works and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian–Soviet Peace Treaty
The Latvian–Soviet Peace Treaty, also known as the Treaty of Riga, was signed on 11 August 1920 by representatives of the Republic of Latvia and Soviet Russia. It officially ended the Latvian War of Independence. In Article II of the treaty, Soviet Russia recognised the independence of Latvia as inviolable "for all future time". Timeline *11 November 1918: The end of World War I *18 November 1918: Republic of Latvia is proclaimed *1 December 1918: The Red Army invades Latvia *17 December 1918: The Latvian Socialist Soviet Republic is formed *13 January 1920: Government of the Latvian Socialist Soviet Republic resigns *1 February 1920: A ceasefire between Russia and Latvia is signed *11 August 1920: The Latvian–Soviet Peace Treaty is signed *4 October 1920: Ratifications are exchanged in Moscow and the treaty goes into effect. Background After World War I, Soviet Russia wanted to regain Latvia, since it had once been a part of the Russian Empire. The Red Army inva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian Army
The Latvian Land Forces () together with the Latvian National Guard form the land warfare branch of the Latvian National Armed Forces. From 2007 to 2024, the Land Forces were organized as a fully professional standing army until the re-introduction of conscription. Mission The main missions of the national Land Forces are to: * Provide for the defense of all national territories; * Ensure combat readiness and the mobilization of units; * Dispose of explosive ordnance; * Provide public assistance. Structure * Land Forces Mechanized Infantry Brigade ** Headquarters (''SzS KBde)'' ** Headquarters and Signal Company (''SzS KBde Štāba un sakaru rota'') ** 1st Mechanized Infantry Battalion (LATBAT, ''1. MKB'') *** Headquarters and Support Company *** 1st Mechanized Infantry Company *** 2nd Mechanized Infantry Company *** 3rd Mechanized Infantry Company *** Combat Service Support Company ** 2nd Mechanized Infantry Battalion (''2. MKB'') *** Headquarters and Support Company * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
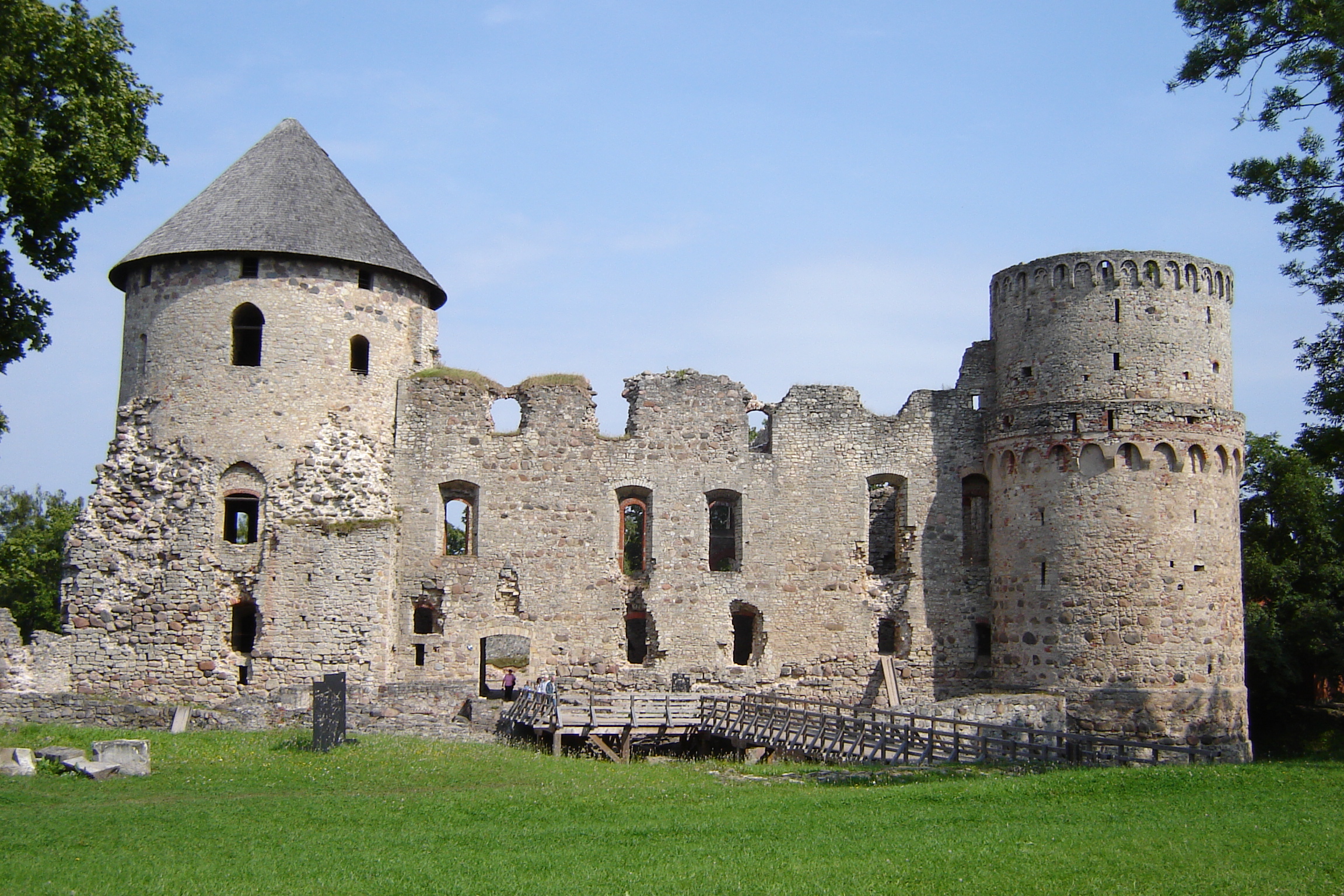
Cēsis
Cēsis (; (, , , ) is a town in Latvia located in the northern part of the Central Vidzeme Upland. Cēsis is on the Gauja River valley, and is built on a series of ridges above the river, overlooking the woods below. Cēsis was selected to be one of the candidate cities for the title of the European Capital of Culture 2014 (Riga was the Latvian city that won the title), as well as for the European Capital of Culture 2027 (Liepāja took the title). Castle The oldest settlement in Cēsis is the hillfort on Riekstu Hill, a fortified wooden castle built by a tribe known as the Vends. The mound with its partly preserved fortification system can still be seen in the Castle park. This settlement was located near major trade routes from west to east and dominated the regional countryside. German crusaders known as the Livonian Brothers of the Sword began construction of Wenden Castle near the hill fort in 1209. When the castle was enlarged and fortified, it served as the resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
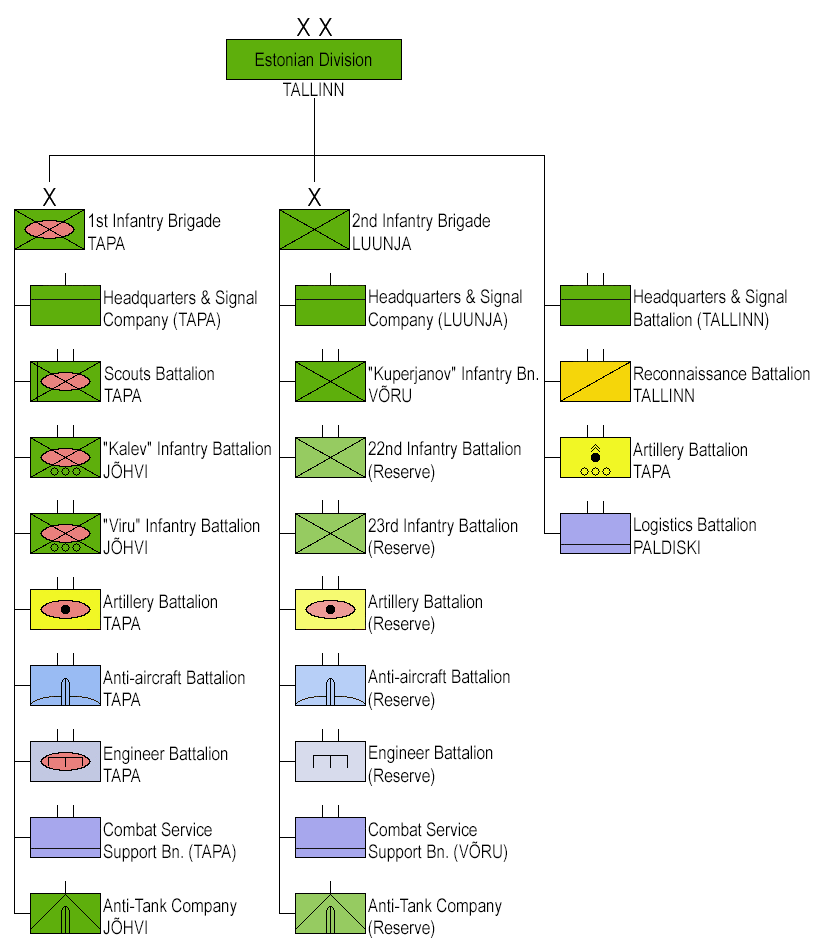
Estonian Army
The Estonian Land Forces (), unofficially referred to as the Estonian Army, is the name of the unified ground forces among the Estonian Defense Forces where it has an offensive military formation role. The Estonian Land Forces is currently the largest Estonian military branch, with an average size of approximately 6,000 soldiers, conscripts, and officers during peacetime. The ''Maavägi'' development priorities are the capability to participate in missions outside the national territory and perform operations to protect the territory of Estonia, also in co-operation with the Allies. The ''Maavägi'' component of the operational structure consists of an infantry brigade and a homeland security structure. Deployable infantry battalion tactical group and some deployable CS, CSS units will develop in the Army structure in accordance with NATO Force Proposals requirements. The infantry brigade will be a training and support frame for deployable units. Homeland security structure uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvian Socialist Soviet Republic
The Latvian Socialist Soviet Republic (, LSPR) was a short-lived socialist republic formed during the Latvian War of Independence. It was proclaimed on 17 December 1918 with the political, economic, and military backing of Vladimir Lenin and his Bolshevik government in the Russian SFSR. The head of government was Pēteris Stučka with Jūlijs Daniševskis as his deputy. History The LSPR armed forces, which consisted of the Red Latvian Riflemen and other units of the Red Army, quickly captured most of the territory of present-day Latvia, forcing Kārlis Ulmanis's provisional government into a small pocket of territory around the city of Liepāja. Stučka's government introduced sweeping communist reforms, resuming the radical policy direction from the abortive Iskolat government. Some reforms were initially popular, such as the expropriation of property from the bourgeoisie. The decision to unilaterally nationalise all agrarian land, however, had dire economic consequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |