|
Lysithea (moon)
Lysithea is a prograde irregular satellite of Jupiter. It was discovered by Seth Barnes Nicholson in 1938 at Mount Wilson Observatory and is named after the mythological Lysithea, daughter of Oceanus and one of Zeus' lovers. Lysithea did not receive its present name until 1975; before then, it was simply known as . It was sometimes called "Demeter" from 1955 to 1975. It belongs to the Himalia group, moons orbiting between 11 and 13 Gm from Jupiter at an inclination of about 28.3°. Its orbital elements are as of January 2000. They are continuously changing due to solar Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ... and planetary perturbations. See also * Irregular satellites * Jupiter's moons in fiction References External linksLysithea: OverviewbNASA's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2MASS
The Two Micron All-Sky Survey, or 2MASS, was an astronomical survey of the whole sky in infrared light. It took place between 1997 and 2001, in two different locations: at the U.S. Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory on Mount Hopkins, Arizona, and at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile, each using a 1.3-meter telescope for the Northern and Southern Hemisphere, respectively. It was conducted in the short-wavelength infrared at three distinct frequency bands ( J, H, and K) near 2 micrometres, from which the photometric survey with its HgCdTe detectors derives its name. 2MASS produced an astronomical catalog with over 300 million observed objects, including minor planets of the Solar System, brown dwarfs, low-mass stars, nebulae, star clusters and galaxies. In addition, 1 million objects were cataloged in the ''2MASS Extended Source Catalog'' (''2MASX''). The cataloged objects are designated with a "2MASS" and "2MASX"-prefix respectively. Catalog The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Objects Discovered In 1938
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Satellites
In astronomy, an irregular moon, irregular satellite or irregular natural satellite is a natural satellite following a distant, inclined, and often eccentric and retrograde orbit. They have been captured by their parent planet, unlike regular satellites, which formed in orbit around them. Irregular moons have a stable orbit, unlike temporary satellites which often have similarly irregular orbits but will eventually depart. The term does not refer to shape as Triton is a round moon, but is considered irregular due to its orbit. As of December 2022, 149 irregular moons are known, orbiting all four of the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune). The largest of each planet are Himalia of Jupiter, Phoebe of Saturn, Sycorax of Uranus, and Triton of Neptune. It is currently thought that the irregular satellites were captured from heliocentric orbits near their current locations, shortly after the formation of their parent planet. An alternative theory, that they orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moons Of Jupiter
There are 82 known moons of Jupiter, not counting a number of moonlets likely shed from the inner moons. All together, they form a satellite system which is called the Jovian system. The most massive of the moons are the four Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, which were independently discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and Simon Marius and were the first objects found to orbit a body that was neither Earth nor the Sun. Much more recently, beginning in 1892, dozens of far smaller Jovian moons have been detected and have received the names of lovers (or other sexual partners) or daughters of the Roman god Jupiter or his Greek equivalent Zeus. The Galilean moons are by far the largest and most massive objects to orbit Jupiter, with the remaining 78 known moons and the rings together composing just 0.003% of the total orbiting mass. Of Jupiter's moons, eight are regular satellites with prograde and nearly circular orbits that are not greatly incli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott S
Scott may refer to: Places Canada * Scott, Quebec, municipality in the Nouvelle-Beauce regional municipality in Quebec * Scott, Saskatchewan, a town in the Rural Municipality of Tramping Lake No. 380 * Rural Municipality of Scott No. 98, Saskatchewan United States * Scott, Arkansas * Scott, Georgia * Scott, Indiana * Scott, Louisiana * Scott, Missouri * Scott, New York * Scott, Ohio * Scott, Wisconsin (other) (several places) * Fort Scott, Kansas * Great Scott Township, St. Louis County, Minnesota * Scott Air Force Base, Illinois * Scott City, Kansas * Scott City, Missouri * Scott County (other) (various states) * Scott Mountain, a mountain in Oregon * Scott River, in California * Scott Township (other) (several places) Elsewhere * 876 Scott, minor planet orbiting the Sun * Scott (crater), a lunar impact crater near the south pole of the Moon *Scott Conservation Park, a protected area in South Australia People * Scott (surname), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter's Moons In Fiction
Jupiter, the largest planet in the Solar System, has appeared in works of fiction across several centuries. The way the planet has been depicted has evolved as more has become known about its composition; it was initially portrayed as being entirely solid, later as having a high-pressure atmosphere with a solid surface underneath, and finally as being entirely gaseous. It was a popular setting during the pulp era of science fiction. Life on the planet has variously been depicted as identical to humans, larger versions of humans, and non-human. Non-human life on Jupiter has been portrayed as primitive in some works and more advanced than humans in others. The moons of Jupiter have also been featured in a large number of stories, especially the four Galilean moons— Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Common themes include terraforming and colonizing these worlds. Jupiter Early depictions Jupiter was long believed, incorrectly, to be a solid planet that it would be possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Satellite
In astronomy, an irregular moon, irregular satellite or irregular natural satellite is a natural satellite following a distant, inclined, and often eccentric and retrograde orbit. They have been captured by their parent planet, unlike regular satellites, which formed in orbit around them. Irregular moons have a stable orbit, unlike temporary satellites which often have similarly irregular orbits but will eventually depart. The term does not refer to shape as Triton is a round moon, but is considered irregular due to its orbit. As of December 2022, 149 irregular moons are known, orbiting all four of the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune). The largest of each planet are Himalia of Jupiter, Phoebe of Saturn, Sycorax of Uranus, and Triton of Neptune. It is currently thought that the irregular satellites were captured from heliocentric orbits near their current locations, shortly after the formation of their parent planet. An alternative theory, that they originated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
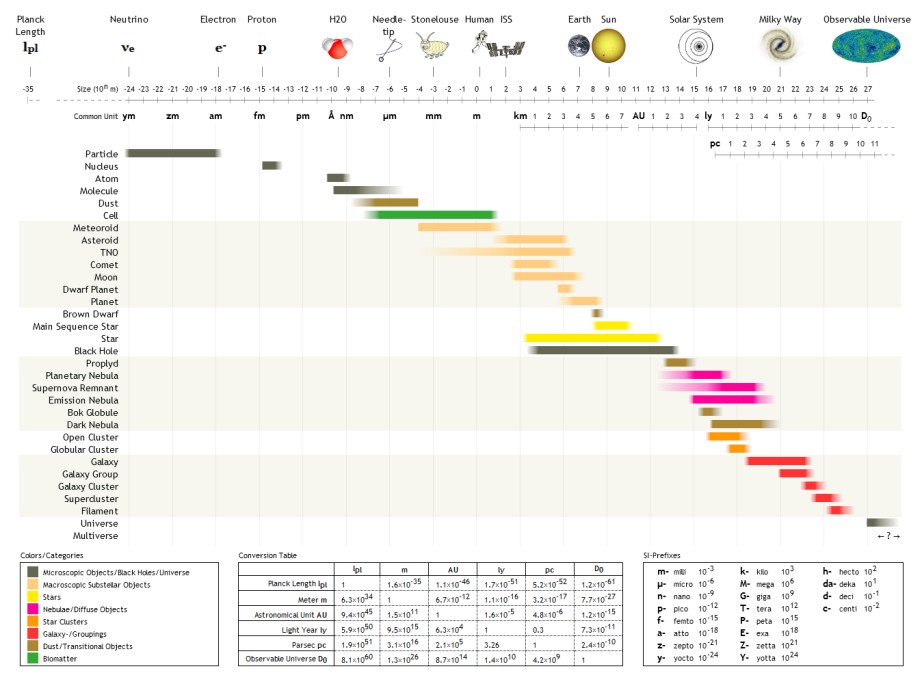
Gigametre
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' ( SI symbol: ') is a unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one octilliont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice-Hall
Prentice Hall was an American major educational publisher owned by Savvas Learning Company. Prentice Hall publishes print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market, and distributes its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. Prentice Hall became known as a publisher of trade books by authors such as Norman Vincent Peale; elementary, secondary, and college textbooks; loose-leaf information services; and professional books. Prentice Hall acquired the training provider Deltak in 1979. Prentice Hall was acquired by Gulf+Western in 1984, and became part of that company's publishing division Simon & Schuster. S&S sold several Prentice Hall subsidiaries: Deltak and Resource Systems were sold to National Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Demeter (; Attic Greek, Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric Greek, Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Twelve Olympians, Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility (soil), fertility of the earth. Although she is mostly known as a grain goddess, she also appeared as a goddess of health, birth, and marriage, and had connections to the Greek Underworld, Underworld. She is also called Deo (). In Greek tradition, Demeter is the second child of the Titans Rhea (mythology), Rhea and Cronus, and sister to Hestia, Hera, Hades, Poseidon, and Zeus. Like her other siblings but Zeus, she was swallowed by her father as an infant and rescued by Zeus. Through her brother Zeus, she became the mother of Persephone, a fertility goddess. One of the most notable Homeric Hymns, the ''Homeric Hymn to Demeter'', tells the story of Persephone's abduction by Hades and Demeter's search for her. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |