|
Lymnaea Acuminata
''Lymnaea acuminata'' is a species of freshwater snail in the family Lymnaeidae. It is native to South Asia, where it occurs in Bangladesh, Burma, India, Nepal, and Pakistan. There it is a widespread and common species.Budha, P.B., Dutta, J. & Daniel, B.A. 2010''Lymnaea acuminata''.The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.2. Downloaded on 22 September 2014. Biology This snail lives in water bodies such as lakes, streams, and wetlands with thick vegetation. It easily survives in polluted waters. Parasites ''Lymnaea acuminata'' is a host for many species of trematoda, trematodes. It is the first intermediate host for ''Schistosoma nasale'' and ''Schistosoma spindale, S. spindale''.Liu L., et al. (2010). The phylogeography of ''Indoplanorbis exustus'' (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Asia. ''Parasites & Vectors'' 3 57. . It is also an intermediate host for the liver flukes ''Fasciola gigantica'' and ''Fasciola hepatica, F. hepatica'', which cause the infectious disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Close-up Acuminata
A close-up or closeup in filmmaking, television production, still photography, and the comic strip medium is a type of shot that tightly frames a person or object. Close-ups are one of the standard shots used regularly with medium and long shots (cinematic techniques). Close-ups display the most detail, but they do not include the broader scene. Moving toward or away from a close-up is a common type of zooming. A close up is taken from head to neck, giving the viewer a detailed view of the subject's face. History Most early filmmakers, such as Thomas Edison, Auguste and Louis Lumière and Georges Méliès, tended not to use close-ups and preferred to frame their subjects in long shots, similar to the stage. Film historians disagree as to the filmmaker who first used a close-up. One of the best claims is for George Albert Smith in Hove, who used medium close-ups in films as early as 1898 and by 1900 was incorporating extreme close-ups in films such as ''As Seen Through a T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
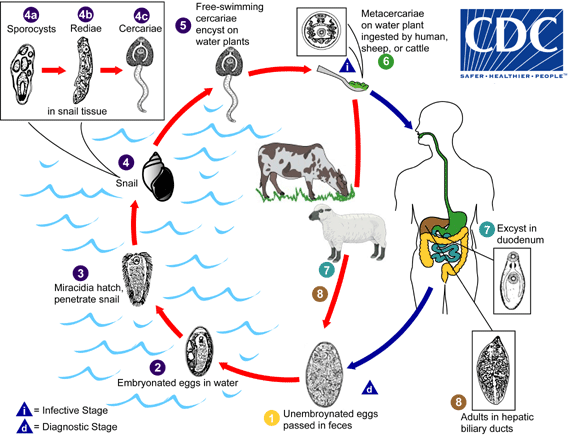
Fasciolosis
Fasciolosis is a parasitic worm infection caused by the common liver fluke ''Fasciola hepatica'' as well as by '' Fasciola gigantica''. The disease is a plant-borne trematode zoonosis, and is classified as a neglected tropical disease (NTD). It affects humans, but its main host is ruminants such as cattle and sheep. The disease progresses through four distinct phases; an initial incubation phase of between a few days up to three months with little or no symptoms; an invasive or acute phase which may manifest with: fever, malaise, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal symptoms, urticaria, anemia, jaundice, and respiratory symptoms. The disease later progresses to a latent phase with fewer symptoms and ultimately into a chronic or obstructive phase months to years later. In the chronic state the disease causes inflammation of the bile ducts, gall bladder and may cause gall stones as well as fibrosis. While chronic inflammation is connected to increased cancer rates, it is unclear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola Hepatica
''Fasciola hepatica'', also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitism, parasitic trematode (fluke (flatworm), fluke or flatworm, a type of helminth) of the class (biology), class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans, and is transmitted by sheep and cattle to humans all over the world. The disease caused by the fluke (flatworm), fluke is called fasciolosis or fascioliasis, which is a type of helminthiasis and has been classified as a neglected tropical disease. Fasciolosis is currently classified as a plant/food-borne trematode infection, often acquired through eating the parasite's Trematode life cycle stages, metacercariae encysted on plants. ''F. hepatica'', which is distributed worldwide, has been known as an important parasite of sheep and cattle for decades and causes significant economic losses in these livestock species, up to £23'' ''million in the UK alone. Because of its relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciola Gigantica
''Fasciola gigantica'' is a parasitic flatworm of the Class (biology), class Trematoda, which causes tropical fascioliasis. It is regarded as one of the most important single platyhelminth infections of ruminants in Asia and Africa. The infection is commonly called fasciolosis. The prevalence of ''F. gigantica'' often overlaps with that of ''Fasciola hepatica'', and the two species are so closely related in terms of genetics, behaviour, and morphology (biology), morphological and anatomy, anatomical structures that distinguishing them is notoriously difficult. Therefore, sophisticated molecular techniques are required to correctly identify and diagnose the infection. Distribution ''Fasciola gigantica'' causes outbreaks in tropical areas of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Africa. The geographical distribution of ''F. gigantica'' overlaps with ''F. hepatica'' in many African and Asian countries and sometimes in the same country, although in such cases, the ecological requirement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Fluke
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes. They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also in bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver parenchyma. In these organs, they produce pathological lesions leading to parasitic diseases. They have complex life cycles requiring two or three different hosts, with free-living larval stages in water. Biology The body of liver flukes is leaf-like and flattened. The body is covered with a tegument. They are hermaphrodites having complete sets of both male and female reproductive systems. They have simple digestive systems and primarily feed on blood. The anterior end has the oral sucker opening into the mouth. Inside, the mouth leads to a small pharynx which is followed by an extended intestine that runs the entire length of the body. The intestine is heavily branched and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasites & Vectors
''Parasites & Vectors'' is a peer-reviewed open-access medical journal published by BioMed Central. The journal publishes articles on the biology of parasites, parasitic diseases, intermediate hosts, vectors and vector-borne pathogens. ''Parasites & Vector'' was established in 2008 as a merger of ''Filaria Journal'' and ''Kinetoplastid Biology,'' and its launch editor-in-chief was Chris Arme. Since 2013 it has published an associated blog A blog (a Clipping (morphology), truncation of "weblog") is an informational website consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries also known as posts. Posts are typically displayed in Reverse chronology, reverse chronologic ... for the parasites and vectors community called BugBitten, and it awards the ' Odile Bain Memorial Prize' (OBMP) to perpetuate the memory of the parasitologist Odile Bain who died in 2012. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Parasites and Vectors BioMed Central academic journals Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Spindale
''Schistosoma spindale'' is a species of digenetic trematode in the family Schistosomatidae. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis in the ruminants. The distribution of ''Schistosoma spindale'' includes Sri Lanka, India, Bangladesh, Thailand, Malaysia, and Laos. The tegument of ''Schistosoma spindale'' under scanning electron microscope was studied in 1983. It is non-tuberculated. The first intermediate host is a freshwater snail '' Indoplanorbis exustus'' that may be the sole natural intermediate host for ''Schistosoma spindale'' (and other two ''Schistosoma'' species) on the Indian sub-continent. One snail can produce up to 7,000 cercariae in one day. The cercariae usually infect some hairy host (low host specificity) in shallow and muddy waters. The definitive hosts of ''Schistosoma spindale'' are (mainly) ruminants and ''Schistosoma spindale'' cause intestinal schistosomiasis of ruminants (Artiodactyla, Ruminantia). Surveillance for cattle schistosomiasis is generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Nasale
''Schistosoma nasale'' is a species of digenetic trematode in the family Schistosomatidae. ''S. nasale'' inhabits blood vessels of the nasal mucosa and causes " snoring disease" in cattle, but remains symptomless in buffaloes though extruding its eggs in nasal discharge. The first intermediate host is a freshwater snail '' Indoplanorbis exustus'' that may be the sole natural intermediate host for ''Schistosoma nasale'' (and other two ''Schistosoma'' species) on the Indian sub-continent. Signs and symptoms The clinical symptoms in cattle include a cauliflower-like growth or granuloma in the nasal cavity, associated with a "snoring" sound and profuse mucopurulent discharge. In the endemic areas, there are some local cattle which remain negative for ''S. nasale'' eggs, others excrete eggs but without exhibiting symptoms, while a large number exhibit symptoms with presence of the eggs in nasal discharge.Agrawal MC 2012. Schistosomes and schistosomiasis in South Asia. Springer (India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |