|
Lydia Litvyak
Lydia Vladimirovna Litvyak (; 18 August 1921 – 1 August 1943), also known as Lilya, was a fighter pilot in the Soviet Air Force during World War II. Historians' estimates for her total victories range from thirteen to fourteen solo victories and four to five shared kills in her 66 combat sorties. In about two years of operations, she was the first female fighter pilot to shoot down an enemy aircraft, the first of two female fighter pilots who have earned the title of Flying ace, fighter ace and the holder of the record for the greatest number of kills by a female fighter pilot. She was shot down near Orel, Russia, Orel during the Battle of Kursk as she attacked a formation of German aircraft. Early life Lydia Litvyak was born in Moscow into a Russians, Russian family. Her mother Anna Vasilievna Litvyak was a shop assistant; her father Vladimir Leontievich Litvyak (1892–1937) worked as a railwayman, train driver and clerk. During the Great Purge, her father was arrested as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the laboring and exploited people, article I. was a socialist state from 1917 to 1922, and afterwards the largest and most populous constituent republic of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1922 to 1991, until becoming a sovereign part of the Soviet Union with priority of Russian laws over Union-level legislation in 1990 and 1991, the last two years of the existence of the USSR.The Free Dictionary Russian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic . Encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved on 22 June 2011. The Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Purge
The Great Purge, or the Great Terror (), also known as the Year of '37 () and the Yezhovshchina ( , ), was a political purge in the Soviet Union that took place from 1936 to 1938. After the Assassination of Sergei Kirov, assassination of Sergei Kirov by Leonid Nikolaev in 1934, Joseph Stalin launched a series of show trials known as the Moscow trials to remove suspected party dissenters from the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, especially those aligned with the Bolsheviks, Bolshevik party. The term "great purge" was popularized by the historian Robert Conquest in his 1968 book ''The Great Terror (book), The Great Terror'', whose title was an allusion to the French Revolution's Reign of Terror. The purges were largely conducted by the NKVD (People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs), which functioned as the Ministry of home affairs, interior ministry and secret police of the USSR. Starting in 1936, the NKVD under chief Genrikh Yagoda began the removal of the central pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raisa Belyaeva
Raisa Vasilyevna Belyayeva (; 25 December 1912 19 July 1943) was one of the first Russian female fighter pilots. She fought alongside Lydia Litvyak and was credited with up to three aerial victories. She died in combat, from causes unknown, in 1943. Early life Belyayeva attended a technical institute for tanners in Kirov. After graduation she asked her old friend Olga Yamshchikova, a Leningrad flight instructor, to teach her to fly. Belyayeva soon proved herself an enthusiastic and indefatigable alumna. Before the war, she accumulated more than 1,000 hours of flight time and a hundred parachute jumps, instructing hundreds of parachutists. She also took part in many airshows over Tushino airfield, near Moscow. Military career She took part in the Battle of Stalingrad and flew as an escort pilot for Nikita Khrushchev Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariya Kuznetsova (pilot)
Mariya Mikhailovna Kuznetsova (; 14 April 1918 – 12 October 1990) was a Soviet fighter pilot who originally flew with the women's 586th Fighter Aviation Regiment but was later transferred to the 437th Fighter Aviation Regiment with Yekaterina Budanova, Lydia Litvyak, and several other members of the unit in September 1942. While she did not become an ace, she made it through Battle of Stalingrad unlike many of her colleagues transferred there. Civilian life Kuznetsova was born on 4 April 1918 to a Russian peasant family in Yazvishchi village, Moscow Governorate, RSFSR. She began flying when she was 18, but her father was arrested during the Red Terror in 1937, forcing her to note the arrest in applications and documents, resulting in her being kicked out of flight training several times for being related to an "enemy of the people"; however, her friends spoke up on her behalf and managed to convince the head of the flight school to let her stay. After the war she married Vladim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yekaterina Budanova
Yekaterina Vasilyevna Budanova (), nicknamed Katya (Катя) (6 December 1916 – 19 July 1943), was a fighter pilot in the Soviet Air Force during World War II. Usually credited with five or more aerial victories,Jackson 2003, p. 57. along with Lydia Litvyak, she is often considered one of the world's two female fighter aces. She was shot down by either Luftwaffe ace Georg Schwientek of ''JG 52'' or ace Emil Bitsch, of ''JG 3''. Early life Budanova was born into a peasant family in Konoplanka village in Smolensk Governorate. After leaving elementary school with the highest grades, she had to abandon her studies due to her father's death, and began working as a nanny. At the age of thirteen her mother sent her to join her sister in Moscow, where she began working as a carpenter in an aircraft factory.Milanetti, p. 126. It was there that she began an interest in aviation, and she joined an aeroclub's parachutist section, obtaining her flying license in 1934 and graduating to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalingrad
Volgograd,. geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn. (1589–1925) and Stalingrad. (1925–1961), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Volgograd Oblast, Russia. The city lies on the western bank of the Volga, covering an area of , with a population of slightly over one million residents. Volgograd is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, 16th-largest city by population size in Russia, the third-largest city of the Southern Federal District, and the Volga#Biggest cities on the shores of the Volga, fourth-largest city on the Volga. The city was founded as the fortress of ''Tsaritsyn'' in 1589. By the 19th century, Tsaritsyn had become an important river-port and commercial centre, leading to its rapid population growth. In November 1917, at the start of the Russian Civil War, Tsaritsyn came under Bolshevik control. It fell briefly to the White Army in mid-1919 but Battle of Tsaritsyn, returned to Bolshevik control in January 1920. In 1925, the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saratov
Saratov ( , ; , ) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Saratov Oblast, Russia, and a major port on the Volga River. Saratov had a population of 901,361, making it the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, 17th-largest city in Russia by population. Saratov is north of Volgograd, south of Samara, and southeast of Moscow. The city stands near the site of Ukek, Uvek, a city of the Golden Horde. Tsar Feodor I of Russia likely developed Saratov as a fortress to secure Russia's southeastern border. Saratov developed as a shipping port along the Volga and was historically important to the Volga Germans, who settled in large numbers in the city before they were expelled before and during World War II. Saratov is home to a number of cultural and educational institutions, including the Saratov Drama Theater, Saratov Conservatory, Radishchev Art Museum, Saratov State Technical University, and Saratov State Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 101I-345-0780-14A, Frankreich, Abgestürztes Flugzeug
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media (Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest documents in this collection dated back to the y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
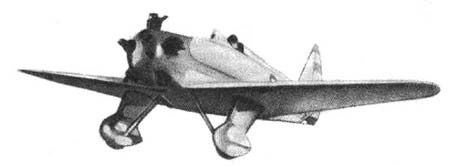
Yakovlev Yak-1
The Yakovlev Yak-1 () was a Soviet fighter aircraft of World War II. The Yak-1 was a single-seat monoplane with a composite structure and wooden wings; production began in early 1940.Angelucci and Matricardi 1978, p. 239. The Yak-1 was a maneuverable, fast and competitive fighter aircraft. The composite-wooden structure made it easy to maintain and the engine proved to be reliable.Snedden 1997, p. 71. It formed the basis for subsequent developments from the Yakovlev bureau and was the founder of a family of aircraft, with some 43,000 being built.Gunston 1998, p. 88.Ethell 1995, p. 163. As a reward, designer Alexander Yakovlev was awarded the Order of Lenin ( Russian: ) (the highest civilian decoration bestowed by the Soviet Union), a 100,000 ruble prize, and a ZIS motor car.Jackson 2003, p. 160.Matricardi 2006, p. 77. Design and development Before the war, Yakovlev was best known for building light sports aircraft. His Yak-4 light bomber impressed the Soviet government eno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marina Raskova
Marina Mikhaylovna Raskova ( rus, Мари́на Миха́йловна Раско́ва, , mɐˈrʲinə mʲɪˈxajləvnə rɐˈskovə; née Malinina; 28 March 1912 – 4 January 1943) was the first woman in the Soviet Union to achieve the diploma of professional air navigator. Raskova went from a young woman with aspirations of becoming an opera singer to a military instructor to the Soviet's first female navigator. She was the navigator to many record-setting as well as record-breaking flights and the founding and commanding officer of the 125th Guards Bomber Aviation Regiment, 587th Bomber Aviation Regiment, a women's aviation regiment which was renamed the 125th M.M. Raskova Borisov Guards Dive Bomber Regiment in her honor. Raskova became one of over 800,000 women in the military service, founding three female air regiments, one of which eventually flew over 30,000 sorties in World War II and produced at least 30 Hero of the Soviet Union, Heroes of the Soviet Union. Early lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tver
Tver (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative centre of Tver Oblast, Russia. It is situated at the confluence of the Volga and Tvertsa rivers. Tver is located northwest of Moscow. Population: The city is situated where three rivers meet, splitting the town into northern and southern parts by the Volga, and divided again into quarters by the Tvertsa River, which splits the left (northern) bank into east and west halves, and the Tmaka River which does the same along the southern bank. Tver was formerly the capital of a powerful medieval state and a model provincial town in the Russian Empire, with a population of 60,000 by 14 January 1913. The city was known as Kalinin () from 1931 to 1990. Etymology According to one hypothesis, the name of the city is of Finnic languages, Finnic origin, ''*Tiheverä''. History Medieval origins Tver's foundation year is officially accepted to be 1135.Charter of Tver, Article 1 Originally a minor se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Instructor
A flight instructor is a person who teaches others to operate aircraft. Specific privileges granted to holders of a flight instructor qualification vary from country to country, but very generally, a flight instructor serves to enhance or evaluate the knowledge and skill level of an aviator in pursuit of a higher pilot's license, certificate or rating. United States Privileges A person who holds a flight instructor certificate (called a "certificated flight instructor" (CFI) is authorized to give training and endorsements required for and relating to: *a student, private, commercial or other pilot certificate; *the three hours of training with reference only to instruments in preparation for a private pilot certificate. Note that this does not need to be a CFII. *an instrument rating, only if the CFI has an instrument instructor rating (CFII); This cannot be given by a "safety pilot". A safety pilot can only be used to help maintain instrument proficiency with an instrument-rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |