|
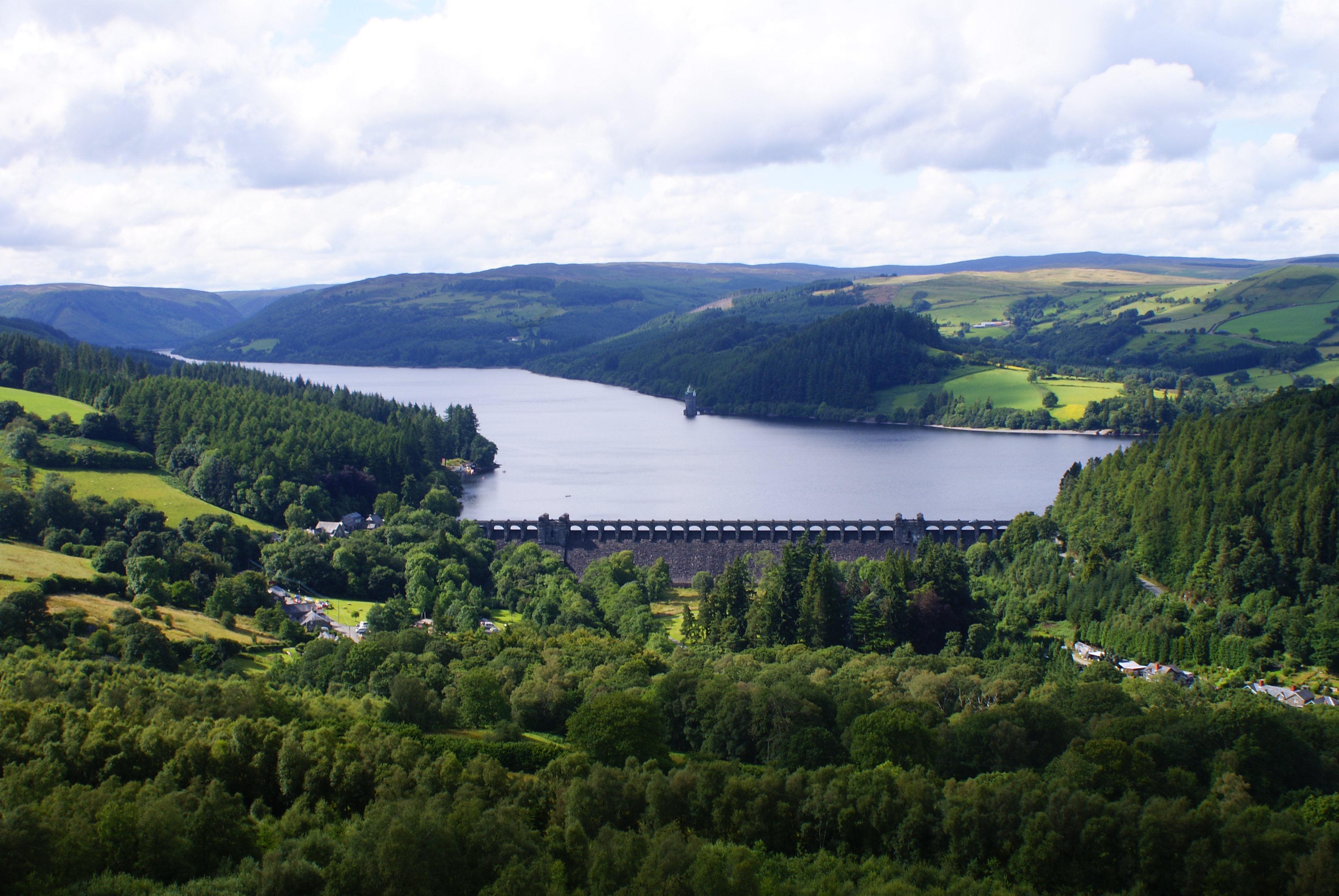
Lussa Loch
Lussa Loch is an artificial reservoir in Kintyre, Scotland, roughly 8 km north of Campbeltown. It was constructed between 1947 and 1956 by damming the Strathduie Water, as part of a larger hydroelectric scheme in Kintyre. The damming submerged one farm (Gobagrennan), and caused another (Stramollach) to be abandoned. The loch's name may derive from the same Scottish Gaelic root as the village of Luss in Argyll and Bute, ''luibh'' meaning "herb". Loch Lussa has a large stock of brown and rainbow trout, and Kintyre Angling Club holds angling Angling (from Old English ''angol'', meaning "hook") is a fishing technique that uses a fish hook attached to a fishing line to tether individual fish in the mouth. The fishing line is usually manipulated with a fishing rod, although rodless te ... competitions on the loch. The Kintyre Way runs along a small road on the loch's western shore. References {{Reflist Freshwater lochs of Scotland Lochs of Argyll and Bute Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but from c. 1841 and for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation. Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an Bay, embayment within it, excavating, or building any number of retaining walls or levees to enclose any area to store water. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam constructed across a valley and rely on the natural topography to provide most of the basin of the reservoir. These reservoirs can either be ''on-stream reservoirs'', which are located on the original streambed of the downstream river and are filled by stream, creeks, rivers or rainwater that surface runoff, runs off the surrounding forested catchments, or ''off-stream reservoirs'', which receive water diversion, diverted water from a nearby stream or aqueduct (water supply), aq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintyre
Kintyre (, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East Loch Tarbert, Argyll, East and West Loch Tarbert, Argyll, West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately north of Kintyre is known as Knapdale. Kintyre is long and narrow, at no point more than from west coast to east coast, and is less than wide where it connects to Knapdale at the north. Kintyre is the lower Firth of Clyde western coast and protects the Firth from the Atlantic Ocean. The southerly tip of Kintyre is on the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel that separates southwestern Scotland from Northern Ireland. The east side of the Kintyre Peninsula is bounded by Kilbrannan Sound, with a number of coastal peaks such as Torr Mor. The central spine of the peninsula is mostly hilly moorland, the highest point being Beinn an Tuirc at . The coastal areas and hinterland, however, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbeltown
Campbeltown (; or ) is a town and former royal burgh in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies by Campbeltown Loch on the Kintyre Peninsula. Campbeltown became an important centre for Scotch whisky, and a busy fishing port. The 2018 population estimate was 4,600, indicating a reduction since the 2011 census. History Originally known as Kinlochkilkerran (an anglicization of the Gaelic, which means 'head of the loch by the kirk of Ciarán'), Campbeltown was renamed in the 17th century as ''Campbell's Town'' after Archibald Campbell ( Earl of Argyll) was granted the site in 1667. Campbeltown Town Hall was completed in 1760. The Royal National Lifeboat Institution opened Campbeltown Lifeboat Station in 1861. The present building dates from 1996. Economy In addition to the benefits of distilling, and whisky tourism, there were two major employers in 2018, Campbeltown Creamery and CS Wind UK, who provided "a substantial portion of the Campbeltown area’s high skilled jobs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Scotsman
''The Scotsman'' is a Scottish compact (newspaper), compact newspaper and daily news website headquartered in Edinburgh. First established as a radical political paper in 1817, it began daily publication in 1855 and remained a broadsheet until August 2004. Its parent company, National World, also publishes the ''Edinburgh Evening News''. It had an audited print circulation of 8,762 for July to December 2022. Its website, Scotsman.com, had an average of 138,000 unique visitors a day as of 2017. The title celebrated its bicentenary on 25 January 2017. History ''The Scotsman'' was conceived in 1816 and first launched on 25 January 1817 as a liberal weekly newspaper by lawyer William Ritchie (Newspaper Editor), William Ritchie and customs official Charles Maclaren in response to the "unblushing subservience" of competing newspapers to the Edinburgh establishment. These two plus John Ramsay McCulloch were co-founders of the venture. The paper was pledged to "impartiality, firm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongside both Irish language, Irish and Manx language, Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a Classical Gaelic, common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names. In the 2011 United Kingdom census#2011 Census for Scotland, 2011 census of Scotland, 57,375 people (1.1% of the Scottish population, three years and older) reported being able to speak Gaelic, 1,275 fewer than in 2001. The highest percentages of Gaelic speakers were in the Outer Hebrides. Nevertheless, there is a language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luss
Luss (, 'herb') is a village in Argyll and Bute, Scotland, on the west bank of Loch Lomond. The village is within the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park. History Historically in the County of Dunbarton, its original name is ''Clachan dhu'', or 'dark village'. Ben Lomond, the most southerly Munro, dominates the view north over the loch, and the Luss Hills rise to the west of the village. Saint Kessog brought Christianity to Luss at the early 6th century in the Early Middle Ages. A number of early medieval and medieval monuments survive in the present churchyard, including simple cross-slabs which may date to as early as the 7th century AD, and a hogback (sculpture), hogback grave-cover of the 11th century. A well-preserved late medieval effigy of a bishop is preserved within the modern church. The present Church of Scotland Luss Parish Church, place of worship was built in 1875 by Sir James Colquhoun, 5th Baronet, in memory of his father, who had drowned in the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyll And Bute
Argyll and Bute (; , ) is one of 32 unitary authority, unitary council areas of Scotland, council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod (14 July 2020). The administrative centre for the council area is in Lochgilphead at Kilmory Castle, a 19th-century Gothic Revival building and estate. The current council leader is Councillor Jim Lynch. Argyll and Bute covers the second-largest administrative area of any Scottish council. The council area adjoins those of Highland (council area), Highland, Perth and Kinross, Stirling (council area), Stirling and West Dunbartonshire. History The County of County of Bute, Bute and the County of Argyll were two of the shires of Scotland, historic counties of Scotland. They were both "''shires''" (context; the area controlled by a sheriff principal, sheriff) in the Middle Ages. From 1890 until 1975 both counties had individual separate ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a species of salmonid ray-finned fish and the most widely distributed species of the genus ''Salmo'', endemic to most of Europe, West Asia and parts of North Africa, and has been widely introduced globally as a game fish, even becoming one of the world's worst invasive species outside of its native range. Brown trout are highly adaptable and have evolved numerous ecotypes/subspecies. These include three main ecotypes: a riverine ecotype called river trout or ''Salmo trutta'' morpha ''fario''; a lacustrine ecotype or ''S. trutta'' morpha ''lacustris'', also called the lake trout (not to be confused with the lake trout in North America); and anadromous populations known as the sea trout or ''S. trutta'' morpha ''trutta'', which upon adulthood migrate downstream to the oceans for much of its life and only returns to fresh water to spawn in the gravel beds of headstreams. Sea trout in Ireland and Great Britain have many regional names: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to Spawn (biology), spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and Fish hatchery, hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except Antarctica. Introductions to locations outside their nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |