|
Luso-Brazilian
Portuguese Brazilians () are Brazilian citizens whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Portugal. Most of the Portuguese who arrived throughout the centuries in Brazil sought economic opportunities. Although present since the onset of the colonization, Portuguese people began migrating to Brazil in larger numbers and without state support in the 18th century. The Portuguese prerogative According to the Constitution of Brazil, the Portuguese people have a special status in Brazil. Article 12, first paragraph of the Constitution, grants to citizens of Portugal with permanent residence in Brazil "the rights attached to Brazilians", excluded from the constitutional prerogatives of Brazilian born. Requirements for the granting of equality are: habitual residence (permanent), the age of majority and formulation of request from the Minister of Justice. In Brazil, the Portuguese may require equal treatment with regard to civil rights; moreover, they may ask to be granted polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese People
The Portuguese people ( – masculine – or ''Portuguesas'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation Ethnic groups in Europe, indigenous to Portugal, a country that occupies the west side of the Iberian Peninsula in Southern Europe, south-west Europe, who share Culture of Portugal, culture, ancestry and Portuguese language, language. The Portuguese state began with the founding of the County of Portugal in 868. Following the Battle of São Mamede (1128), Portugal gained international recognition as a Kingdom of Portugal, kingdom through the Treaty of Zamora and the papal bull Manifestis Probatum. This Portuguese state paved the way for the Portuguese people to unite as a nation. The Portuguese Portuguese maritime exploration, explored Hic sunt Dracones, distant lands previously unknown to Europeans—in the Americas, Africa, Asia and Oceania (southwest Pacific Ocean). In 1415, with the conquest of Ceuta, the Portuguese took a significant role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of the Gospel, Christian gospel. The term evangelical is derived from the Koine Greek word ''euangelion'', meaning “good news,” in reference to the message of salvation through Jesus Christ. Evangelicalism typically places a strong emphasis on personal conversion to Christianity, conversion, often described as being “born again (Christianity), born again,” and regards the Bible as the ultimate authority in matters of Christian theology, faith and practice. The definition and scope of evangelicalism are subjects of debate among theology, theologians and religious studies, scholars. Some critics argue that the term encompasses a wide and diverse range of beliefs and practices, making it difficult to define as a coherent or unified movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Citizenship
The primary law governing nationality of Portugal is the Nationality Act, which Coming into force, came into force on 3 October 1981. Portugal is a member state of the European Union (EU) and all Portuguese nationals are Citizenship of the European Union, EU citizens. They are entitled to Citizens' Rights Directive, free movement rights in EU and European Free Trade Association (EFTA) countries and may vote in elections to the European Parliament. All persons born in Portugal before 3 October 1981 are automatically citizens by birth regardless of the nationalities of their parents. Individuals born in the country since that date receive Portuguese citizenship at birth if at least one of their parents is a Portuguese citizen or has resided in the country for at least one year. Foreign nationals may become citizens by Naturalization, naturalisation after living in Portugal for more than five years and showing proficiency in the Portuguese language. Due to Portugal's historical st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afro-Brazilians
Afro-Brazilians (; ), also known as Black Brazilians (), are Brazilians of total or predominantly Sub-Saharan African ancestry. Most multiracial Brazilians also have a range of degree of African ancestry. Brazilians whose African features are more evident are generally seen by others as Blacks and may identify themselves as such, while the ones with less noticeable African features may not be seen as such. However, Brazilians rarely use the term "Afro-Brazilian" as a term of ethnic identity and never in informal discourse. '' Preto'' ("black") and '' pardo'' ("brown/mixed") are among five ethnic categories used by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), along with '' branco'' ("white"), '' amarelo'' ("yellow", ethnic East Asian), and '' indígena'' (indigenous). In the 2022 census, 20.7 million Brazilians (10,2% of the population) identified as ''preto'', while 92.1 million (45,3% of the population) identified as ''pardo'', together making up 55.5% of Brazil's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
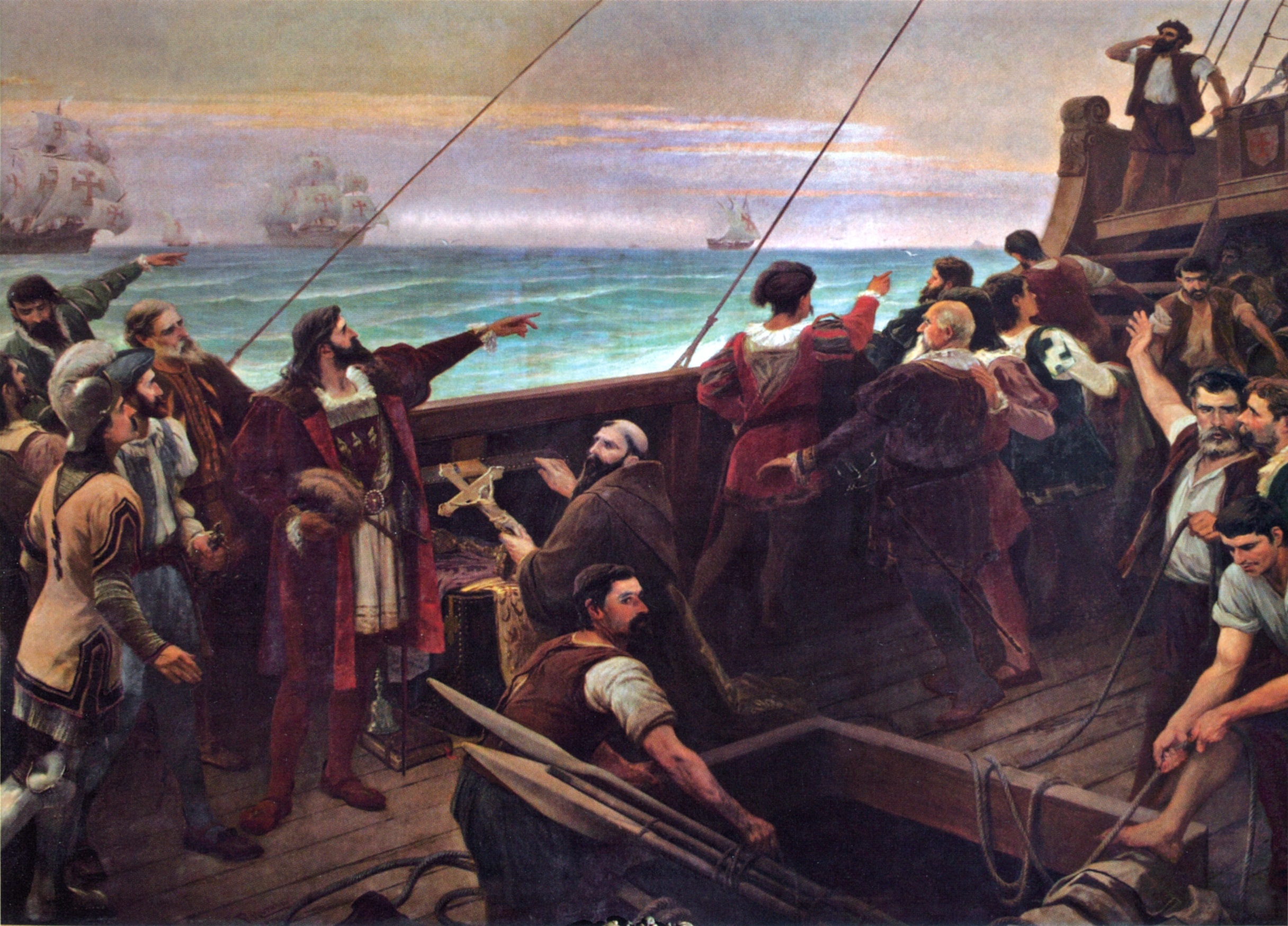
Pedro Alvares Cabral Discovery Of Brazil 1500
Pedro is a masculine given name. Pedro is the Spanish language, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, and Galician language, Galician name for ''Peter (given name), Peter''. Its French equivalent is Pierre while its English and Germanic form is Peter. The counterpart patronymic surname of the name Pedro, meaning "son of Peter" (compared with the English surname Peterson (name), Peterson) is Pérez in Spanish, Peres in Galician and Portuguese, Pires also in Portuguese, and Peiris in coastal area of Sri Lanka (where it originated from the Portuguese version), with all ultimately meaning "son of Pero". The name Pedro is derived via the Latin word "petra", from the Greek word "η πέτρα" meaning "stone, rock". The name Peter (name), Peter itself is a translation of the Aramaic language, Aramaic ''Kephas'' or ''Aramaic of Jesus#Cephas .28.CE.9A.CE.B7.CF.86.CE.B1.CF.82.29, Cephas'' meaning "stone". An alternative archaic variant is Pero. Notable people with the name Pedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sine Qua Non
A ''sine qua non'' (, ) or ''condicio sine qua non'' (plural: ''condiciones sine quibus non'') is an indispensable and essential action, condition, or ingredient. It was originally a Latin legal term for " conditionwithout which it could not be", "but for...", or "without which here isnothing." Also, "''sine qua non'' causation" is the formal terminology for "but-for causation." Origin and spread As a Latin term, it occurs in the work of Boethius and originated in Aristotelian expressions. In Classical Latin, the form uses the word (from the verb , , to agree upon), but in later Latin the phrase is also used with , an error in translation as means ''construction'' and not ''condition''. It has passed from a merely legal usage to a more general usage in many languages, including English, German, French, Italian and Spanish. General usage US President Andrew Jackson once gave a toast on the occasion of his receiving an honorary doctorate from Harvard University, respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice, is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a very few countries) or a secretary of justice. In some countries, the head of the department may be called the attorney general, for example in the United States. Monaco is an example of a country that does not have a ministry of justice, but rather a Directorate of Judicial Services (head: Secretary of Justice) that oversees the administration of justice. Vatican City, a country under the sovereignty of the Holy See, also does not possess a ministry of justice. Instead, the Governorate of Vatican City State (head: President of the Governorate of Vatican City State), the legislative body of the Vatican, includes a legal office. Depending on the country, specific duties may relate to organizing the justice system, overseeing the public p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Majority
The age of majority is the threshold of legal adulthood as recognized or declared in law. It is the moment when a person ceases to be considered a minor (law), minor, and assumes legal control over their person, actions, and decisions, thus terminating the control and legal responsibilities of their parents or guardian over them. Most countries set the age of majority at 18, but some jurisdictions have a higher age and others lower. The word ''majority'' here refers to having greater years and being of full age as opposed to ''minority'', the state of being a minor. The law in a given jurisdiction may not actually use the term "age of majority". The term refers to a collection of laws bestowing the status of adulthood. Explanation The term ''age of majority'' can be confused with the similar concept of the ''age of license''. As a legal term, ''license'' means ''permission'', referring to a legally enforceable right or privilege. Thus, the age of license for a specific activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitual Residence
In conflict of laws, habitual residence is the standard used to determine the law which should be applied to determine a given legal dispute or entitlement. It can be contrasted with the law on domicile, traditionally used in common law jurisdictions to do the same thing. Habitual residence is determined based on the totality of circumstances which may include both future intention and past experience. There is normally only one habitual residence where the individual usually resides and routinely returns to after visiting other places. It is the geographical place considered "home" for a reasonably significant period of time. Description In conflict of laws there are three personal connecting factors that help courts determine which law should apply to a particular dispute or issue. These are nationality, domicile, and habitual residence. Habitual residence is the newest concept of the three and is becoming a more commonly used factor than domicile in many common law jurisd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Brazil
The Constitution of the Federative Republic of Brazil () is the Constitution, supreme law of Brazil. It is the foundation and source of the legal authority underlying the existence of Brazil and the federal government of Brazil. It replaced the Brazilian Constitution of 1967, autocratic 1967 constitution capping 21 years of Military dictatorship in Brazil, military dictatorship and establishing Brazil's current republic, often referred to as the History of Brazil (1985–present), New Republic. Made in the light of the Redemocratization in Brazil, Brazilian transition to democracy, it resignified the role of the state in the citizens' lives, providing a vast system of human and individual rights protection, social welfare, and democratic tools. Overview The 1988 Brazilian Constitution is the seventh enacted since the country's independence in 1822, and the sixth since the proclamation of the republic in 1889. It was promulgated on 5 October 1988, after a two-year process in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Colonization Of The Americas
Portuguese colonization of the Americas () constituted territories in the Americas belonging to the Kingdom of Portugal. Portugal was the leading country in the European exploration of the world in the 15th century. The Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 divided the Earth outside Europe into Castilian and Portuguese global territorial hemispheres for exclusive conquest and colonization. Portugal colonized parts of South America (Brazil, Uruguay), but also made some unsuccessful attempts to colonize North America (Newfoundland and Labrador and Nova Scotia in Canada). Settlements in North America Based on the terms defined in the Treaty of Tordesillas, the Portuguese Crown claimed it had territorial rights in the area visited by the explorer John Cabot in 1497 and 1498 on behalf of the Crown of England. To that end, in 1499 and 1500, the Portuguese mariner João Fernandes Lavrador visited the northeast Atlantic coast and Greenland, which accounts for the appearance of "Labrador ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |