|
Lushootseed
Lushootseed ( ), historically known as Puget Salish, Puget Sound Salish, or Skagit-Nisqually, is a Central Coast Salish language of the Salishan language family. Lushootseed is the general name for the dialect continuum composed of two main dialects, Northern Lushootseed and Southern Lushootseed, which are further separated into smaller sub-dialects. Lushootseed was historically spoken across southern and western Puget Sound roughly between modern-day Bellingham and Olympia by a number of Indigenous peoples. Lushooteed speakers were estimated to number 12,000 at the peak. Today, however, it is primarily a ceremonial language, spoken for heritage or symbolic purposes. There are about 472 known second-language speakers of Lushootseed. It is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger and classified as Reawakening by Ethnologue. Many Lushootseed-speaking tribes are attempting to revitalize the daily use of their language. Seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snoqualmie People
The Snoqualmie people () are a List of Lushootseed-speaking peoples, Lushootseed-speaking Coast Salish, Southern Coast Salish people indigenous to the Snoqualmie Valley, located in east King County, Washington, King and Snohomish County, Washington, Snohomish counties in the state of Washington (state), Washington. Today, they are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes: Snoqualmie Indian Tribe and Tulalip Tribes, Tulalip Tribes of Washington. Name The name "Snoqualmie" is derived from the Lushootseed Endonym and exonym, endonym of the Snoqualmie: . The name is composed of a Root (linguistics), root, , and the suffix , meaning "people of." The name was traditionally the name for the Snoqualmie River and all related villages located on it, not the name of a united ethnic group as it is today. The etymology of the root is contested. According to the Snoqualmie Tribe, the name means "people of the moon," with the root referring to , the Transformer (spirit-being), Changer, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Lushootseed-speaking Peoples
The Lushootseed-speaking peoples, sometimes known as the Lushootseed people, are a group of peoples Indigenous to the Pacific Northwest who are linguistically related along the Lushootseed dialect continuum. Lushootseed-speaking groups were traditionally politically autonomous at the local, or village, level, so there was no historical term to refer to all Lushootseed-speaking peoples. Words like or (lit. "Lushootseed peoples" or "Peoples who speak Lushootseed") are sometimes used in modern times. All historically attested extended village groups or bands are listed, grouped by modern-day tribal units, sub-units, and further sub-units: Northern Lushootseed Northern Lushootseed () is spoken by peoples living generally in Island, Skagit, Snohomish, and parts of Whatcom counties. Northern Lushootseed-speaking communities include: *Upper Skagit – ** Nuwhaha – ''dxʷʔaha'' *** Lake Whatcom village – ''sx̌ačuʔabš'' *** Lake Samish village – ''stiksabš'' ** Nook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
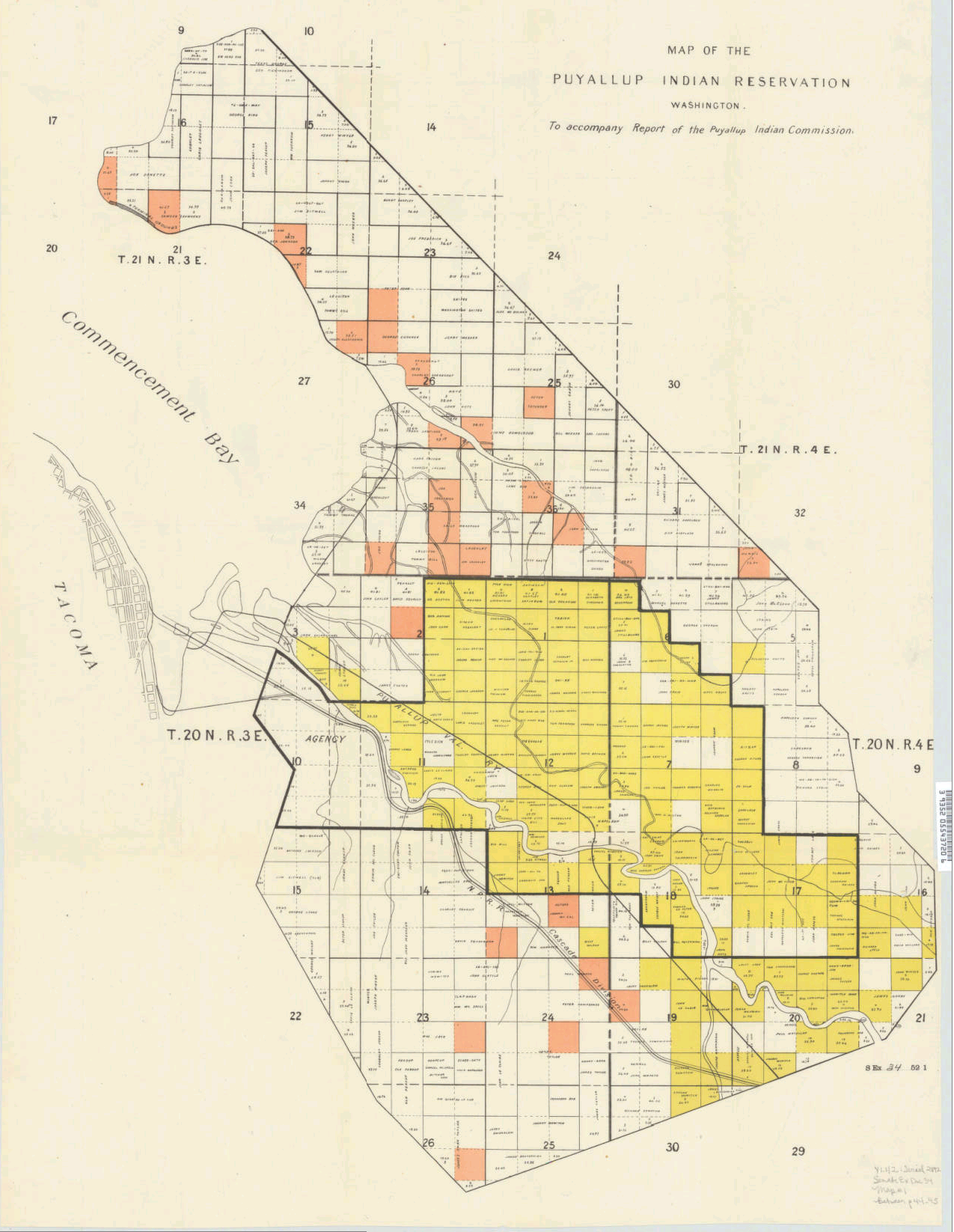
Puyallup Tribe Of Indians
The Puyallup Tribe of Indians ( ; ; commonly known as the Puyallup Tribe) is a federally-recognized tribe of Puyallup people from western Washington state, United States. The tribe is primarily located on the Puyallup Indian Reservation, although they also control off-reservation trust lands. The Puyallup Tribe was established in 1936 after the Indian Reorganization Act, although the reservation was established in 1854 in the Treaty of Medicine Creek. Currently, the tribe has approximately 4,000 citizens. Its membership is descended from the aboriginal Puyallup peoples, as well as other non-Puyallup peoples who were moved to the reservation. Other Puyallup citizens are descendants of other tribes. The population of Puyallup citizens who reside on the reservation is 2,500, which is 3.2% of the reservation's 41,000 total population. The tribe's government is enshrined in its constitution, and is composed of an elected government, the Puyallup Tribal Council, and the three tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Lushootseed
Southern Lushootseed, also called Twulshootseed () or Whulshootseed () in the Muckleshoot and Snoqualmie dialects, is the southern dialect of Lushootseed, a Coast Salish language in western Washington State. It was historically spoken by the Muckleshoot, Puyallup, Suquamish, Duwamish, Nisqually, and Squaxin Island tribes. The last native speaker was Ellen Williams (1923–2016) and her death rendered the language extinct. Whulshootseed is taught at the Muckleshoot Language Program of the Muckleshoot Tribal College in Auburn, Washington, at a local school, and by the Puyallup Tribal Language Program. A 1999 video, ''Muckleshoot: a People and Their Language'' profiles the Muckleshoot Whulshootseed Language Preservation Project. See also *Lushootseed language Lushootseed ( ), historically known as Puget Salish, Puget Sound Salish, or Skagit-Nisqually, is a Central Coast Salish language of the Salishan language family. Lushootseed is the general name for the dialect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salishan
The Salishan languages ( ), also known as the Salish languages ( ), are a family of languages found in the Pacific Northwest in North America, namely the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana. They are characterised by agglutinativity and syllabic consonants. For instance the Nuxalk word (), meaning 'he had had n his possessiona bunchberry plant', has twelve obstruent consonants in a row with no phonetic or phonemic vowels. The Salishan languages are a geographically contiguous block, with the exception of the Nuxalk (Bella Coola), in the Central Coast of British Columbia, and the extinct Tillamook language, to the south on the central coast of Oregon. The terms ''Salish'' and ''Salishan'' are used interchangeably by linguists and anthropologists. The name ''Salish'' or ''Selisch'' is the endonym of the Flathead Nation. Linguists later applied the name Salish to related languages in the Pacific Northwest. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vi Hilbert
Vi Hilbert (; ; July 24, 1918 – December 19, 2008) was an Upper Skagit elder and conservationist of her traditional culture and of the Lushootseed language, of which she was the last fully fluent heritage speaker. She taught Lushootseed at the University of Washington for 17 years (1971–1988), where she also transcribed and translated Lushootseed recordings from the 1950s. This work is preserved in the university's audio library. Hilbert was an enrolled member of the Upper Skagit Indian Tribe, a tribe located in Skagit County, Washington. She was named a Washington Living Treasure in 1989, and received a National Heritage Fellowship from the National Endowment for the Arts, presented by President Bill Clinton, in 1994. She co-wrote Lushootseed grammars and dictionaries, partially with linguist Thom Hess, and published books of stories, teachings, and place names related to her native region, the Puget Sound (). Childhood Hilbert was born to Charlie () and Louise () Anderson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salishan Languages
The Salishan languages ( ), also known as the Salish languages ( ), are a Language family, family of languages found in the Pacific Northwest in North America, namely the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington (state), Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and Montana. They are characterised by agglutinative, agglutinativity and syllabic consonants. For instance the Nuxalk language, Nuxalk word (), meaning 'he had had [in his possession] a Cornus canadensis, bunchberry plant', has twelve obstruent consonants in a row with no phonetic or phonemic vowels. The Salishan languages are a geographically contiguous block, with the exception of the Nuxalk (Bella Coola), in the British Columbia Coast, Central Coast of British Columbia, and the extinct Tillamook language, to the south on the central coast of Oregon. The terms ''Salish'' and ''Salishan'' are used interchangeably by linguists and anthropologists. The name ''Salish'' or ''Selisch'' is the endonym o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muckleshoot
The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe ( ; ), also known as the Muckleshoot Tribe, is a federally-recognized tribe located in Auburn, Washington. The tribe governs the Muckleshoot Reservation and is composed of descendants of the Duwamish, Stkamish, Smulkamish, Skopamish, Yilalkoamish, and Upper Puyallup peoples. The Muckleshoot Indian Tribe was formally established in 1936, after the Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, but its origins lie in the creation of the Muckleshoot Reservation in 1874 and the treaties of Medicine Creek (1854) and Point Elliott (1855). Name The name "Muckleshoot" is an anglicization of the Lushootseed word . originally referred only to a prairie, located between the White and Green rivers, and never as a word to refer to the peoples living in this area. Prior to the establishment of the Muckleshoot reservation, the Indigenous peoples of the Green-White river systems were variously called "Green River Indians", "White River Indians", or by their nativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound (geography), sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel. Puget Sound extends approximately from Deception Pass in the north to Olympia, Washington, Olympia in the south. Its average depth is and its maximum depth, off Jefferson Point between Indianola, Washington, Indianola and Kingston, Washington, Kingston, is . The depth of the main basin, between the southern tip of Whidbey Island and Tacoma, Washington, Tacoma, is approximately . In 2009, the term Salish Sea was established by the United States Board on Geographic Names as the collective wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Salish Languages
The Coast Salish languages, also known as the Central Salish languages, are a branch of the Salishan language family. These languages are spoken by First Nations or Native American peoples inhabiting the Pacific Northwest, in the territory that is now known as the southwest coast of British Columbia around the Strait of Georgia and Washington State around Puget Sound. The term "Coast Salish" also refers to the cultures in British Columbia and Washington who speak one of these languages or dialects. Geography The Coast Salish languages are spoken around most of the Georgia and Puget Sound Basins, an area that encompasses the sites of the modern-day cities of Vancouver, British Columbia, Seattle, Washington, and others. Archeological evidence indicates that Coast Salish peoples may have inhabited the area as far back as 9000 BCE. What is now Seattle, for example, has been inhabited since the end of the last glacial period (c. 8,000 BCE—10,000 years ago). In the past, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twana Language
The Twana () language, also known as Skokomish, is a Coast Salish language of the Salishan language family, spoken by the Twana, the Indigenous people of Hood Canal, in Washington. The name "Skokomish" is an Anglicization of the Twana word ' and means "river people" or "people of the river". History It is believed by some elders within the Skokomish community (such as Bruce Subiyay Miller) that the language branched off from Lushootseed (a neighboring related Coast Salish language) because of the region-wide tradition of not speaking the name of someone who died for a year after their death. Substitute words were found in their place and often became normalizing in the community, generating differences from one community to the next. Subiyay speculated that this process increased the drift rate between languages and separated Twana firmly from Lushootseed. The last fluent speaker died in 1980. The Skokomish Indian Tribe released an online Twana dictionary in 2020, and the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |