|
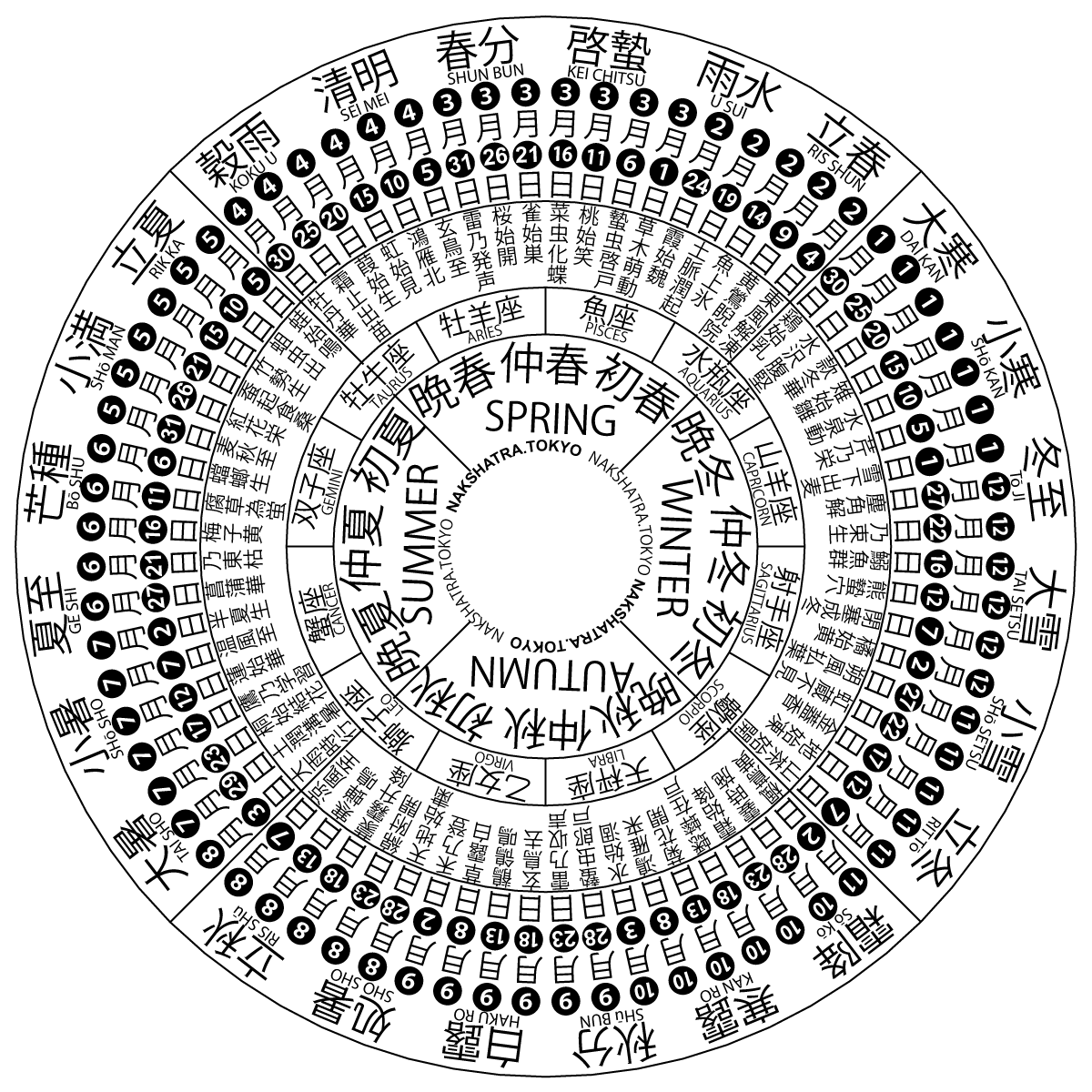
Lunar Station
Often called lunar mansion, a lunar station or lunar house is a segment of the ecliptic through which the Moon passes in its orbit around the Earth. The concept was used by several ancient cultures as part of their calendrical system. Stations in different cultures In general, though not always, the zodiac is divided into 27 or 28 segments relative to the vernal equinox point or the fixed stars – one for each day of the lunar month. (A sidereal month lasts about days.) The Moon's position is charted with respect to those fixed segments. Since the Moon's position at any given stage will vary according to Earth's position in its own orbit, lunar stations are an effective system for keeping track of the passage of seasons. Various cultures have used sets of lunar stations astrologically; for example, the Jyotisha astrological ''nakshatras'' of Hindu culture, the Arabic manzils (''manāzil al-qamar''), the Twenty-Eight Mansions of Chinese astronomy, and the 36 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the fixed stars, background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important Plane of reference, reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrological Sign
In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up ecliptic, Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the Equinox (celestial coordinates), vernal equinox. The astrological signs are Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. The Western zodiac originated in Babylonian astrology, and was later influenced by the Hellenistic astrology, Hellenistic culture. Each sign was named after a constellation planets in astrology, the sun annually moved through while crossing the sky. This observation is emphasized in the simplified and popular sun sign astrology. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Culture
Chinese culture () is one of the Cradle of civilization#Ancient China, world's earliest cultures, said to originate five thousand years ago. The culture prevails across a large geographical region in East Asia called the Sinosphere as a whole and is extremely diverse, with customs and traditions varying greatly between regions. The terms 'China' and the geographical landmass of 'China' have shifted across the centuries, before the name 'China' became commonplace. Chinese civilization is historically considered a dominant culture of East Asia. Chinese culture exerted profound influence on the philosophy, customs, politics, and traditions of Asia. Chinese characters, Chinese ceramics, ceramics, Chinese architecture, architecture, Chinese music, music, History of Chinese dance, dance, Chinese literature, literature, Chinese martial arts, martial arts, Chinese cuisine, cuisine, Chinese art, arts, Chinese philosophy, philosophy, etiquette, Religion in China, religion, Legalism (Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Symbols
The Four Symbols are mythological creatures appearing among the Chinese constellations along the ecliptic, and viewed as the guardians of the four cardinal directions. These four creatures are also referred to by a variety of other names, including "Four Guardians", "Four Gods", and "Four Auspicious Beasts". They are the Azure Dragon of the East, the Vermilion Bird of the South, the White Tiger of the West, and the Black Tortoise (also called "Black Warrior") of the North. Each of the creatures is most closely associated with a cardinal direction and a color, but also additionally represents other aspects, including a season of the year, an emotion, virtue, and one of the Chinese " five elements" (wood, fire, earth, metal, and water). Each has been given its own individual traits, origin story and a reason for being. Symbolically, and as part of spiritual and religious belief and meaning, these creatures have been culturally important across countries in the Sinosphere. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Term
A solar term (or ''jiéqì'', zh, t=節氣, s=节气) is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the '' Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient type of sundial called (). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; not until the Taichu Calendar of 104 BC were all twenty-four solar terms officially included in the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky – as viewed from the Earth or another celestial body of the Solar System – thus completing a full cycle of astronomical seasons. For example, it is the time from vernal equinox to the next vernal equinox, or from summer solstice to the next summer solstice. It is the type of year used by tropical solar calendars. The tropical year is one type of astronomical year and particular orbital period. Another type is the sidereal year (or sidereal orbital period), which is the time it takes Earth to complete one full orbit around the Sun as measured with respect to the fixed stars, resulting in a duration of 20 minutes longer than the tropical year, because of the precession of the equinoxes. Since antiquity, astronomers have progressively refined the definition of the tropical year. The entry for "year, tropical" in the '' Astronomical Almanac Onlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereal Month
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month. Variations In Shona, Middle Eastern, and European traditions, the month starts when the young crescent moon first becomes visible, at evening, after conjunction with the Sun one or two days before that evening (e.g., in the Islamic calendar). In ancient Egypt, the lunar month began on the day when the waning moon could no longer be seen just before sunrise. Others run from full moon to full moon. Yet others use calculation, of varying degrees of sophistication, for example, the Hebrew calendar, the Chinese calendar, or the ecclesiastical lunar calendar. Calendars count integer days, so months may be 29 or 30 days in length, in some regular or irregular sequence. Lunar cycles are prominent, and calculated with great precision in the ancient Hindu Panchangam calendar, widely use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian Cultural Sphere
The Sinosphere, also known as the Chinese cultural sphere, East Asian cultural sphere, or the Sinic world, encompasses multiple countries in East Asia and Southeast Asia that were historically heavily influenced by Chinese culture. The Sinosphere comprises Greater China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. Other definitions may include the regions of modern-day Mongolia and Singapore, due either to historical Chinese influence or a contemporary overseas Chinese population. The Sinosphere is different from the Sinophone world, which indicates regions where the Chinese language is spoken. Imperial China was a major regional power in Eastern Asia and exerted influence on tributary states and neighboring states, including Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. These interactions brought ideological and cultural influences rooted in Confucianism, Buddhism, and Taoism. The four cultures were ruled by their respective emperors under similar imperial systems. Chinese inventions influenced, and were in turn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Century BC
The 6th century BC started on the first day of 600 BC and ended on the last day of 501 BC. In Western Asia, the first half of this century was dominated by the Neo-Babylonian Empire, which had risen to power late in the previous century after successfully rebelling against Assyrian rule. The Kingdom of Judah came to an end in 586 BC when Babylonian forces under Nebuchadnezzar II captured Jerusalem, and removed most of its population to their own lands. Babylonian rule was ended in the 540s by Cyrus, who founded the Persian Empire in its stead. The Persian Empire continued to expand and grew into the greatest empire the world had known at the time. In Iron Age Europe, the Celtic expansion was in progress. China was in the Spring and Autumn period. *Mediterranean: Beginning of Greek philosophy, flourishes during the 5th century BC *The late Hallstatt culture period in Eastern and Central Europe, the late Bronze Age in Northern Europe *East Asia: the Spring and Autumn perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the end of the urban Indus Valley Civilisation and a second urbanisation, which began in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain BCE. The Vedas are liturgical texts which formed the basis of the influential Brahmanical ideology, which developed in the Kuru Kingdom, a tribal union of several Indo-Aryan tribes. The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred. The Vedas were composed and orally transmitted with precision by speakers of an Old Indo-Aryan language who had migrated into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copts
Copts (; ) are a Christians, Christian ethnoreligious group, ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptians, Egyptian population, descended from the ancient Egyptians. Copts predominantly follow the Coptic Orthodox Church in Alexandria. They are the largest Christianity in Egypt, Christian denomination in Egypt and the Christianity in the Middle East, Middle East, as well as in Christianity in Sudan, Sudan and Christianity in Libya, Libya.Coptic Orthodox Church Listings for Libya, p. 136 Copts in Egypt, Copts account for roughly 5 to 15 percent of the Demographics of Egypt, population of Egypt. Originally referring to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haly Abenragel
Abū l-Ḥasan 'Alī ibn Abī l-Rijāl al-Shaybani () (commonly known in European languages as ''Haly'', ''Hali'', ''Albohazen Haly filii Abenragel'' or ''Haly Abenragel'', from ''ibn Rijal'') was an Arab astrologer of the 10th to 11th century CE / 4th to 5th century AH best known for his ''Kitāb al-bāri' fī aḥkām an-nujūm''. Life He was a court astrologer to the Tunisian prince al-Mu'izz ibn Bâdis in the first half of the 11th century CE / 5th century AH. Haly died after 1037/428 in Kairouan in what is now Tunisia. Works His ''Kitāb al-bāri' fī aḥkām an-nujūm'' was translated by Yehudā ben Moshe into Old Castilian for Alfonso X of Castile in 1254 under the title ''El libro conplido en los iudizios de las estrellas'' ("The complete book on the judgment of the stars"). The only surviving manuscript of the Old Castilian translation is MS 3065 at the National Library in Madrid, which however only contains 5 of the 8 books of the complete Old Castilian translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |