|
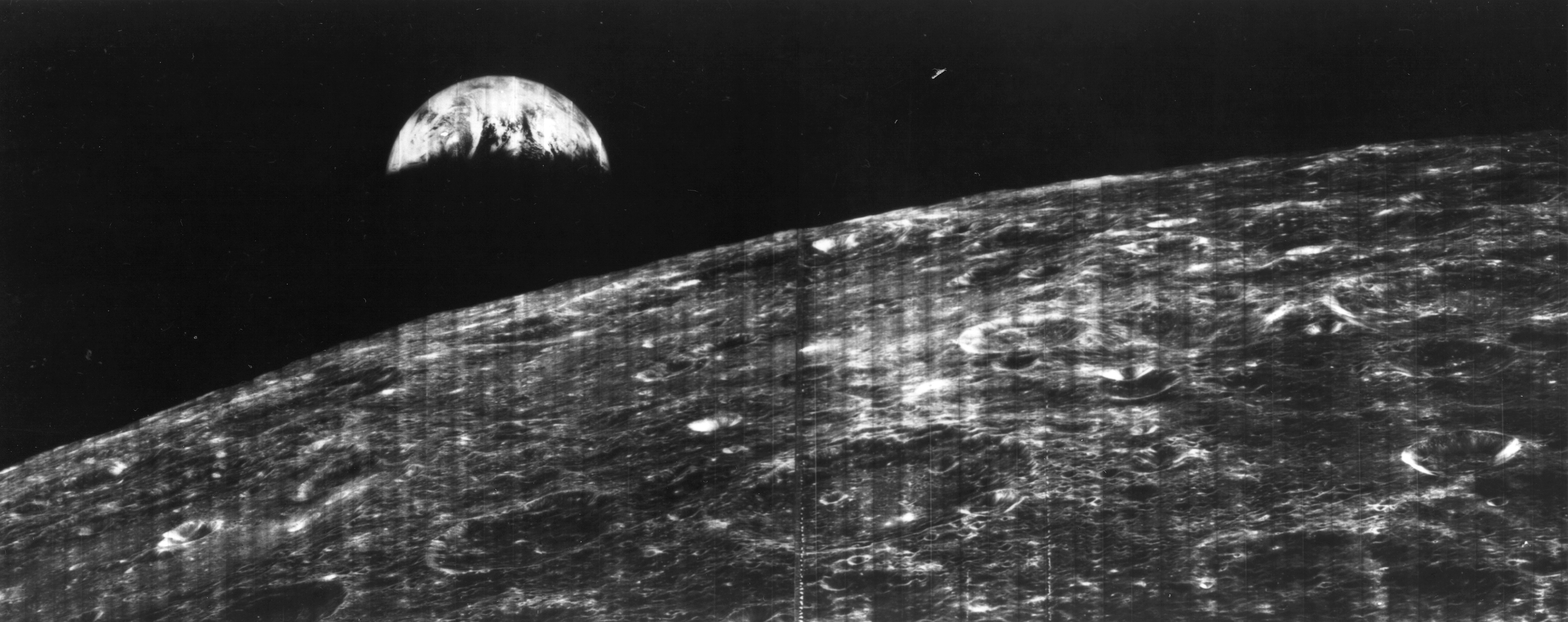
Lunar Orbiter 2
The 1966 Lunar Orbiter 2 robotic spacecraft mission, part of the Lunar Orbiter program, Lunar Orbiter Program, was designed primarily to photograph smooth areas of the lunar surface for selection and verification of safe landing sites for the Surveyor program, Surveyor and Project Apollo, Apollo missions. It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data. Mission summary The spacecraft was placed in a Free-return trajectory, cislunar trajectory and injected into an elliptical near-equatorial lunar orbit for data acquisition after 92.6 hours' flight time. The initial orbit was at an inclination of 11.8 degrees. The perilune was lowered to five days later after 33 orbits. A failure of the amplifier on the final day of readout, December 7, resulted in the loss of six photographs. On December 8, 1966 the inclination was altered to 17.5 degrees to provide new data on lunar gravity. The spacecraft acquired photographic data from Nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
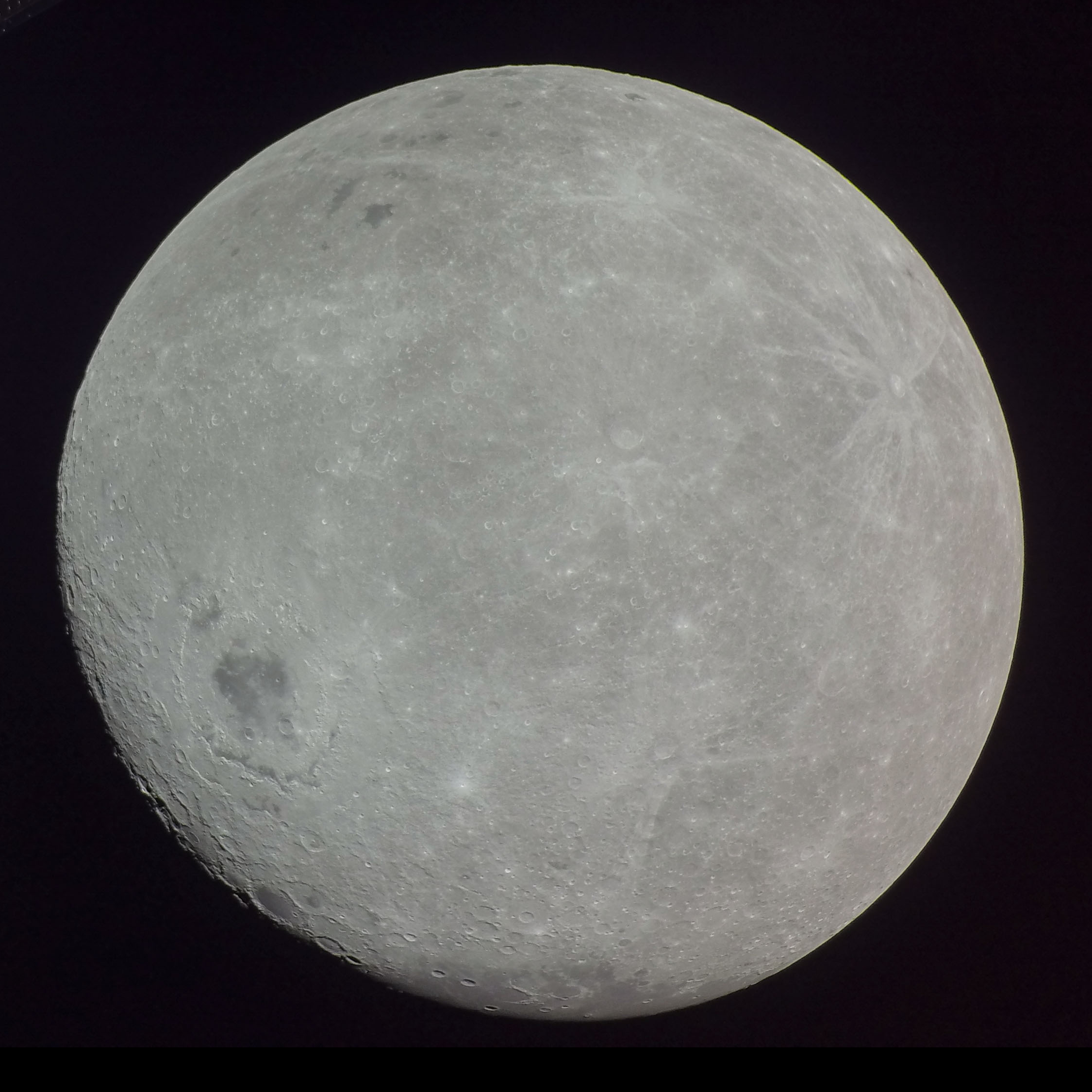
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-return Trajectory
In orbital mechanics, a free-return trajectory is a trajectory of a spacecraft traveling away from a primary body (for example, the Earth) where gravity due to a secondary body (for example, the Moon) causes the spacecraft to return to the primary body without Spacecraft propulsion, propulsion (hence the term ''free''). Many free-return trajectories are designed to intersect the atmosphere; however, periodic versions exist which pass the moon and Earth at constant periapsis, which have been proposed for cyclers. Earth–Moon The first spacecraft to use a free-return trajectory was the Soviet Luna 3 mission in October 1959. It used the Moon's gravity to send it back towards the Earth so that the photographs it had taken of the far side of the Moon could be downloaded by radio. Symmetrical free-return trajectories were studied by Arthur Schwaniger of NASA in 1963 with reference to the Earth–Moon system. He studied cases in which the trajectory at some point crosses at a right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbiter 4
Lunar Orbiter 4 was a robotic U.S. spacecraft, part of the Lunar Orbiter program, Lunar Orbiter Program, designed to orbit the Moon, after the three previous orbiters had completed the required needs for Project Apollo, Apollo mapping and site selection. It was given a more general objective, to "perform a broad systematic photographic survey of lunar surface features in order to increase the scientific knowledge of their nature, origin, and processes, and to serve as a basis for selecting sites for more detailed scientific study by subsequent orbital and landing missions". It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data. Mission summary The spacecraft was placed in a Free-return trajectory, cislunar trajectory and injected into an elliptical near polar high lunar orbit for data acquisition. The orbit was with an inclination of 85.5 degrees and a period of 12 hours. After initial photography on May 11, 1967 problems started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missions To The Moon
Missions to the Moon have been numerous and include some of the earliest space missions, conducting exploration of the Moon since 1959. The first partially successful lunar mission was Luna 1 (January 1959), the first probe to leave Earth and fly past another astronomical body. Soon after that the first Moon landing and the first landing on any extraterrestrial body was performed by Luna 2, which intentionally impacted the Moon on 14 September 1959. The far side of the Moon, which is always facing away from Earth due to tidal locking, was seen for the first time by Luna 3 in (7 October 1959). In 1966, Luna 9 became the first spacecraft to achieve a controlled soft landing, while Luna 10 became the first mission to enter orbit, and in 1968 Zond 5 became the first mission to carry terrestrial lifeforms (tortoises) to close proximity of the Moon through a circumlunar approach. The first crewed missions to the Moon were pursued by the Soviet Union and the United States, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Artificial Objects On The Moon
This is a partial list of artificial materials left on the Moon, many during the missions of the Apollo program. The table below does not include lesser Apollo mission artificial objects, such as a hammer and other tools, Laser Ranging Retroflector, retroreflectors, Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Packages, or the commemorative, artistic, and personal objects left by the twelve Project Apollo, Apollo astronauts, such as the Lunar Flag Assembly, United States flags, the Lunar plaque, commemorative plaques attached to the ladders of the six Apollo Lunar Modules, the silver astronaut pin left by Alan Bean in honor of Clifton C. Williams whom he replaced, the Bible left by David Scott, the ''Fallen Astronaut'' statuette and memorial plaque placed by the crew of Apollo 15, the Apollo 11 goodwill messages disc, or the golf balls Alan Shepard hit during an Apollo 14 moonwalk. Five S-IVB third stages of Saturn V rockets from the Apollo program crashed into the Moon, and are the heaviest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of The Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made a deliberate impact on the surface of the Moon on 14 September, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of lunar exploration had been observations from Earth. The invention of the optical telescope brought about the first leap in the quality of lunar observations. Galileo Galilei is generally credited as the first person to use a telescope for astronomical purposes, having made his own telescope in 1609, the mountains and craters on the lunar surface were among his first observations using it. Human exploration of the Moon since Luna 2 has consisted of both crewed and uncrewed missions. NASA's Apollo program has been the only program to successfully land humans on the Moon, which it did six times on the near side in the 20th century. The first human landing took place in 1969, when the Apollo 11 astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong touched down on the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbiter Image Recovery Project
The Lunar Orbiter Image Recovery Project (LOIRP) was a project to digitize the original analog data tapes from the five Lunar Orbiter spacecraft that were sent to the Moon in 1966 and 1967; it was funded by NASA, SkyCorp, SpaceRef Interactive, and private individuals. The first image to be successfully recovered by the project was released in November 2008. It was the first photograph of the Earth from the Moon, taken in August 1966. On February 20, 2014, the project announced it had completed the primary tape capture portion of the project. One medium resolution image, most of one high resolution image and parts of three others are missing, apparently due to lapses at the time they were being recorded. The rest of the Lunar Orbiter images have been successfully recovered and have been published in NASA's Planetary Data System. Background The images taken by the Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were primarily used to locate landing sites for the crewed Apollo missions. Once those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunowsky (lunar Crater)
Kunowsky is a small lunar impact crater on the Mare Insularum, in the western half of the Moon's near side. It is named after the German astronomer Georg Karl Friedrich Kunowsky. It lies about one third the distance from Encke to the west-northwest and Lansberg to the east-southeast. This formation is surrounded by lunar mare, and the interior has been flooded by basaltic lava Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ..., leaving only a roughly circular rim projecting above the surface. The rim is slender and sharp-edged, with no significant erosion. Apart from a tiny craterlet at the midpoint of the interior floor, this crater has no other significant features. It does lie in a region of the mare where Ray system, rays from the craters Kepler (lunar crater), Kepler to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mare Insularum
Mare Insularum (Latin ''īnsulārum'', the "sea of islands") is a lunar mare located in the Insularum basin just south of the western Mare Imbrium. The basin material is of the Lower Imbrian epoch, with the mare material of the Upper Imbrian epoch. The mare is bordered by the craters Copernicus on the east, and Kepler on the west. Oceanus Procellarum joins the mare to the southwest. Copernicus is one of the most noticeable craters on the Moon. The rays from both Kepler and Copernicus protrude into the mare. It is located near the crater Fra Mauro, the site of the Apollo 14 Apollo 14 (January 31February 9, 1971) was the eighth crewed mission in the United States Apollo program, the third to Moon landing, land on the Moon, and the first to land in the Geology of the Moon#Highlands, lunar highlands. It was the las ... landing. Sinus Aestuum forms a northeastern extension to the mare. The name was suggested by lunar geologist Don E. Wilhelms.To a Rocky Moon: A Geologist' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambart (crater)
Gambart is a small lunar impact crater on the Mare Insularum, near the central region of the Moon. It is named after French astronomer Jean-Félix Adolphe Gambart. It can be located to the south-southeast of the prominent ray crater Copernicus. In the past, the floor of Gambart has been flooded with lava, leaving a relatively flat surface surrounded by a smooth but somewhat polygon-shaped outer rim. To the southwest of Gambart is an area of hilly terrain deposited from ejecta during the Mare Imbrium impact, known as the Fra Mauro Formation. The smaller Gambart C crater is located to the northeast of Gambart itself. Roughly between Gambart and Gambart C is a lunar dome, a type of shield volcano. The Surveyor 2 probe crashed to the northeast of Gambart C. Satellite craters By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Gambart. Images File:Gambart A crater 4121 h1.jpg, Lunar Orbiter 4 ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariadaeus (crater)
Ariadaeus is a small, bowl-shaped lunar impact crater on the western shores of Mare Tranquillitatis. It lies to the north of the crater Dionysius, and to the west-southwest of Arago. The crater is joined along the northeast rim by the slightly smaller Ariadaeus A, and the two form a double-crater. Its diameter is 10.4 km. This crater marks the eastern extent of the rille designated Rima Ariadaeus. This wide rille extends in a nearly straight line to the west-northwest, passing just to the north of the crater Silberschlag. Other rille systems lie in the vicinity, including the Rimae Ritter to the southeast and Rimae Sosigenes to the northeast. The crater was named after Philip III of Macedon Philip III Arrhidaeus (; BC – 317 BC) was king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia from 323 until his execution in 317 BC. He was a son of King Philip II of Macedon by Philinna of Larissa, and thus an elder half-brother of Alexander th ... (Arrhidaeus).Antonín Rükl, ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric Polar orbit, polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions to the Moon. Its detailed mapping program is identifying safe landing sites, locating potential resources on the Moon, characterizing the radiation environment, and demonstrating new technologies. Launched on June 18, 2009, in conjunction with the LCROSS, Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS), as the vanguard of NASA's Lunar Precursor Robotic Program, LRO was the first United States mission to the Moon in over ten years. LRO and LCROSS were launched as part of the United States's Vision for Space Exploration program. The probe has made a 3-D map of the Moon's surface at 100-meter resolution and 98.2% coverage (excluding polar areas in deep shadow), including 0.5-meter resolution images of Apollo landing sites. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |