|
Lugbara Kari
Lugbara Kari (which can be translated as "House of Lugbara") refers to the official traditional and cultural institution of all Lugbara people on Earth and headed by the Agofe. History Although cultural institutions were abolished in 1967, the 1995 Constitution of Uganda helped revive them. Lugbara Kari started rebuilding by establishing interim county chiefs answerable to the Agofe. The 3rd Agofe of Lugbara Kari is educationist Jason Avutia who will be replaced through elections in 2021 after his 94th birthday. Structure Administratively, Lugbara Kari has county chiefs who answer to the elected Paramount Chief; each chief (from Ayivu, Maracha, Terego, Vurra, Aringa, Madi, Kebu, etc) is a potential future agofe. The Lugbara have no ''opi'' ranslated from Lugbara: king Functions and objectives of Lugbara Kari include enhancing cooperation among Lugbara and promoting heritage plus the Lugbara language. With the motto "MUNGU le Lugbara ambo OD loves the Lugbara very much, Lugbara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugbara People
The Lugbara are a Central Sudanic ethnic group who live primarily in the West Nile region of Uganda, in the adjoining area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) with a few living in South Sudan. They speak the Lugbara language, a Central Sudanic language similar to the language spoken by the Madi, with whom they also share many cultural similarities. Traditions and culture Traditionally, the Lugbara are farmers who rear some livestock and poultry, mainly guineafowl locally known as ''ope''; they are the predominant keepers of guineafowl in Uganda. Lugbara occupy the West Nile region of Uganda (Arua City, Arua, Maracha, Terego, Madi-Okollo, Yumbe and Koboko districts of Uganda to be specific). The Lugbara are divided into many dialects which are easily understandable to each other. These include: Ayivu, Maracha, Terego, Vurra and Aringa. Tribes related to the Lugbara in language include Madi and Kaliko in South Sudan. The Lugbara also have a special name-giving ceremon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agofe
Agofe is the noble title for the chief cultural leader among all the Lugbara people or King of Lado Kingdom which covers the regions of West Nile, Ituri, Torit, Uele and Yei. The term means 'Pillar' or 'Paramount Chief' (Chief of chiefs) and was the title given to Jalusiga (an Alur chosen by the British). A king is also called ''opi'' in Lugbara though an opi is usually a chief or the clan leader of a Lugbara lineage. Around 1967, President Milton Obote abolished kingdoms, but then the 1995 Uganda Constitution reinstated cultural institutions and by 2000, the Lugbara Cultural Institution had evolved. In 2015, the Government of Uganda finally accepted this revised Agofe institution among the 17 recognised cultural institutions in Uganda. The Agofe's duty is to preserve Lugbara culture through literature and other assignments. Paramount Chiefs Jalwere Jalusiga (1896-1978) from Alur Tribe was appointed Paramount Chief over the whole of West Nile by British colonialists in 1922. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugbara Language
Lugbara, or Lugbarati, is the language of the Lugbara people. It is spoken in the West Nile region in northwestern Uganda, as well as the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Orientale Province with a little extension to the South Sudan as the Zande or Azande people. Classification and dialects The Aringa language, also known as Low Lugbara, is closely related, and sometimes considered a dialect of Lugbara. In fact, among the Lugbara of Uganda, it is one of the five clans (Ayivu clan, Vurra clan, Terego clan, Maracha clan, and Aringa clan). Some scholars classify the Lugbara language itself as a dialect of the Maʼdi language, though this is not generally accepted. An SIL survey report concluded that the Okollo, Ogoko, and Rigbo dialects, called "Southern Maʼdi", should be classified as dialects of Lugbara. Phonology Vowels * /ɛ, ɔ/ can also be heard as , oas a result of vowel harmony. * /a/ can have an allophone of �when after sounds /k, ɡ/. Consonants * /l/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
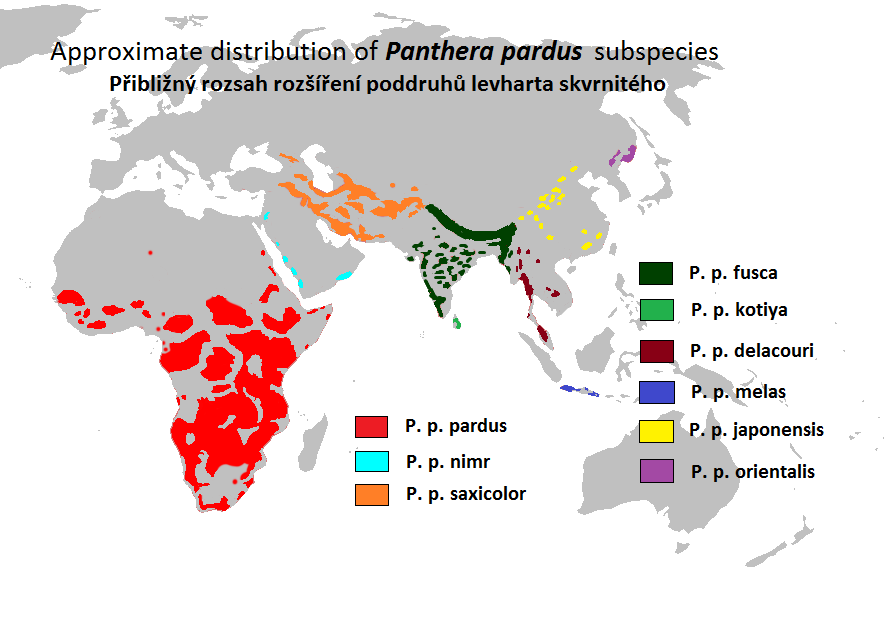
Leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a long tail and a shoulder height of . Males typically weigh , and females . The leopard was first described in 1758, and several subspecies were proposed in the 19th and 20th centuries. Today, eight subspecies are recognised in its wide range in Africa and Asia. It initially evolved in Africa during the Early Pleistocene, before migrating into Eurasia around the Early–Middle Pleistocene transition. Leopards were formerly present across Europe, but became extinct in the region at around the end of the Late Pleistocene-early Holocene. The leopard is adapted to a variety of habitats ranging from rainforest to steppe, including arid and montane areas. It is an opportunistic predator, hunting mostly ungulates and primates. It relies on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiefdom
A chiefdom is a political organization of people representation (politics), represented or government, governed by a tribal chief, chief. Chiefdoms have been discussed, depending on their scope, as a stateless society, stateless, state (polity), state analogue or early state system or institution. Usually a chief's position is based on kinship, which is often monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites can form a political-ideological aristocracy relative to the general group. Chiefdoms and chiefs are sometimes identified as the same as kingdoms and kings, and therefore understood as monarchy, monarchies, particularly when they are understood as not necessarily states, but having monarchic representation or government. Concept In anthropology, anthropological theory, one model of human social development rooted in ideas of cultural evolution describes a chiefdom as a form of social organization more complex than a tribe or a band s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugbara
{{disambig ...
Lugbara may refer to: *Lugbara people *Lugbara language Lugbara, or Lugbarati, is the language of the Lugbara people. It is spoken in the West Nile region in northwestern Uganda, as well as the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Orientale Province with a little extension to the South Sudan as the Za ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |