|
Lueders Formation
The Lueders Formation is a geologic formation in Texas. It is the top formation of the Albany Group and preserves fossils dating back to the Permian period. Description Paleogeography At the time of deposition, a broad sea connected to the Panthalassic Ocean covered much of the central United States, including Texas. The Lueders Formation would have been located in the northern tropics or subtropics. Climatically, after the retreat of an early Artinskian glacial maximum, the deserts of the North American craton experienced fluctuation and growth during this time period, and the associated aridity decrease impacted seabed deposition in localities across the basin. Depositional environment The Lueders Formation represents a deltaic environment, with terrestrial sediments being deposited onto the muddy bottom of a shallow estuary by shifting freshwater streams. In the Maybelle Member, the dolomite likely represents marine deposits, preserving marine sharks and fish, whereas dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilbarger County, Texas
Wilbarger County ( ) is a county located in the North Texas region of the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,887. The county seat is Vernon. The county was created in 1858 and later organized in 1881. Wilbarger is named for Josiah Pugh Wilbarger and Mathias Wilbarger, two early settlers. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which are land and (0.7%) are covered by water. Major highways * U.S. Highway 70 * U.S. Highway 183 * U.S. Highway 283 * U.S. Highway 287 Adjacent counties * Tillman County, Oklahoma (north) * Wichita County (east) * Baylor County (south) * Foard County (west) * Hardeman County (west) * Jackson County, Oklahoma (northwest) Demographics Census-designated places * Harrold * Lockett * Oklaunion Population ''Note: the US Census treats Hispanic/Latino as an ethnic category. This table excludes Latinos from the racial categories and assigns them to a separate cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Maximum
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and greenhouse periods, during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the Quaternary glaciation. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed ''glacial periods'' (or, alternatively, ''glacials, glaciations, glacial stages, stadials, stades'', or colloquially, ''ice ages''), and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called ''interglacials'' or ''interstadials''. In glaciology, ''ice age'' implies the presence of extensive ice sheets in both northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, Earth is currently in an interglacial period—the Holocene. The amount of anthropogenic greenhouse gases emitted into Earth's oceans and atmosphere is predicted to prevent the next glacial period for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eryopidae
Eryopidae were a group of medium to large amphibious temnospondyli, known from North America and Europe. They are defined as all eryopoids with interpterygoid vacuities (spaces in the interpterygoid bone) that are rounded at the front; and large external nares (Laurin and Steyer 2000). Not all of the genera previously included in the Eryopidae (Carroll 1988) are retained under the cladistic revisions. Gallery File:Eryops1DB.jpg, '' Eryops megacephalus'', of the late Carboniferous to early Permian of North America File:Onchiodon12DB.jpg, '' Onchiodon'', of the late Carboniferous to early Permian of Europe and North America File:Actinodon frossardi 1DB.jpg, '' Actinodon frossardi'', of the early Permian of France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ... File:Clamorosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
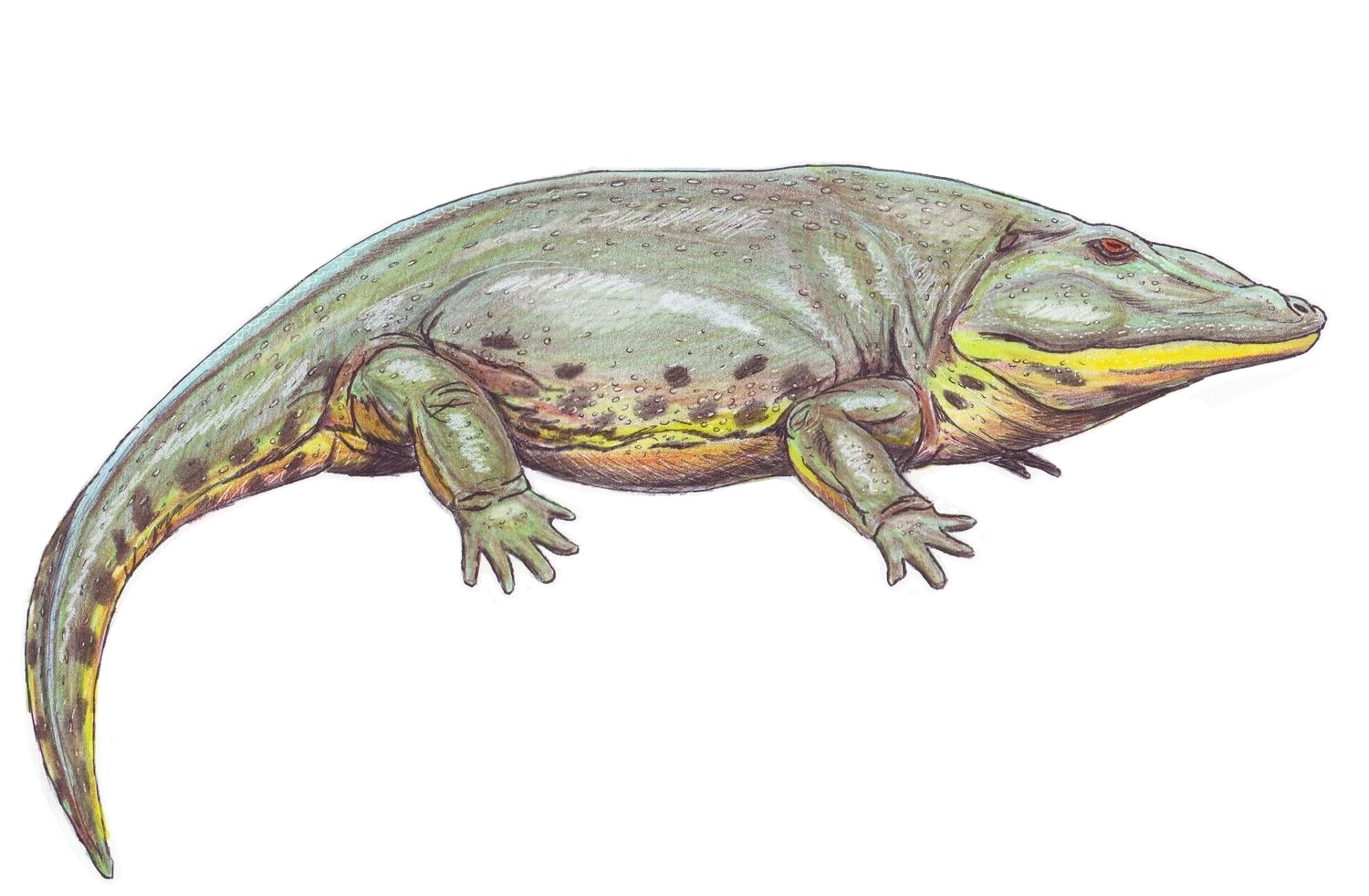
Eryops
''Eryops'' (; from Greek , , 'drawn-out' + , , 'face', because most of its skull was in front of its eyes) is a genus of extinct, amphibious temnospondyls. It contains the single species , the fossils of which are found mainly in early Permian (about 295 million years ago) rocks of the Texas Red Beds, located in Archer County, Texas. Fossils have also been found in late Carboniferous period rocks from New Mexico. Several complete skeletons of ''Eryops'' have been found in lower Permian rocks, but skull bones and teeth are its most common fossils. Description ''Eryops'' averaged a little over long and could grow up to , making them among the largest land animals of their time. Adults weighed between . The skull was proportionately large, being broad and flat and reaching lengths of . It had an enormous mouth with many curved teeth like the frog. Its teeth had enamel with a folded pattern, leading to its early classification as a "labyrinthodont" ("maze toothed"). The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplocaulus Underside (Updated)
''Diplocaulus'' (meaning "double caul") is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibians which lived from the Late Carboniferous to the Late Permian of North America and Africa. ''Diplocaulus'' is by far the largest and best-known of the lepospondyls, characterized by a distinctive boomerang-shaped skull. Remains attributed to ''Diplocaulus'' have been found from the Late Permian of Morocco and represent the youngest-known occurrence of a lepospondyl. Description ''Diplocaulus'' had a stocky, salamander-like body, but was relatively large, reaching up to in length. Although a complete tail is unknown for the genus, a nearly complete articulated skeleton described in 1917 preserved a row of tail vertebrae near the head. This was construed as circumstantial evidence for a long, thin tail capable of reaching the head if the animal was curled up. Most studies since this discovery have argued that anguiliform (eel-like) tail movement was the main force of locomotion utilized by ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
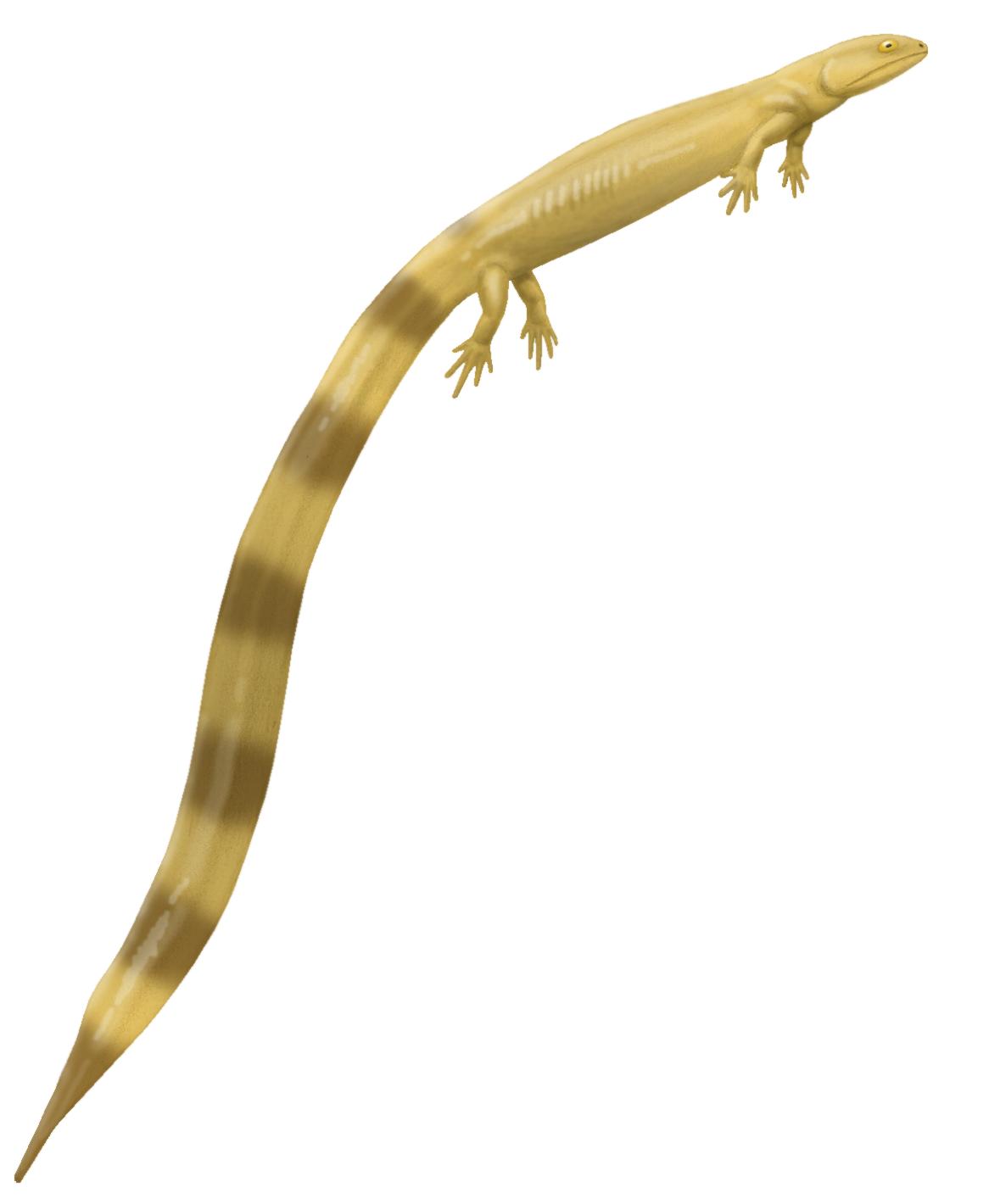
Diplocaulus
''Diplocaulus'' (meaning "double caul") is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibians which lived from the Late Carboniferous to the Late Permian of North America and Africa. ''Diplocaulus'' is by far the largest and best-known of the lepospondyls, characterized by a distinctive boomerang-shaped skull. Remains attributed to ''Diplocaulus'' have been found from the Late Permian of Morocco and represent the youngest-known occurrence of a lepospondyl. Description ''Diplocaulus'' had a stocky, salamander-like body, but was relatively large, reaching up to in length. Although a complete tail is unknown for the genus, a nearly complete articulated skeleton described in 1917 preserved a row of tail vertebrae near the head. This was construed as circumstantial evidence for a long, thin tail capable of reaching the head if the animal was curled up. Most studies since this discovery have argued that anguiliform (eel-like) tail movement was the main force of locomotion utilized by ''Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectridean
Nectridea is the name of an extinct order of lepospondyl tetrapods from the Carboniferous and Permian periods, including animals such as ''Diplocaulus''. In appearance, they would have resembled modern newts or aquatic salamanders, although they are not close relatives of modern amphibians. They were characterized by long, flattened tails to aid in swimming, as well as numerous features of the vertebrae. Description Nectrideans are a diverse group of tetrapods, including the aquatic Urocordylidae, the presumably terrestrial Scincosauridae, and the bizarre horned members of Diplocaulidae (also known as Keraterpetonidae), which includes the "boomerang-headed" ''Diplocaulus'', one of the most famous genera of prehistoric amphibians (in the traditional sense of the word). By the time the earliest known nectrideans appeared in the Late Carboniferous fossil record, they had already diversified into these families, indicating that basal nectrideans are unknown. These different fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossotelos
''Crossotelos'' is an extinct genus of nectridean lepospondyl within the family Urocordylidae. It contains a single species, ''Crossotelos annulatus''. ''Crossotelos'' lived in modern-day Oklahoma and Texas, United States during the Early to Lower Permian. See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... References Holospondyls {{Lepospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
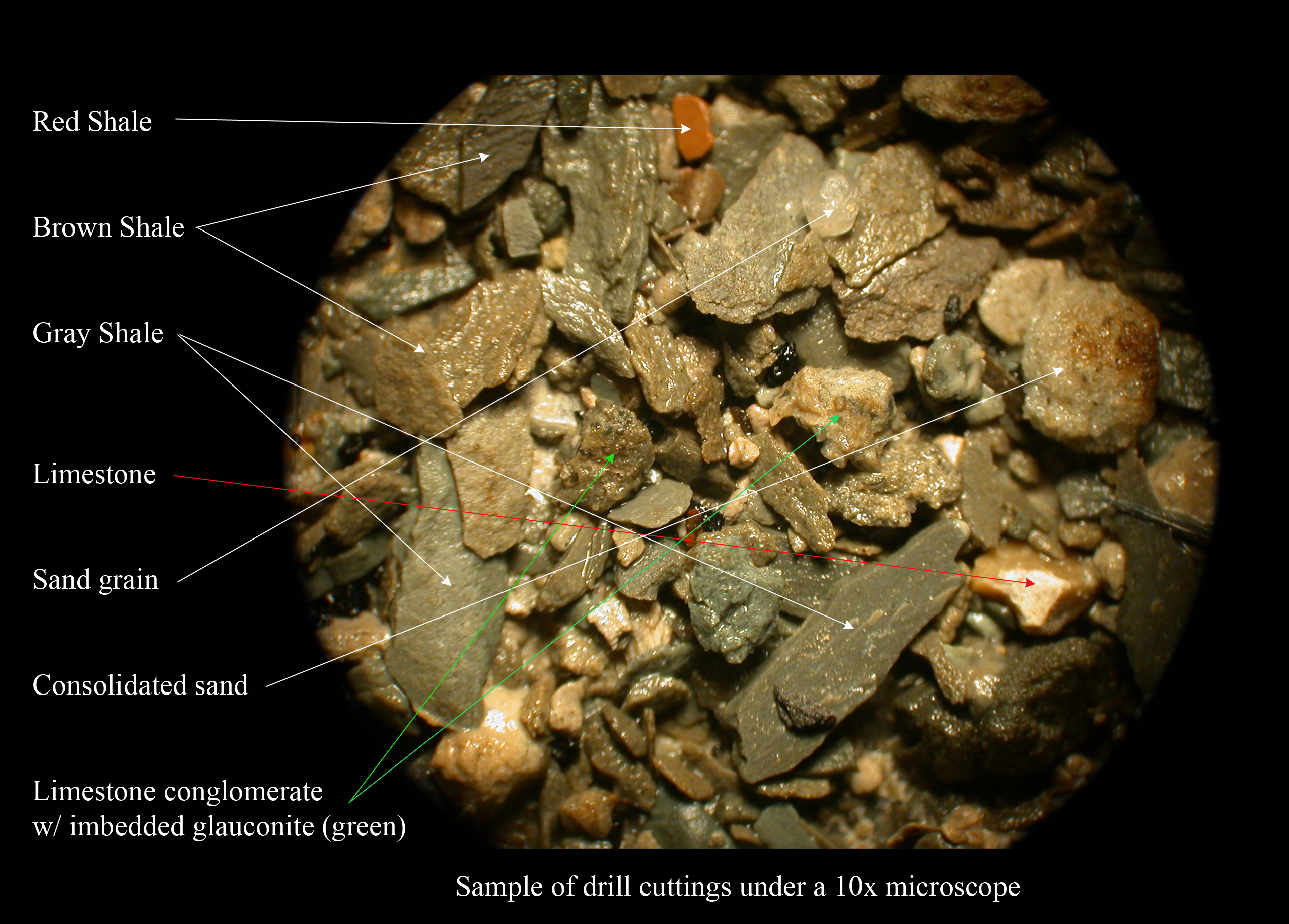
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic'', 2nd ed., Freeman, pp. 281–292 Shale is characterized by its tendency to split into thin layers ( laminae) less than one centimeter in thickness. This property is called '' fissility''. Shale is the most common sedimentary rock. The term ''shale'' is sometimes applied more broadly, as essentially a synonym for mudrock, rather than in the more narrow sense of clay-rich fissile mudrock. Texture Shale typically exhibits varying degrees of fissility. Because of the parallel orientation of clay mineral flakes in shale, it breaks into thin layers, often splintery and usually parallel to the otherwise indistinguishable bed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (rock)
Dolomite (also known as dolomite rock, dolostone or dolomitic rock) is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2. It occurs widely, often in association with limestone and evaporites, though it is less abundant than limestone and rare in Cenozoic rock beds (beds less than about 66 million years in age). The first geologist to distinguish dolomite rock from limestone was Belsazar Hacquet in 1778. Most dolomite was formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or of lime mud before lithification. The geological process of conversion of calcite to dolomite is known as dolomitization and any intermediate product is known as dolomitic limestone. The "dolomite problem" refers to the vast worldwide depositions of dolomite in the past geologic record in contrast to the limited amounts of dolomite formed in modern times. Recent research has revealed sulfate-reducing bacteria living in anoxic conditions precipitate dolomite whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)




.png)