|
Ludvig Fabritius
Ludvig (Lodewyck) Fabritius (14 September 1648, Dutch Brazil – 6 October 1729, Stockholm) was the Swedish Empire, Swedish ambassador to Safavid Iran during the reign of King Charles XI of Sweden, Charles XI (r. 1660–1697) and Charles XII of Sweden, Charles XII (r. 1697–1718). After an early career in the Russian army, he became a diplomat representing the Swedish crown. Fabritius led three missions to the Safavid court: in 1679–80, 1683–84, and 1697–1700. His efforts were characterized by the desire to establish a new transit route between Sweden and Iran through Tsardom of Russia, Russia (with Narva as its hub), and several attempts to establish a fruitful alliance against the common enemy: the Ottoman Empire. Fabritius presented an invitation to the Safavid king from the Swedish king to join the Holy League (1684), Holy League, and was involved in the establishment of several Safavid-Swedish economic and trade agreements. Life Fabriutius was born Lodewyck Fabritius in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Mijtens The Elder
Peter Martin Mijtens the Elder, also spelled Meytens or Mytens (1648- 1736) was a Dutch-Swedish painter. Trained in the Netherlands, he worked principally in the Dutch Republic. Biography He was born at The Hague in the Dutch Republic into a family of artists. His father was Isaac Mijtens (1602-1666), the son of an art dealer and saddler from Brussels. His father and his son Martin van Meytens, known as "The Younger" were both painters. His uncle Daniël Mijtens, and his cousins Daniel Mijtens the Younger and Johannes Mytens were painters as well. He went to Stockholm with his older brother Dietrich Mijtens (d. 1679) where his portraits were well received. In 1681, he decided to stay and shortly after was married to Johanna de Bruyn. Martin Mijtens d. ä. adelsvapen.com His earliest works were very simple compared with n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safavid Empire
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the beginning of History of Iran, modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires. The Safavid List of monarchs of Persia, Shāh Ismail I, Ismā'īl I established the Twelver denomination of Shia Islam, Shīʿa Islam as the Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam, official religion of the empire, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam. An Iranian dynasty rooted in the Sufi Safavid order founded by sheikhs claimed by some sources to be of Kurds, Kurdish origin, it heavily intermarried with Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman, Georgians, Georgian, Circassians, Circassian, and Pontic Greeks, Pontic GreekAnthony Bryer. "Greeks and Türkmens: The Pontic Exception", ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 29'' (1975), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland
Courland is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. Courland's largest city is Liepāja, which is the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke. The literal meaning of the name is "Land of Curonians". Geography and climate Situated in western Latvia, Courland roughly corresponds to the former Latvian districts of Kuldīga, Liepāja, Saldus, Talsi, Tukums and Ventspils. When combined with Semigallia and Selonia, Courland's northeastern boundary is the Daugava River, which separates it from the regions of Latgale and Vidzeme. To the north, Courland's coast lies along the Gulf of Riga. On the west it is bordered by the Baltic Sea, and on the south by Lithuania. It lies between 55° 45′ and 57° 45′ North and 21° and 27° East. The name is also found in the Curonian Spit and Lithuanian ''Karšuvos giria'' - the Courland wood. The area c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, existing from 1569 to 1795. This state was among the largest, most populated countries of 16th- to 18th-century Europe. At its peak in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth spanned approximately and supported a multi-ethnic population of around 12 million as of 1618. The official languages of the Commonwealth were Polish language, Polish and Latin Language, Latin, with Catholic Church, Catholicism as the state religion. The Union of Lublin established the Commonwealth as a single entity on 1 July 1569. The two nations had previously been in a personal union since the Union of Krewo, Krewo Agreement of 1385 (Polish–Lithuanian union) and the subsequent marriage of Queen Jadwiga of Poland to Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania, who was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engelbert Kaempfer
Engelbert Kaempfer (16 September 16512 November 1716) was a German natural history, naturalist, physician, exploration, explorer, and writer known for his tour of Russia, Iran, Persia, India, Southeast Asia, and Japan between 1683 and 1693. He wrote two books about his travels. ''Amoenitatum exoticarum'', published in 1712, is important for its medical observations and the first extensive description of Flora of Japan, Japanese plants (''Flora Japonica''). His ''History of Japan'', published posthumously in 1727, was the chief source of Western knowledge about the country throughout the 18th and mid-19th centuries, when it was closed to foreigners. Early life Kaempfer was born at Lemgo in the Principality of Lippe, within the Holy Roman Empire. His father was a pastor and his mother helped support the congregation. He studied at Hameln, Lüneburg, Hamburg, Lübeck and Danzig (Gdańsk), and after graduating at Kraków, spent four years at Königsberg in Prussia, studying medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
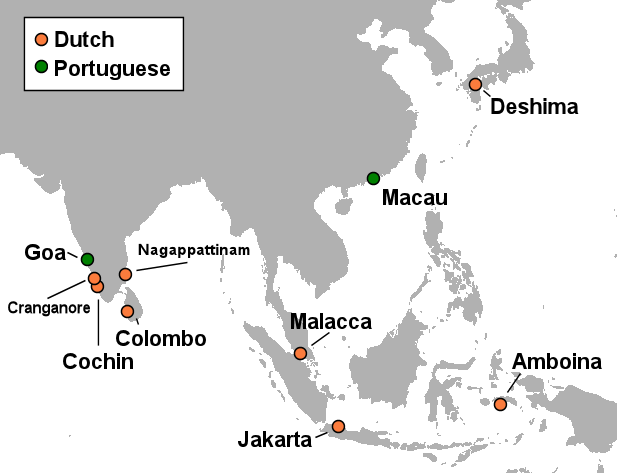
Dutch Empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Dutch East India Company (1602–1799) and Dutch West India Company (1621–1792)—and subsequently governed by the Dutch Republic (1581–1795) and modern Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1975). Following the ''de facto'' independence of the Dutch Republic from the Spanish Empire in the late 16th century, various trading companies known as '' voorcompagnie'' led maritime expeditions overseas in search of commercial opportunities. By 1600, Dutch traders and mariners had penetrated the lucrative Asian spice trade but lacked the capital or manpower to secure or expand their ventures; this prompted the States General in 1602 to consolidate several trading enterprises into the semi-state-owned Dutch East India Company (, VOC), which was g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Julfa
New Julfa (, ''Now Jolfā'', or , ''Jolfâ-ye Now''; , ''Nor Jugha'') is the Armenians, Armenian quarter of Isfahan, Iran, located along the south bank of the Zayanderud. Established and named after the Gülüstan, Nakhchivan, older city of Julfa in the early 17th century (now divided as Jolfa, Iran and Julfa, Azerbaijan (city), Julfa, Azerbaijan), it is still one of the oldest and largest List of Armenian ethnic enclaves, Armenian quarters in the world (:hy:Նոր Ջուղայի գաղութ, hy). History New Julfa was established in 1606 as an Armenian quarter by the mandate of Abbas the Great, sultan of Safavid Iran. Over 150,000 Armenians of Julfa, Armenians were Great Surgun, forcibly moved there from Gülüstan, Nakhchivan, Julfa (also known as ''Jugha'' or ''Juła'', and now as Old Julfa) (:hy:Հայերի բռնագաղթն Իրան (1603-1604), hy). Iranian sources state that the Armenians came to Iran fleeing the Ottoman Empire's persecution. Nevertheless, historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman I Of Persia
Suleiman I (; born Sam Mirza, February or March 1648 – 29 July 1694) was the eighth Shah of Safavid Iran from 1666 to 1694. He was the eldest son of Abbas II and his concubine, Nakihat Khanum. Born as Sam Mirza, Suleiman spent his childhood in the harem among women and eunuchs and his existence was hidden from the public. In 1666, after the death of his father, the nineteen-year-old Sam Mirza was crowned king under the regnal name, Safi II, after his grandfather, Safi I. He had a troublesome reign as Safi II, which convinced his court astrologers that he should undergo a coronation once again. Thus, in 20 March 1668, simultaneously with Nowruz, he was crowned king with a new name, Suleiman I. After his second coronation, Suleiman retreated into his harem to enjoy sexual activities and excessive drinking. He was indifferent to the state affairs, and often would not appear in the public for months. Suleiman's reign was devoid of spectacular events in the form of major wars an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of . It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. The name of the Caspian Sea is derived from the ancient Iranian peoples, Iranic Caspians, Caspi people. The sea stretches from north to south, with an average width of . Its gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Iranica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacular language), size (few or many volumes), intent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ) is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river and numerous islands of its delta. Arkhangelsk was the chief seaport of medieval and early modern Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly founded Saint Petersburg. A railway runs from Arkhangelsk to Moscow via Vologda and Yaroslavl, and air travel is served by the Talagi Airport and the smaller Vaskovo Airport. As of the 2021 Census, the city's population was 301,199. Coat of arms The arms of the city display the Archangel Michael in the act of defeating the Devil. Legend states that this victory took place near where the city stands, hence its name, and that Michael still stands watch over the city to prevent the Devil's return. History Early history Vikings knew the area around Arkhangelsk as Bjarmaland. Ohthere of Hålogaland told circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |