|
Ludus Ludovico
Ludus may refer to: * ''Ludus'' (ancient Rome) (plural ''ludi''), several meanings around "play, game, sport, training" **''Ludi'', public games held for the benefit and entertainment of the Roman people * Luduș, a town in Transylvania, Romania * Ludus Magnus and other gladiatorial training schools * Ludus (love), a type of love/sex in the color wheel theory of love * Ludus (band), a British post-punk band 1978–1983 * "Ludus", one of two movements in Tabula Rasa (Pärt) ''Tabula Rasa'' is a musical composition written in 1977 by the Estonian composer Arvo Pärt. The piece contains two movements, "Ludus" and "Silentium," and is a double concerto for two solo violins, prepared piano, and chamber orchestra. His ..., a 1977 musical composition by the Estonian composer Arvo Pärt See also * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludus (ancient Rome)
''Ludus'' (plural ''ludi'') in ancient Rome could refer to a primary school, a board game, or a gladiator training school. The various meanings of the Latin word are all within the semantic field of "play, game, sport, training" (see also ludic). An elementary or primary school or the school of the "litterator" attended by boys and girls up to the age of 11 was a ''ludus''. ''Ludi'' were to be found throughout the city, and were run by a '' ludi magister'' (schoolmaster) who was often an educated slave or freedman. School started around six o'clock each morning and finished just after midday. Students were taught math, reading, writing, poetry, geometry and sometimes rhetoric. The word ''ludus'' also referred to a training school for gladiators; see Gladiator: Schools and training. Examples include the Ludus Magnus and Ludus Dacicus. ''Ludus'' was also the word for a board game, examples of which include ''ludus latrunculorum'' and ''ludus duodecim scriptorum'', or a game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludi
''Ludi'' (Latin:games; plural of "ludus") were public games held for the benefit and entertainment of the Roman people (''populus Romanus''). ''Ludi'' were held in conjunction with, or sometimes as the major feature of, Roman religious festivals, and were also presented as part of the cult of state. The earliest ''ludi'' were horse races in the circus (''ludi circenses''). Animal exhibitions with mock hunts ('' venationes'') and theatrical performances (''ludi scaenici'') also became part of the festivals. Because some of these entertainments are not competitive "games", ''ludi'' may also be translated more generally as "shows". Days on which ''ludi'' were held were public holidays, and no business could be conducted—"remarkably," it has been noted, "considering that in the Imperial era more than 135 days might be spent at these entertainments" during the year. Although their entertainment value may have overshadowed religious sentiment at any given moment, even in lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luduș
Luduș (; Hungarian: ''Marosludas'' or ''Ludas''; Hungarian pronunciation: , German: ''Ludasch'') is a town in Transylvania, Romania in Mureș County, south-west from the county's capital, Târgu Mureș. Six villages are administered by the town: Avrămești (''Eckentelep''), Cioarga (''Csorga''), Ciurgău (''Csorgó''), Fundătura (''Mezőalbisitelep'' or ''Belsőtelep''), Gheja (''Marosgezse''), and Roșiori (''Andrássytelep''). History * 1330 – First mentioned as Plehanus de Ludas. * 1377 – Mentioned in a transaction between two Hungarian nobles. * 1930 – 5,085 inhabitants. * 1940 to 1944, Hungarians occupied the town. The Jewish population is murdered during the Luduș massacre from 5 to 13 September 1944. * 1960 - Luduș became a town. * 1966 - 11,794 inhabitants. * 2002 - 17,497 inhabitants. Demographics In 1850, the town had 1,166 inhabitants; the ethnic composition of the town according to the 1850 census was: 1,065 (91.34%) Romanians and 34 (2.92%) Hungarians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
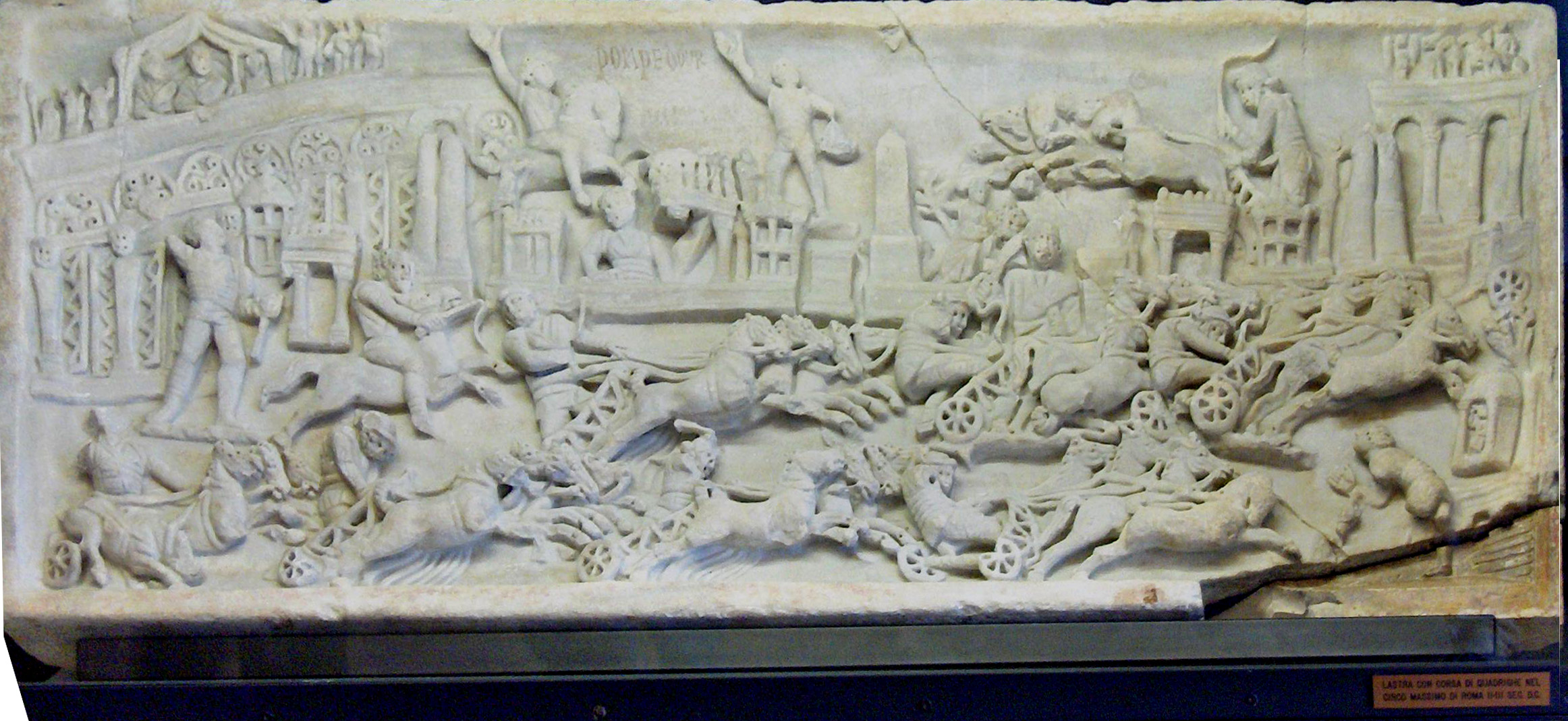
Ludus Magnus
The Ludus Magnus (lat.:''Domus Vectiliana''), also known as the Great Gladiatorial Training School, was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian (r. 81–96 C.E.) in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects undertaken by him such as three other gladiatorial schools across the Roman Empire. The training school is situated directly east of the Colosseum in the valley between the Esquiline and the Caelian hills, an area already occupied by Republican and Augustan structures. While there are remains that are visible today, they belong to a reconstruction that took place under the emperor Trajan (r. 98–117) where the Ludus plane was raised by about 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in). The Ludus Magnus was essentially a gladiatorial arena where gladiators from across the Roman Empire would live, eat, and practice while undergoing gladiatorial training in preparation for fighting at the gladiatorial games held at the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
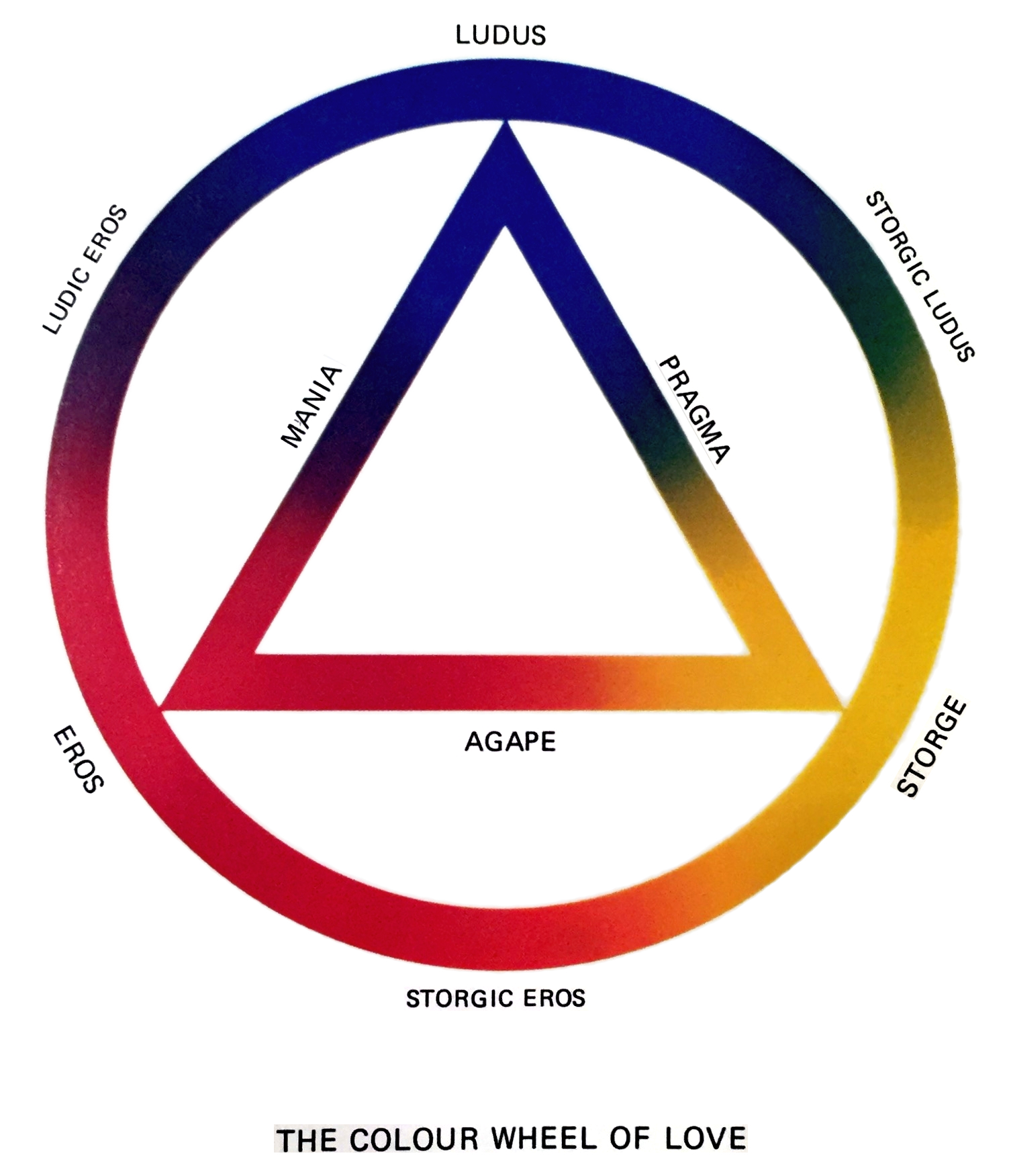
Ludus (love)
The colour wheel theory of love is an idea created by the Canadian psychologist John Alan Lee that describes six love styles, using several Latin and Greek words for love. First introduced in his book ''Colours of Love: An Exploration of the Ways of Loving'' (1973), Lee defines three primary, three secondary, and nine tertiary love styles, describing them in the traditional colour wheel. The three primary types are called Eros (concept), Eros, Ludus, and Storge, and the three secondary types are called Mania, Pragma, and Agape. Eros focuses on the sexual life, Ludus on the playful life, and Storge on the serious life. For the secondary types, Mania (Eros & Ludus) is characterized by obsession and overattachment, Agape (Eros & Storge) by altruism and trust, and Pragma (Ludus & Storge) by realism and practicality. Primary types of love Eros ''Eros (concept), Eros'' is the Greek term for romantic, passionate, or sexual love, from which the term ''erotic'' is derived. Lee des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludus (band)
Ludus was a British post-punk band formed in Manchester in 1978, which featured artist, designer and singer Linder Sterling. They played jazz-, avant-garde- and punk- oriented material. The band influenced singer Morrissey, later of The Smiths and a solo artist, who remains one of the group's most vocal fans. History The band was founded by Linder Sterling, who in the arts and music scene is credited as Linder, having designed the cover of Buzzcocks' single " Orgasm Addict" and Magazine's debut album ''Real Life''; and Arthur Kadmon, formerly of Manicured Noise. Shortly after the formation, ex-Nosebleeds drummer Philip "Toby" Tomanov and bassist Willie Trotter joined to complete the band. It debuted live at the Factory Club, supporting The Pop Group, in October 1978, recording a studio demo the same month. The following month, Ludus played shows at well-known 'punk' venues like Eric's Club in Liverpool and, travelling with Magazine, The Venue in London. Since its live debu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |