|
Ludi Megalenses
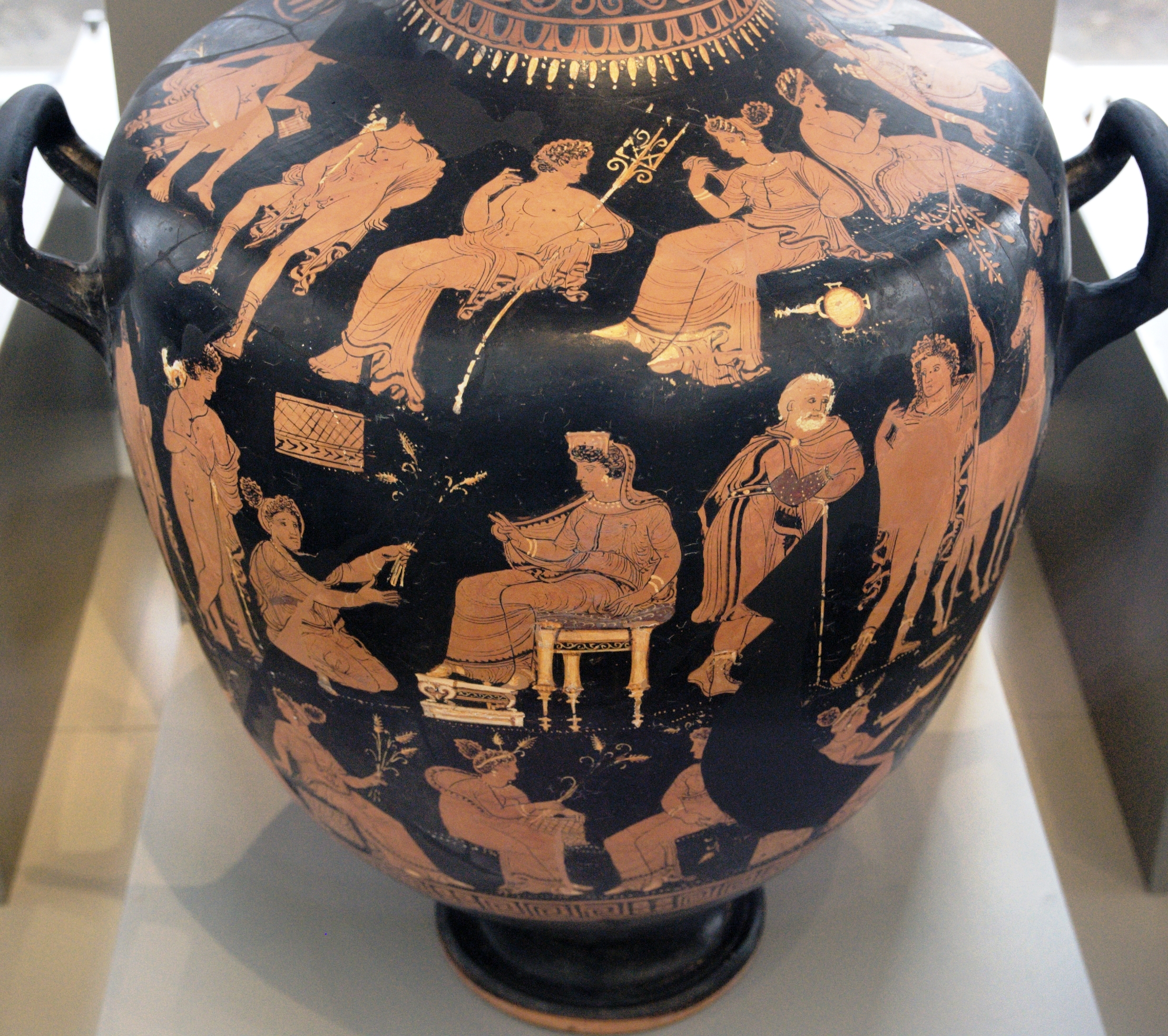
The Megalesia, Megalensia, or Megalenses Ludi was a festival celebrated in ancient Rome from April 4 to April 10, in honour of Cybele, whom the Romans called ''Magna Mater'' ("Great Mother"). The name of the festival derives from Greek ''megalē'' (μϵγάλη), meaning "great". The festival was one of several on the Roman calendar celebrated with ''ludi'', games and performances. Background Cybele's cult image was brought to Rome from Pessinus in 204 BC, along with the goddess's Gallae priestesses. As the "Great Mother of the Gods" and a purported ancestral Trojan goddess of Rome's ruling patrician caste, she was recruited to act on Rome's behalf in the war against Carthage. Her arrival was solemnized with a magnificent procession, sacred feasts ('' lectisternia''), games, and offerings to her at the temple of Victory on the Palatine Hill, where her image was temporarily housed. In 203 Cybele was promised a temple of her own. Games in her honour were celebrated in 193. Regul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
From The Founding Of The City/Book 36
{{disambig ...
From may refer to: People *Isak From (born 1967), Swedish politician *Martin Severin From (1825–1895), Danish chess master * Sigfred From (1925–1998), Danish chess master Media * ''From'' (TV series), a sci-fi-horror series that debuted on Epix in 2022 * "From" (Fromis 9 song) (2024) * "From", a song by Big Thief from U.F.O.F. (2019) * "From", a song by Yuzu (2010) * "From", a song by Bon Iver from Sable, Fable (2025) Other * From, a preposition * From (SQL), computing language keyword * From: (email message header), field showing the sender of an email * FromSoftware, a Japanese video game company * Full range of motion, the travel in a range of motion Range of motion (or ROM) is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another. In biomechanics and strength training, ROM refers to the angular distance and direction a joint can move be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
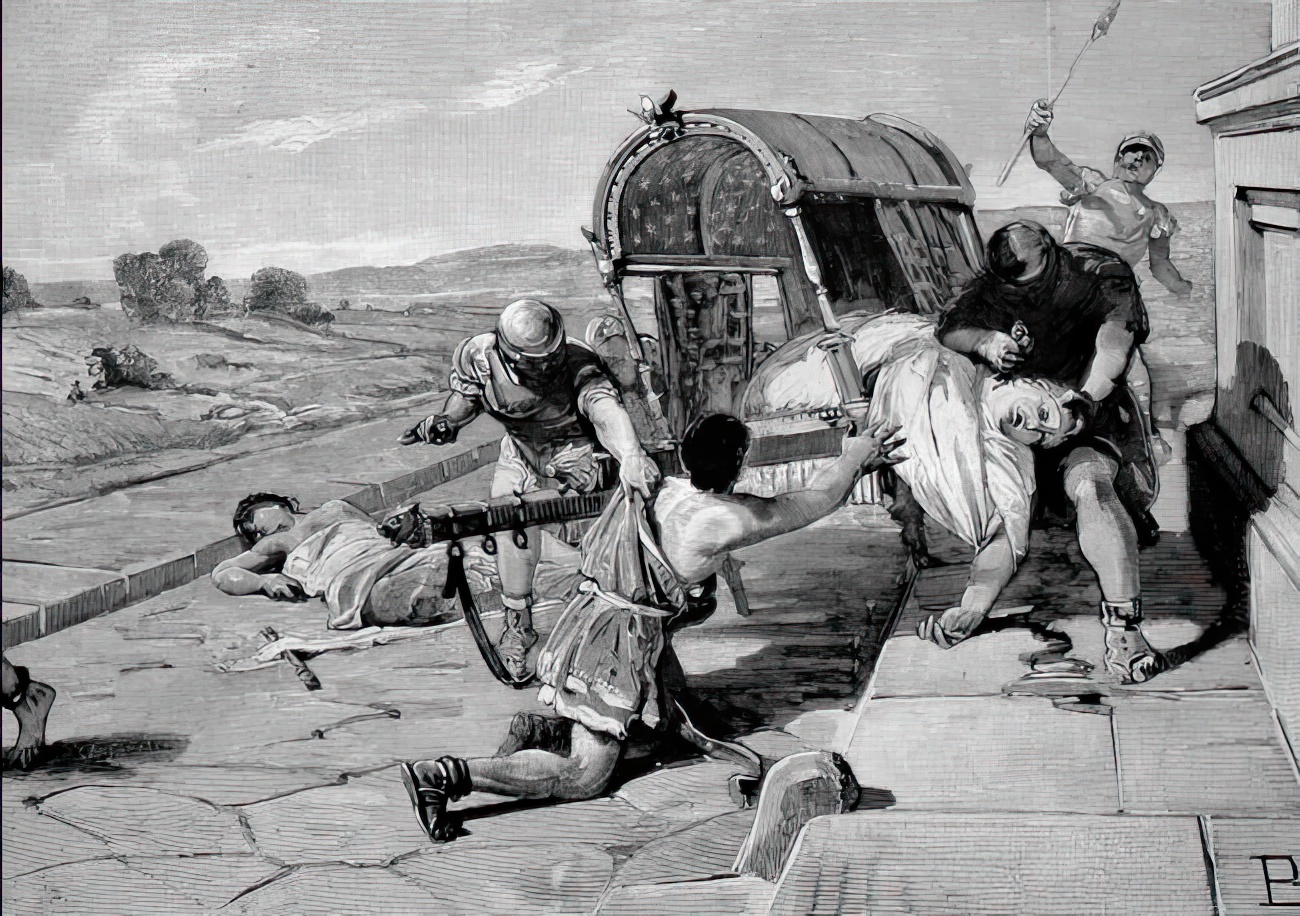
Publius Clodius Pulcher
Publius Clodius Pulcher ( – 18 January 52 BC) was a Roman politician and demagogue. A noted opponent of Cicero, he was responsible during his plebeian tribunate in 58 BC for a massive expansion of the Roman grain dole as well as Cicero's exile from the city. Leader of one of the political mobs in the 50s, his political tactics – combining connections throughout the oligarchy with mass support from the poor plebs – made him a central player in the politics of the era. Born to the influential patrician gens Claudia, he was embroiled early in his political career in a religious scandal which saw him develop a rivalry with the orator Cicero and become a plebeian in order to be eligible for the plebeian tribunate. He successfully stood as tribune of the plebs for 58 BC and passed six laws to restore Rome's collegia (private guilds and fraternities), expand the grain dole (making it free rather than subsidised while also using those collegia as means for distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Gellius
Aulus Gellius (c. 125after 180 AD) was a Roman author and grammarian, who was probably born and certainly brought up in Rome. He was educated in Athens, after which he returned to Rome. He is famous for his ''Attic Nights'', a commonplace book, or compilation of notes on grammar, philosophy, history, antiquarianism, and other subjects, preserving fragments of the works of many authors who might otherwise be unknown today. Name Medieval manuscripts of the ''Noctes Atticae'' commonly gave the author's name in the form of "Agellius", which is used by Priscian; Lactantius, Servius and Saint Augustine had "A. Gellius" instead. Scholars from the Renaissance onwards hotly debated which one of the two transmitted names is correct (the other one being presumably a corruption) before settling on the latter of the two in modern times. Life The only source for the life of Aulus Gellius is the details recorded in his writings. Internal evidence points to Gellius having been born between A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus ( ; ; – October 15, 55 BC) was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is the philosophical poem '' De rerum natura'', a didactic work about the tenets and philosophy of Epicureanism, which usually is translated into English as ''On the Nature of Things''—and somewhat less often as ''On the Nature of the Universe''. Very little is known about Lucretius's life; the only certainty is that he was either a friend or client of Gaius Memmius, to whom the poem was addressed and dedicated. ''De rerum natura'' was a considerable influence on the Augustan poets, particularly Virgil (in his ''Aeneid'' and ''Georgics'', and to a lesser extent on the '' Eclogues'') and Horace. The work was almost lost during the Middle Ages, but was rediscovered in 1417 in a monastery in Germany by Poggio Bracciolini and it played an important role both in the development of atomism (Lucretius was an important influence on Pierre Gassendi) and the efforts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Roman Mysteries
Mystery religions, mystery cults, sacred mysteries or simply mysteries (), were religious schools of the Greco-Roman world for which participation was reserved to initiation rite, initiates ''(mystai)''. The main characteristic of these religious schools was the secrecy associated with the particulars of the initiation and the ritual practice, which may not be revealed to outsiders. The most famous mysteries of Greco-Roman antiquity were the Eleusinian Mysteries, which predated the Greek Dark Ages. The mystery schools flourished in Late Antiquity; Julian the Apostate, Emperor Julian, of the mid-4th century, is believed by some scholars to have been associated with various mystery cults—most notably the mithraism, mithraists. Due to the secret nature of the schools, and because the mystery religions of Late Antiquity were Persecution of Pagans by the Christian Roman Empire, persecuted by the Christian Roman Empire from the 4th century, the details of these religious practices are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysius Of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus (, ; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime. He is known for his work ''Rhōmaikē Archaiologia'' (Roman Antiquities), which describes the history of Rome from its beginnings until the outbreak of the First Punic War in 264 BC. Out of twenty books, only the first nine have survived. Dionysius' opinion of the necessity of a promotion of paideia within education, from true knowledge of classical sources, endured for centuries in a form integral to the identity of the Greek elite. Life He was a Halicarnassian. At some time after the end of the civil wars he moved to Rome, and spent twenty-two years studying Latin and literature and preparing materials for his history. During this period, he gave lessons in rhetoric, and enjoyed the society of many distinguished men. The date of his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists and the innovator of what became known as "Ciceronian rhetoric". Cicero was educated in Rome and in Greece. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. He greatly influenced both ancient and modern reception of the Latin language. A substantial part of his work has survived, and he was admired by both ancient and modern authors alike. Cicero adapted the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy in Latin and coined a large portion of Latin philosophical vocabulary via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Ancient Roman Religion
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on later juridical and religious vocabulary in Europe, particularly of the Christian Church. This glossary provides explanations of concepts as they were expressed in Latin pertaining to Religion in ancient Rome, religious practices and beliefs, with links to articles on major topics such as priesthoods, forms of divination, and rituals. For theonyms, or the names and epithets of gods, see List of Roman deities. For public religious holidays, see Roman festivals. For temples see the List of Ancient Roman temples. Individual landmarks of religious Topography of ancient Rome, topography in ancient Rome are not included in this list; see Roman temple. __NOTOC__ Glossary A abominari The verb ''abominari'' ("to avert an omen", from ''ab-'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronography Of 354 Mensis Aprilis
Chronology (from Latin , from Ancient Greek , , ; and , ''-logia'') is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time. Consider, for example, the use of a timeline or sequence of events. It is also "the determination of the actual temporal sequence of past events".Memidex/WordNet, "chronology,memidex.com (accessed September 25, 2010). Chronology is a part of periodization. It is also a part of the discipline of history including earth history, the earth sciences, and study of the geologic time scale. Related fields Chronology is the science of locating historical events in time. It relies mostly upon chronometry, which is also known as timekeeping, and historiography, which examines the writing of history and the use of historical methods. Radiocarbon dating estimates the age of formerly living things by measuring the proportion of carbon-14 isotope in their carbon content. Dendrochronology estimates the age of trees by correlation of the various growth r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
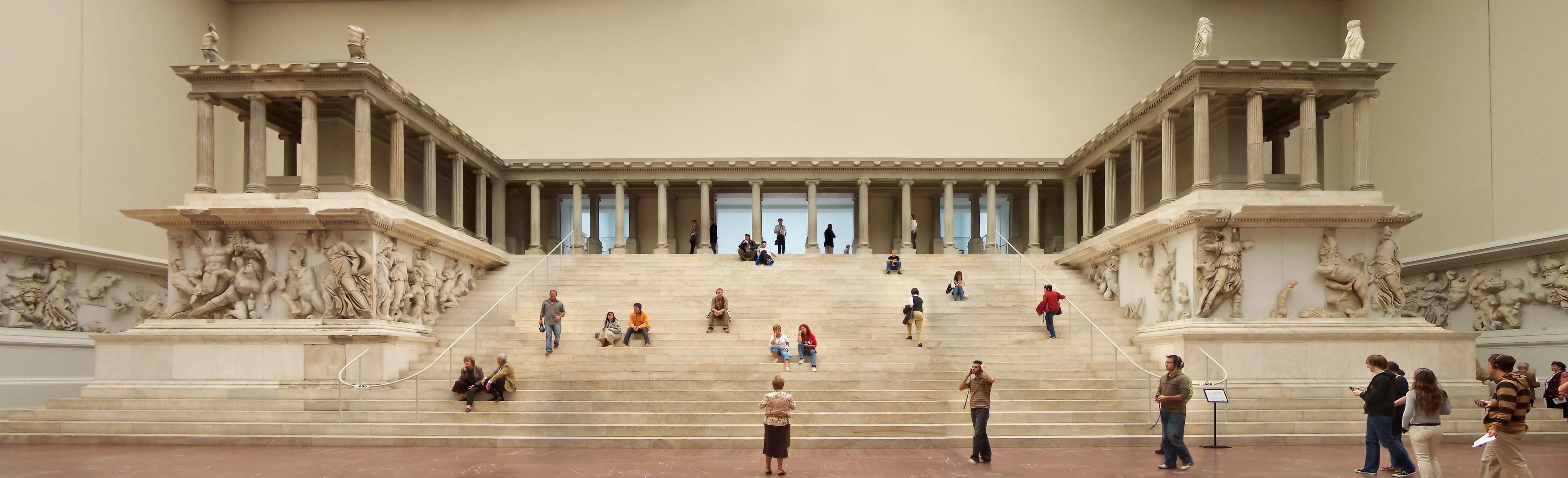
Pergamon Altar
The Pergamon Altar () was a monumental construction built during the reign of the Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek King Eumenes II of the Kingdom of Pergamon, Pergamon Empire in the first half of the 2nd century BC on one of the terraces of the acropolis of Pergamon in Anatolia, Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey). The structure was wide and deep; the front stairway alone was almost wide. The base was decorated with a frieze in high relief showing the battle between the Giants (Greek mythology), Giants and the Twelve Olympians, Olympian gods known as the Gigantomachy. There was a second, smaller and less well-preserved high relief frieze on the inner court walls which surrounded the actual fire altar on the upper level of the structure at the top of the stairs. In a set of consecutive scenes, it depicts events from the life of Telephus, legendary founder of the city of Pergamon and son of the hero Heracles and Auge, one of Tegean king Aleus's daughters. In 1878, the German engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |