|
Lucasuchus
''Lucasuchus'' is an extinct genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Bull Canyon Formation of the Dockum Group outcropping in the Revuelto Creek locality in Quay County, New Mexico. All specimens date back to the Norian stage of the Late Triassic. The genus was named in 1995 after the American paleontologist Spencer G. Lucas. ''Lucasuchus'' was first proposed to be a junior subjective synonym of ''Longosuchus'' in 1999, and several other studies have also considered it to be an invalid genus. However, more recent studies concluded that ''Lucasuchus'' is not congeneric with any other known aetosaur genus, and is likely to be more closely related to ''Desmatosuchus'' and ''Acaenasuchus'' than to ''Longosuchus''. The presence of elongate lateral osteoderm horns is shared by all of these genera, which make up the subfamily Desmatosuchinae.Sereno, P. C. (2005)Desmatosuchinae. Stem Archosauria ''TaxonSearch ersion 1.0, 2005 November 7'. Retrieved on 2009-07-18. It has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaurs Of North America
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmatosuchinae
Desmatosuchinae is a major subfamily of aetosaurs within the clade Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to '' Desmatosuchus'' than to '' Stagonolepis,'' '' Aetosaurus'', or '' Paratypothorax''. The clade Desmatosuchinae has often been restricted to a few closely-related aetosaurs with spiny armor, such as ''Desmatosuchus'', '' Longosuchus'', and '' Lucasuchus''. It was later expanded to include a number of '' Stagonolepis''-like aetosaurs with less specialized armor. Under this more expansive usage, the strongly-supported clade encompassing "traditional" desmatosuchines (''sensu stricto'') was given a new name, Desmatosuchini. Synapomorphies that diagnose this clade can be found in the osteoderms. These include tongue-and-groove articulations for lateral plates present in dorsal presacral paramedian plates and large spikes on the lateral cervical, dorsal, and caudal plates. Timeline of generic descriptions ImageSize = width: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
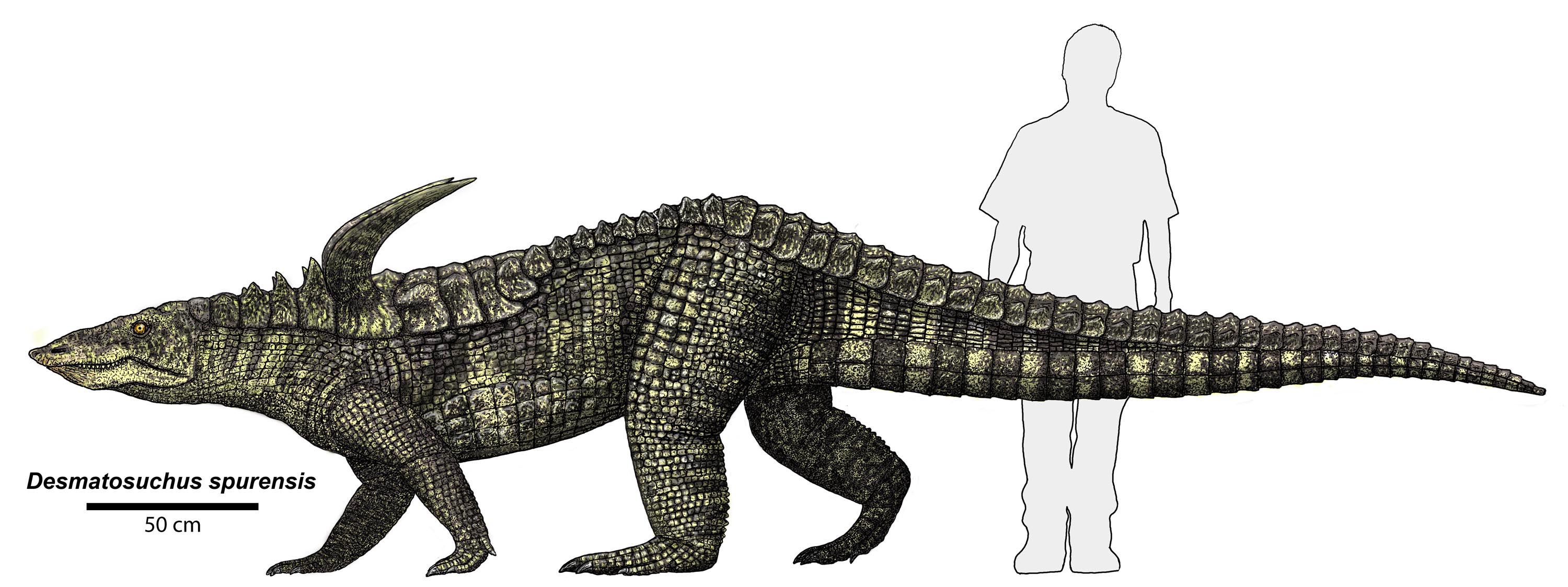
Desmatosuchus
''Desmatosuchus'' (, from Greek δεσμός ''desmos'' 'link' + σοῦχος ''soûkhos'' 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosaur belonging to the Order Aetosauria. It lived during the Late Triassic. Description ''Desmatosuchus'' was a large quadrupedal reptile upwards of to in lengthvon Baczko, M. B., Desojo, J. B., Gower, D. J., Ridgely, R., Bona, P., & Witmer, L. M. (2021)New digital braincase endocasts of two species of Desmatosuchus and neurocranial diversity within Aetosauria (Archosauria: Pseudosuchia) The Anatomical Record, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24798 and in weight. Its vertebral column had amphicoelus centra and 3 sacral vertebrae. This archosaur's most distinguishing anatomical characteristics were its scapulae which possessed large acromion processes commonly referred to as "shoulder spikes". The forelimbs were much shorter than the hindlimbs, with humeri less than two-thirds the length of the femurs. The pelvic girdle consisted of a long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, Ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful sandstone'')'', t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longosuchus
''Longosuchus'' (meaning "Long's crocodile") is an extinct genus of aetosaur from the Late Triassic of North America and Morocco Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria .... It measured about 3 metres in length. Taxonomy ''Longosuchus'' was originally named as a species of '' Typothorax'', ''T. meadei'', in 1947 on the basis of skeletal remains from the Otis Chalk quarries in Howard County, western Texas. Hunt and Lucas (1990) recognized ''T. meadei'' as generically distinct from the type species of ''Typothorax'' and renamed it ''Longosuchus'' in honor of Robert Long.A. P. Hunt and S. G. Lucas. 1990. Re-evaluation of "Typothorax" meadei, a Late Triassic aetosaur from the United States. Paläontologische Zeitschrift 64:317-328. References Aetosaurs of North Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Reptiles Of North America
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily ( Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoological names with "-inae". See also * International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all those "trad ... * International Code of Zoological Nomenclature * Rank (botany) * Rank (zoology) Sources {{biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderm
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans ( armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid and scelidotheriid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acaenasuchus
''Acaenasuchus'' (meaning "thorn crocodile") is an extinct genus of pseudosuchians, endemic to what would be Arizona during the Late Triassic, existing for approximately . Discovery and naming The holotype, UCMP 139576 (a left(?) dorsal paramedian scute), was discovered by Charles Lewis Camp in 1930 and was considered to belong to a juvenile of ''Desmatosuchus''.Heckert, A.B. and Lucas, S. G. (2002). ''Acaenasuchus geoffreyi'' (Archosauria: Aetosauria) from the Upper Triassic Chinle Group: Juvenile of ''Desmatosuchus'' ''haplocerus''. ''Upper Triassic Stratigraphy and Paleontology. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin No. 21''. UCMP 139576 eventually moved into its own taxon, and ''Acaenasuchus'' was named by Long and Murry (1995).R. A. Long and P. A. Murry. (1995). Late Triassic (Carnian and Norian) tetrapods from the southwestern United States. ''New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin'' 4:1-254 The holotype was discovered in the Petrifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |