|
Lucanidae
Stag beetles comprise the family Lucanidae. It has about 1,200 species of beetles in four subfamilies.Smith, A.B.T. (2006). A review of the family-group names for the superfamily Scarabaeoidea (Coleoptera) with corrections to nomenclature and a current classification. The Coleopterists Bulletin 60:144–204. Some species grow to over , but most to about . Overview The English language, English name is derived from the large and distinctive Insect mouthparts, mandibles found on the males of most species, which resemble the antlers of stags. A well-known species in much of Europe is ''Lucanus cervus'', referred to in some European countries (including the United Kingdom) as ''the'' stag beetle; it is the largest terrestrial insect in Europe. Pliny the Elder noted that Nigidius called the beetle ''lucanus'' after the Italian region of Lucania where they were used as Amulet, amulets. The scientific name of ''Lucanus cervus'' adds ''cervus'', Cervus, deer. Male stag beetles are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucanus Cervus
''Lucanus cervus'', known as the European stag beetle, or the greater stag beetle, is one of the best-known species of stag beetle (family Lucanidae) in Western Europe, and is the eponymous example of the genus. ''L. cervus'' is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN Red List. Taxonomy ''Lucanus cervus'' is situated in the genus ''Lucanus'' within the family Lucanidae. In the genus there are two subgenera: ''Lucanus'' Scopoli, 1763 and ''Pseudolucanus'' Hope and Westwood, 1845. The species ''L. cervus'' contains four subspecies. The nominate subspecies ''L. cervus cervus'' (Linnaeus, 1758) was established via the original description of the species in 1758. The three latterly added subspecies are ''L. cervus judaicus'' Planet, 1900, ''L. cervus laticornis'' Deyrolle, 1864, and ''L. cervus turcicus'' Sturm, 1843. Description The European stag beetle is the largest beetle in Europe. Their colour is usually black with reddish Elytron, elytra (and red mandibles in males). Sexual dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucaninae
The Lucaninae comprise the largest subfamily of the stag beetles (Lucanidae). Characteristics include partial to complete division of the eyes by a canthus, geniculate antennae, and distinctly separated coxae. The body is typically elongated and slightly flattened. Genera Some notable species are also listed: * '' Aegognathus'' * '' Aegus'' * '' Agnus'' * '' Allotopus'' * '' Amneidus'' * '' Andinolucanus'' * '' Aphanognathus'' * '' Apterocyclus'' * '' Apterodorcus'' Arrow, 1943 * '' Auxicerus'' * '' Bartolozziolucanus'' * '' Beneshius'' * '' Bomansius'' * '' Brasilucanus'' * '' Cacostomus'' ** '' C. squamosus'' * '' Calcodes'' * '' Cantharolethrus'' ** '' C. luxeri'' * '' Capreolucanus'' * '' Cardanus'' * '' Casignetus'' * '' Charagmophorus'' * '' Chewlucanus'' * '' Chiasognathus'' * '' Cladophyllus'' * '' Cladognathus'' * '' Colophon'' * '' Cyclommatus'' ** '' C. scutellaris'' * '' Dendezia'' * '' Diasomoides'' * '' Dinonigidius'' * '' Dorculus'' * '' Dorcus'' * '' Dynodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprima Aurata
''Lamprima aurata'', the golden stag beetle, is a species of beetle in the family Lucanidae. In Tasmania, this species is referred to by the common name of Christmas beetle, a name that is normally used for beetles in the family Scarabaeidae, genus '' Anoplognathus''. Description This beetle has an oval, shiny body. It measures between 15 and 25 mm in length. It is fairly variable in coloration, so it has been given many names by various authors.C.A.M. Reid, K. Smith, M. Beatson (2018) Revision of the Genus ''Lamprima'' Latreille, 1804 (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). Zootaxa. 4446(2); 151–202. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4446.2.1 The colour of the males is typically metallic golden green or yellow with colorful legs, while females may be blue, blue-green or dull brown. Females are smaller than the males, and males have larger mandibles prolonged forwards used for fighting. Distribution and habitat ''Lamprima aurata'' is native to Australia and can be found in Tasmania and south-eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndesinae
Syndesinae is a subfamily of stag beetles in the family Lucanidae. There are at least two genera and four described species in Syndesinae. Genera These two genera belong to the subfamily Syndesinae: * '' Ceruchus'' MacLeay, 1819 * '' Sinodendron'' Hellwig, 1791 i c g b Data sources: i = ITIS, c = Catalogue of Life, g = GBIF, b = Bugguide.net References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * Lucanidae {{lucanidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetle
Beetles are insects that form the Taxonomic rank, order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described arthropods and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. However, the number of beetle species is challenged by the number of species in Fly, dipterans (flies) and hymenopterans (wasps). Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
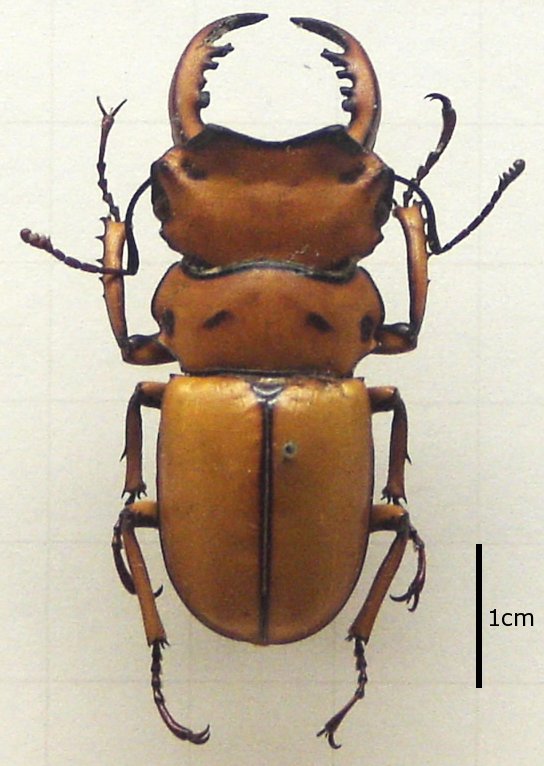
Dorcus Curvidens Hopei Sjh
''Dorcus'' is a genus of beetles in the stag beetle family Lucanidae Stag beetles comprise the family Lucanidae. It has about 1,200 species of beetles in four subfamilies.Smith, A.B.T. (2006). A review of the family-group names for the superfamily Scarabaeoidea (Coleoptera) with corrections to nomenclature and a c .... Of the over 100 species, most occur in Asia and India; two are found in southern Europe, and two species are from North America. Previously, specimens with serriform teeth on the mandibles and sable pigment were called ''Serrognathus'' whereas specimens with but a singular or multiple bulky notches on the mandibles and lustrous sable pigmentation were called ''Dorcus''. Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Dorcus'': *'' Dorcus alcides'' *'' Dorcus alexisi'' - Cyprus *'' Dorcus amamianus'' *'' Dorcus antaeus'' *'' Dorcus arfakianus'' - Papua New Guinea *'' Dorcus arrowi'' - southern and south-eastern Asia *'' Dorcus bandaensis'' - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
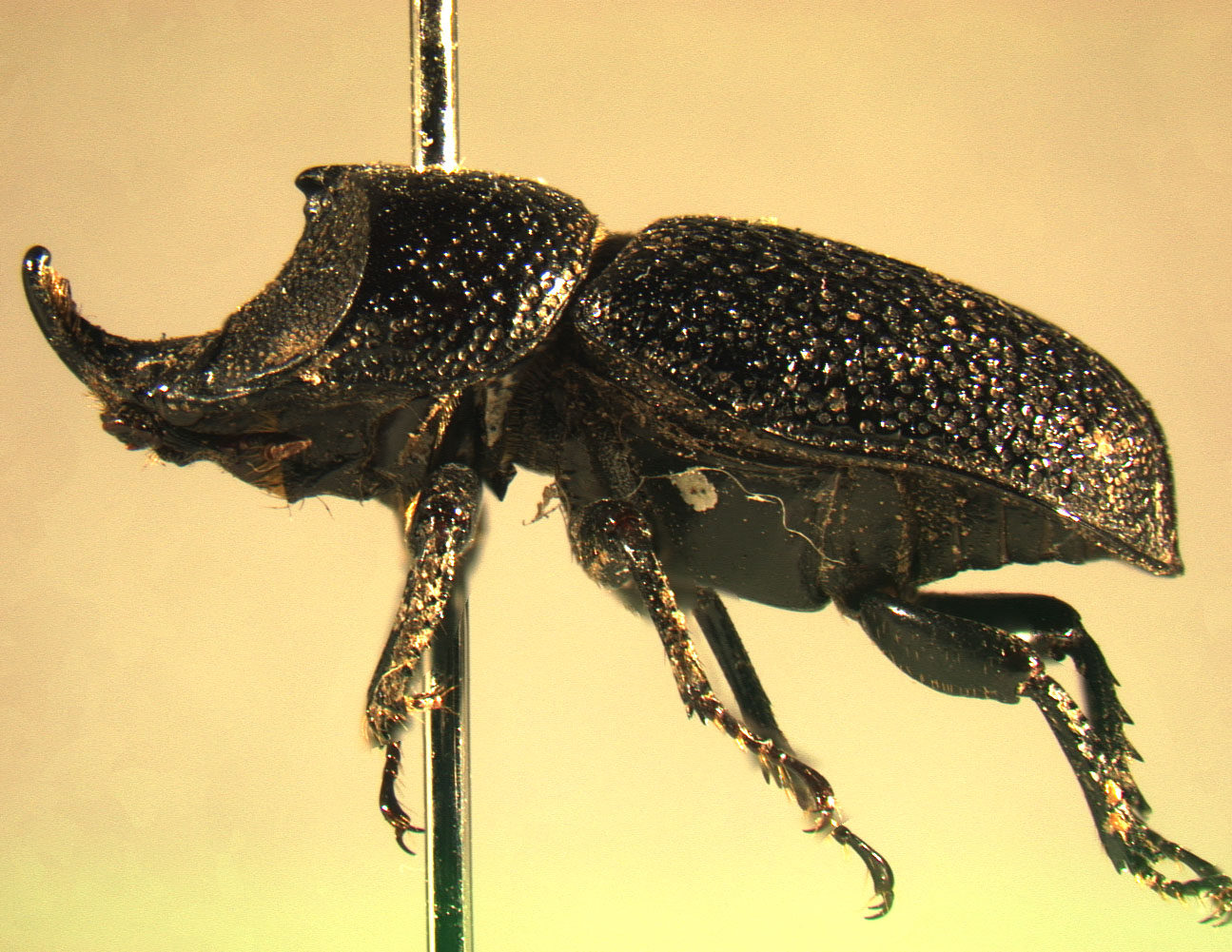
Prosopocoilus Giraffa
''Prosopocoilus giraffa'', the giraffe stag beetle, is the world's largest stag beetle and is a member of the family Lucanidae within the order Coleoptera. They have very long, toothed and notched mandibles that protrude about half the size of their body. They tend to be aggressive and are fierce and powerful. Males fight each other using these strong and enlarged jaws to lift and throw rivals to win a mate. They can grow up to 119 millimetres in length. Several distinctive populations (subspecies) are found in moist forested region areas of Asia, ranging from India to Indonesia Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, .... ''Prosopocoilus giraffa keisukei'' can measure up to 12 centimeters. ''Prosopocoilus giraffa daisukei'' have the brightest elytra of all subspecies and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
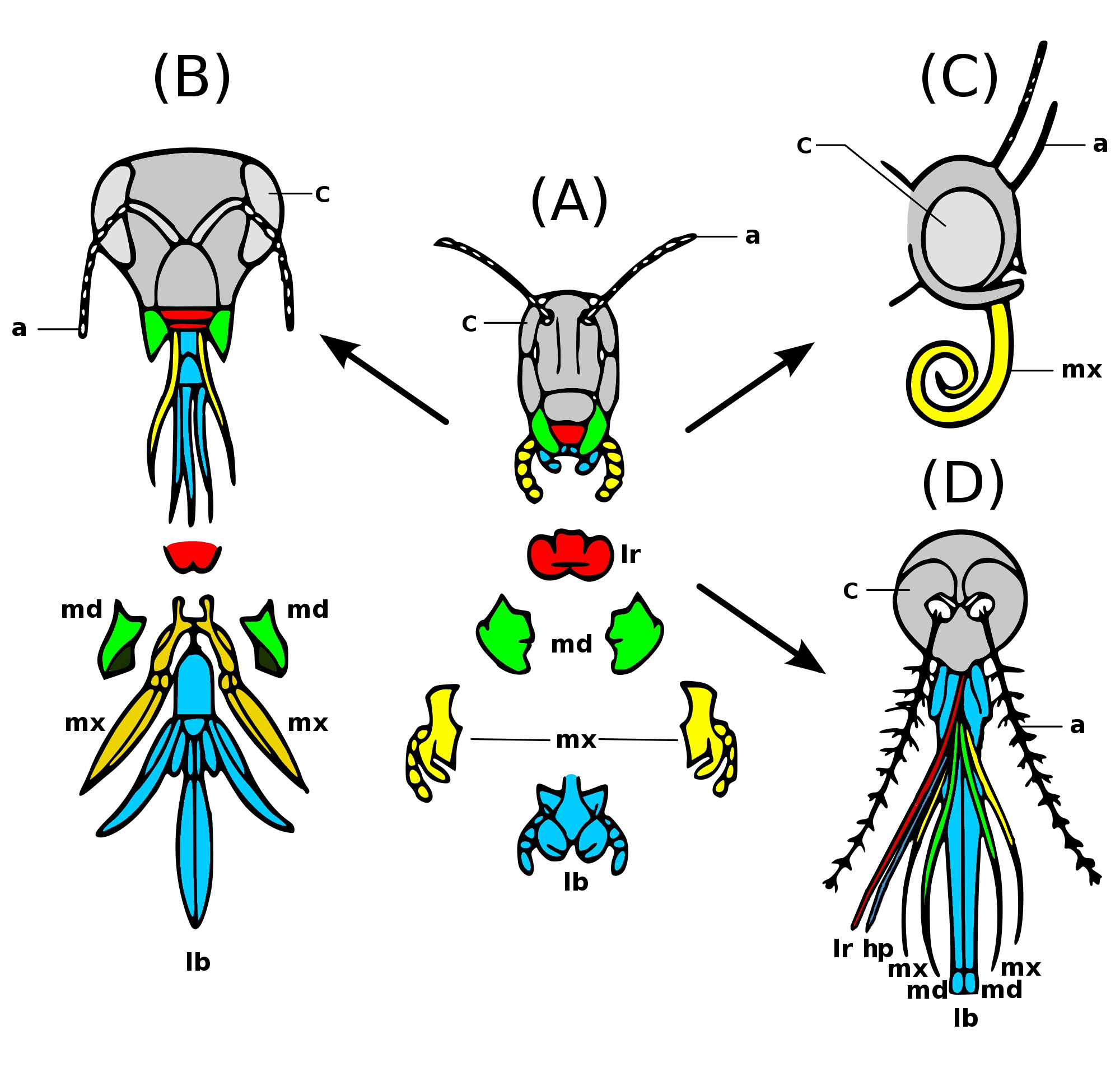
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times independently. For example, mosquitoes (which are true flies) and aphids (which are Hemiptera, true bugs) both pierce and suck, though female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant Homology (biology), homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching Primordium, primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is Cladogram#Homoplasies, homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying pterygota, insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas ''homology (biology), homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) and Capreolinae (which includes, among others reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, roe deer, and moose). Male deer of almost all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. These antlers are bony extensions of the skull and are often used for combat between males. The musk deer ( Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains ( Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in heraldry, such as red deer that app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight
Flight or flying is the motion (physics), motion of an Physical object, object through an atmosphere, or through the vacuum of Outer space, space, without contacting any planetary surface. This can be achieved by generating aerodynamic lift associated with gliding flight, gliding or air propulsion, propulsive thrust, aerostatically using buoyancy, or by ballistics, ballistic movement. Many things can fly, from Flying and gliding animals, animal aviators such as birds, bats and insects, to natural gliders/parachuters such as patagium, patagial animals, anemochorous seeds and ballistospores, to human inventions like aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, airships, balloons, etc.) and rockets which may propel spacecraft and spaceplanes. The engineering aspects of flight are the purview of aerospace engineering which is subdivided into aeronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through the atmosphere, and astronautics, the study of vehicles that travel through space, and ballistics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superstition
A superstition is any belief or practice considered by non-practitioners to be irrational or supernatural, attributed to fate or magic (supernatural), magic, perceived supernatural influence, or fear of that which is unknown. It is commonly applied to beliefs and practices surrounding luck, amulets, astrology, fortune telling, Spirit (animating force), spirits, and certain paranormal wikt: entity, entities, particularly the belief that future events can be foretold by specific unrelated prior events. The word ''superstition'' is also used to refer to a religion not practiced by the majority of a given society regardless of whether the prevailing religion contains alleged superstitions or to all religions by the antireligion, antireligious. Contemporary use Definitions of the term vary, but they commonly describe superstitions as irrational beliefs at odds with scientific knowledge of the world. Stuart Vyse proposes that a superstition's "presumed mechanism of action is inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |