|
Lubusz Military Museum
Lebus () is a historic town in the Märkisch-Oderland District of Brandenburg, Germany. It is the administrative seat of '' Amt'' ("collective municipality") Lebus. The town, located on the west bank of the Oder river at the border with Poland, was the centre of the historical region known as Lubusz Land, which provides the name for the present-day Polish Lubusz Voivodeship. Geography Lebus is situated in the southeast of Märkisch-Oderland District, on a ridge at the left bank of the middle Oder river, which since the implementation of the Oder–Neisse line in 1945 marks the eastern German border with Poland. The town centre is located about north of Frankfurt (Oder). The municipal area comprises the localities of Lebus proper, Mallnow, Schönfließ, and Wulkow. Schönfließ Dorf station is a stop on the Eberswalde–Frankfurt (Oder) railway line served by the '' Niederbarnimer Eisenbahn'' carrier. History Settlement in the Lebus region has been traced as far back as 3,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ortsteil
A village is a human settlement or Residential community, community, larger than a hamlet (place), hamlet but smaller than a town with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Although villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a Church (building), church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semnoni
The Semnones were a Germanic and specifically a Suebi people, located between the Elbe and the Oder in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD. They were described in the late 1st century by Tacitus in his ''Germania'': "The Semnones give themselves out to be the most ancient and renowned branch of the Suebi. Their antiquity is strongly attested by their religion. At a stated period, all the tribes of the same group assemble by their representatives in a grove consecrated by the auguries of their forefathers, and by immemorial associations of terror. Here, having publicly slaughtered a human victim, they celebrate the horrible beginning of their barbarous rite. Reverence also in other ways is paid to the grove. No one enters it except bound with a chain, as an inferior acknowledging the might of the local divinity. If he chance to fall, it is not lawful for him to be lifted up, or to rise to his feet; he must crawl out along the ground. All this superstition implies the belief that from this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lands Of The Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the states in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern periods with feudalism, feudal obligations to the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of Bohemia, an Prince-elector, electorate of the Holy Roman Empire according to the Golden Bull of 1356, the Margraviate of Moravia, the duchies of Silesia, and the two Lusatias, known as the Margraviate of Upper Lusatia and the Margraviate of Lower Lusatia, as well as other territories throughout its history. This agglomeration of states nominally under the rule of the Bohemian kings was referred to simply as Bohemia. They are now sometimes referred to in scholarship as the Czech lands, a direct translation of the Czech abbreviated name. The joint rule of ''Corona regni Bohemiae'' was legally established by decree of King Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV issued on 7 April 1348, on the foundation of the original Cze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margraviate Of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg () was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that, having electoral status although being quite poor, grew rapidly in importance after inheriting the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 and then came to play a pivotal role in the history of Germany and that of Central Europe as core of the Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian kingdom. Brandenburg developed out of the Northern March founded in the territory of the Slavic peoples, Slavic Wends. It derived one of its names from this inheritance, the March of Brandenburg (). Its ruling margraves were established as prestigious prince-electors in the Golden Bull of 1356, allowing them to vote in the election of the Holy Roman Emperor. The state thus became additionally known as Electoral Brandenburg or the Electorate of Brandenburg ( or ). The House of Hohenzollern came to the throne of Brandenburg in 1415. In 1417, Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg, Frederick I moved its capital from Brandenbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Poland (1025–1385)
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the medieval period from 1025 until 1385. Background The West Slavic tribe of Polans who lived in what is today the historic region of Greater Poland, gave rise to a state in the early 10th century, which would become the nascent predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland. Following the Christianization of Poland in 966, and the emergence of the Duchy of Poland during the rule of Mieszko I, his eldest son Bolesław I the Brave inherited his father's dukedom and subsequently was crowned as king. History Establishment In 1025, Bolesław I the Brave of the Piast dynasty was crowned as the first King of Poland at the cathedral in Gniezno and elevated the status of Poland from a duchy to a kingdom after receiving permission for his coronation from Pope John XIX. Following the death of Bolesław, his son Mieszko II Lambert inherited the crown and a vast territory after his fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
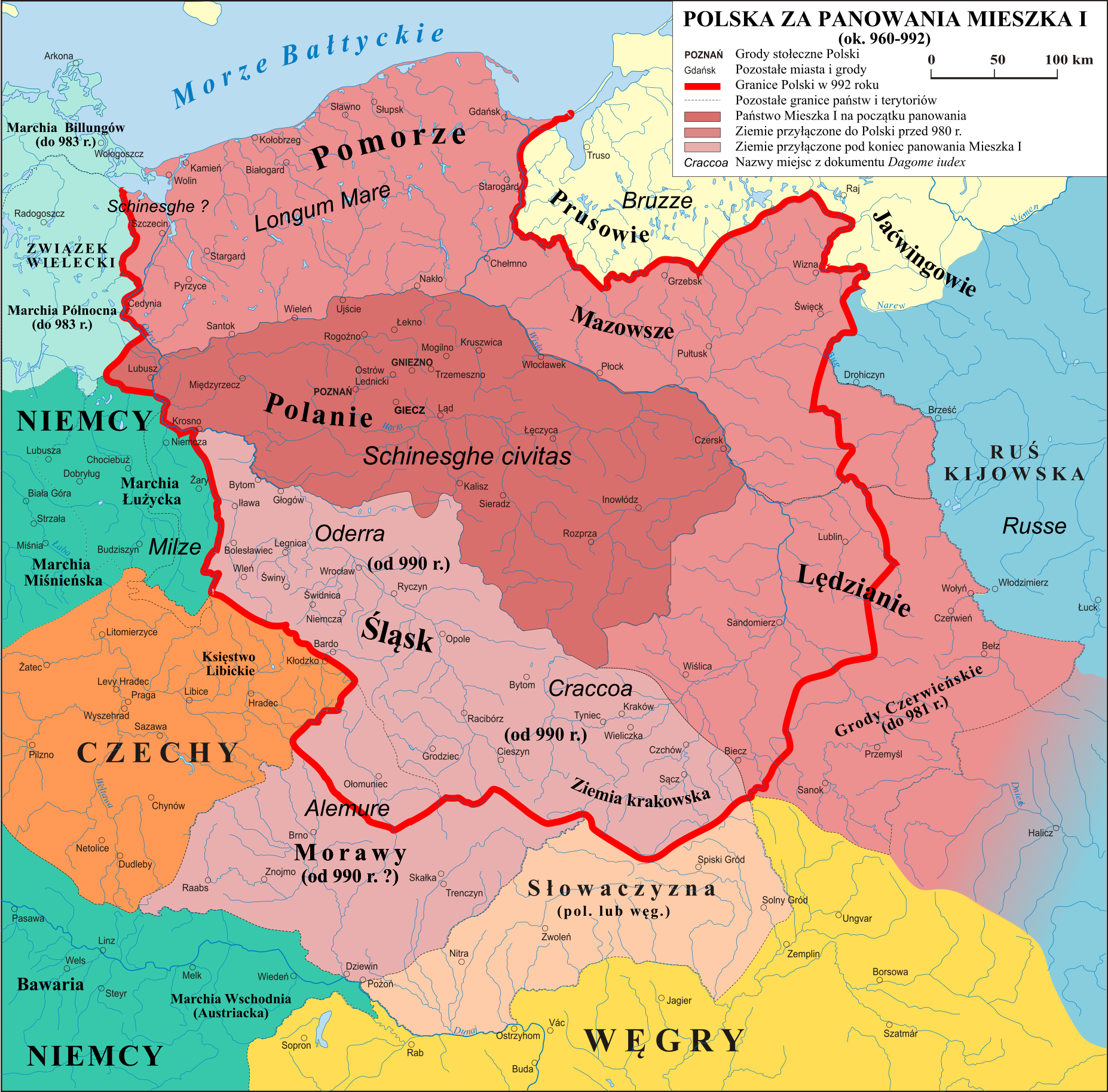
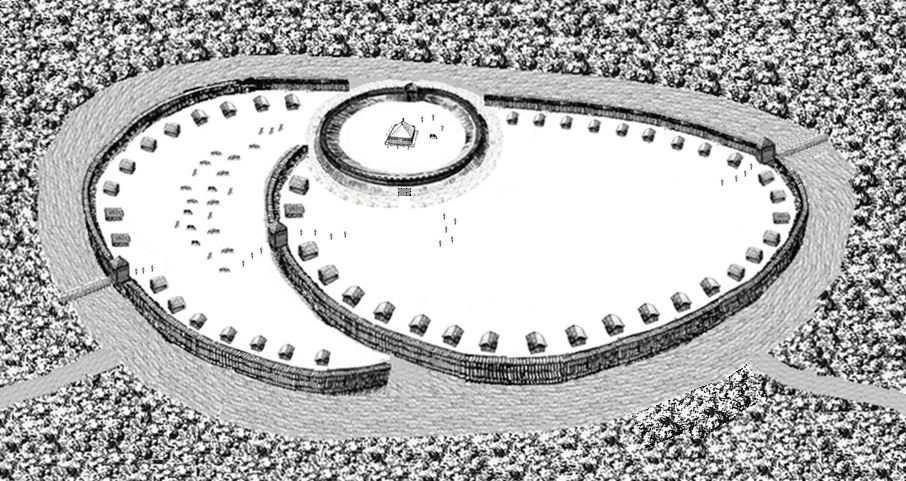
Civitas Schinesghe
Civitas Schinesghe (; ), also known as the Duchy of Poland or the Principality of Poland, is the historiographical name given to a polity in Central Europe, which existed during the medieval period and was the predecessor state of the Kingdom of Poland. States and territories disestablished in the 1020s Etymology Civitas Schinesghe, meaning "Gniezno State", is the first recorded name related to Poland as a political entity, dating to the year 991 and attested to in a later papal regesta called '' Dagome iudex'' from 1080. The document states that the Piast duke Mieszko I and his wife, Oda von Haldensleben, had given the guidance of ''unam civitatem in integro, que vocatur Schinesghe'' ("a whole state, which is called Schinesghe") over to the Holy See. Though the proper Latin name for Poland, ''Polonia'', which came into use some time later, is not explicitly used in the document, the name ''Schinesghe'' presumably refers to Gniezno, which was one of the main gord stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polans (western)
The Polans ( Polish: ''Polanie''; Latin: ''Polani'', ''Polanos''), also known as Polanians or Western Polans ( Polish: ''Polanie Zachodni''; Latin: ''Polani Occidentis''), were a West Slavic and Lechitic tribe who inhabited the Warta River basin of the contemporary Greater Poland region starting in the 6th century. They were one of Central Europe's main tribes and closely related to the Vistulans, Masovians, Czechs and Slovaks. According to Zygmunt Gloger, their name was derived from the word "pole", meaning "field", thus denoting them as "men of the fields". History In the 9th century, the Polans united several West Slavic (Lechitic) groups to the north of Great Moravia. The union led by the Piast dynasty developed into the Duchy of Poland, whose name derives from that of the Polans. The earliest Polan rulers mentioned by name are the legendary figures of Piast the Wheelwright and Popiel (8th–9th centuries). The first historical ruler was Mieszko I (960–992), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the ''Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and medieval History of Poland (966–1385), Poland in the east. The Polabian Slavs, largely conquered by Saxons and Danish people, Danes from the 9th century onwards, were included and gradually cultural assimilation, assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes became gradually Germanization, Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture. The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony () was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 CE and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected List of German monarchs, German king in 919. Upon the deposition of the House of Welf, Welf duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg in 1235. In 1296, the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg and Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg, Saxe-Wittenberg, the latter obtaining the title of Electorate of Saxony, Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. Geography The Saxon stem duchy covered the greater part of present-day Northern Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: the Redarians (Redari, Redarii), Circipanians (Circipani), Kessinians (Kessini, Kycini, Chizzini) and Tollensians (Tholenzi). At least in part, the Lutici were a continuation of the Veleti. In contrast to the former and the neighboring peoples, the Lutici were not led by a Christian monarch or duke, rather power was asserted through consensus formed in central assemblies of the social elites, and the Lutici worshipped nature and several deities. The political and religious center was Radgosc (also referred to by several other names, e.g. Riedegost or Rethra). The Lutici were first recorded by written sources in the context of the uprising of 983, by which they annihilated the rule of the Holy Roman Empire in the Billung and Norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Veletians, Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Western Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, also known as the Union of the Veleti, a loose monarchic confederation of the tribes. Said state existed between the 6th and 10th centuries, after which, it was succeeded by the Lutician Federation. Name The name ''Veleti'' stems from the root ''vel-'' ('high, tall'). The Veleti were called by other names, probably given by their neighbours, such as ''Lutices'', ''Ljutici'', or ''Volki'', ''Volčki''. The latter means 'wolf', and the former probably 'fierce creature' based upon the comparison with the belarusian definition ''lyutyj zvěr''.' In common with other Slavic groups between the Elbe and Oder Rivers, they were often described by Germanic sources as Wends. In the late 10th century, they were continued by the Lutici. In Einhard's ''V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |